Biology:Tersicoccus phoenicis
| Tersicoccus phoenicis | |
|---|---|
| |
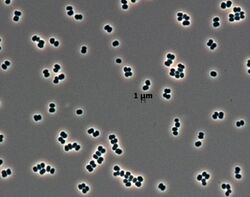
| Microscopic image[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Actinomycetota |
| Class: | Actinomycetia |
| Order: | Micrococcales |
| Family: | Micrococcaceae |
| Genus: | Tersicoccus |
| Species: | T. phoenicis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Tersicoccus phoenicis | |
| Type strain | |
| 1P05MA[3] DSM 30849 NRRL B-59547 | |
Tersicoccus phoenicis is a member of the bacterial family Micrococcaceae. It has only been found in two spacecraft assembly clean room facilities and is resistant to the methods normally used to clean such facilities. The species name is derived from tersi, Latin for clean; coccus, Greek for berry; and phoenicis, from NASA's Phoenix lander, the spacecraft being prepared when these bacteria were first discovered.[1]
Occurrence
Tersicoccus phoenicis are only known to exist at two locations on Earth, and were independently found in geographically separated clean room facilities nearly 4,000 km (2,500 mi) apart.[1][2] One example was located during a 2007 microbial test swabbing of the Phoenix lander's clean room floor in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (Florida, United States),[1][4] while the other was found in the Herschel Space Observatory's clean room at Guiana Space Centre (Kourou, French Guiana).[5]
Parag Vaishampayan, a microbiologist with NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, suggests that this species may exist naturally outside of the clean room environment but has not been seen before due to the difficulty in isolating a single microbe type among the wide variety of different types found in nature.[1]
Characteristics
These bacteria are non-spore-forming, aerobic, non-motile, and Gram-positive.[2][6] They are roughly spherical (coccus) in shape and measure approximately 1 micrometre (0.00004 in) in diameter.[7] This species maintains a coccal morphology throughout their growth; the rod–coccus life cycle typically observed in nearly all Arthrobacter species is not present.[2] They are able to survive in environments with few nutrients.[1]
Two strains of T. phoenicis are known to exist, one at each discovery site: 1P05MAT at the American facility and KO_PS43 at the French Guianan facility.[4][5]
Significance
Because species like T. phoenicis are hardy enough to survive the sterilization measures used in spacecraft clean rooms, scientists study them and index their genetic material so that if a potential extraterrestrial bacterium were returned to Earth aboard a spacecraft, it could be compared to the index and ruled out as something that may have been originally launched with the spacecraft. Additionally, by examining the characteristics of resistant microbes such as T. phoenicis, scientists may be able to develop improved sterilization methods.[1][6][8] This is necessary to prevent the contamination of other celestial bodies by organisms aboard visiting spacecraft,[8] which may have already occurred with the Curiosity rover on Mars.[9][10]
Recognition
On May 23, 2014, the International Institute for Species Exploration (IISE) declared the bacterium as one of its "Top 10 New Species of 2014", selected from species discovered in 2013, due to the unusual location of its discovery and resistance to sterilization.[11][12][13]
See also
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Webster, Guy (November 6, 2013). "Rare New Microbe Found in Two Distant Clean Rooms". NASA.gov. http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?release=2013-319.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Vaishampayan, Parag; Moissl-Eichinger, Christine; Pukall, Rüdiger; Schumann, Peter; Spröer, Cathrin et al. (July 2013). "Description of Tersicoccus phoenicis gen. nov., sp. nov. isolated from spacecraft assembly clean room environments". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 63 (Pt 7): 2463–2471. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.047134-0. PMID 23223813.
- ↑ "Tersicoccus phoenicis". List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN). https://lpsn.dsmz.de/species/tersicoccus-phoenicis.
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 "Details: DSM-30849". Leibniz Institut DSMZ. http://www.dsmz.de/catalogues/details/culture/DSM-30849.html.
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 "Details: DSM-30842". Leibniz Institut DSMZ. http://www.dsmz.de/catalogues/details/culture/DSM-30842.html.
- ↑ Jump up to: 6.0 6.1 Vaishampayan, Parag; Venkateswaran, Kasthuri; Schwendner, Petra; Moissl-Eichinger, Christine (June 1, 2012). "Hardy Bacterium Isolated From Two Geographically Distinct Spacecraft Assembly Cleanroom Facilities". NASA Tech Briefs. http://www.techbriefs.com/component/content/article/13890.
- ↑ "New life found in Nasa's spacecraft clean rooms". The Daily Telegraph. November 7, 2013. https://www.telegraph.co.uk/science/science-news/10432816/New-life-found-in-Nasas-spacecraft-clean-rooms.html.
- ↑ Jump up to: 8.0 8.1 Kooser, Amanda (November 7, 2013). "New species of microbe thrives in spacecraft clean rooms". CNET.com. http://news.cnet.com/8301-17938_105-57611307-1/new-species-of-microbe-thrives-in-spacecraft-clean-rooms/.
- ↑ David, Leonard (December 1, 2011). "NASA's Mars Rover Curiosity Had Planetary Protection Slipup". Scientific American. http://www.scientificamerican.com/article/nasas-mars-rover-curiositt/.
- ↑ Madhusoodanan, Jyoti (May 19, 2014). "Microbial stowaways to Mars identified". Nature. doi:10.1038/nature.2014.15249. http://www.nature.com/news/microbial-stowaways-to-mars-identified-1.15249. Retrieved May 23, 2014.
- ↑ "Clean Room Microbes: Alien Invaders?". State University of New York College of Environmental Science and Forestry. http://www.esf.edu/top10/08.htm.
- ↑ Frazer, Jennifer (May 22, 2014). "Top 10 New Species of 2014". National Geographic. http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2014/05/140522-top-ten-new-species-2014-biodiversity/.
- ↑ Ahlstrom, Dick (May 22, 2014). "Tinkerbell and cuddly bears top new species list". The Irish Times. http://www.irishtimes.com/news/environment/tinkerbell-and-cuddly-bears-top-new-species-list-1.1804252.
External links
- T. phoenicis at the National Center for Biotechnology Information
- T. phoenicis type strain at BacDive
Wikidata ☰ Q15139876 entry
 |

