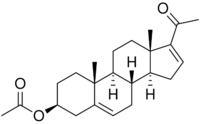
Chemistry:16-Dehydropregnenolone acetate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
20-Oxopregna-5,16-dien-3β-yl acetate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3aS,3bR,7S,9aR,9bS,11aS)-1-Acetyl-9a,11a-dimethyl-3a,3b,4,6,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-dodecahydro-3H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-7-yl acetate | |
| Other names
16-DPA; 5,16-Pregnadien-3β-ol-20-one acetate; 3β-Hydroxy-5,16-pregnadien-20-one acetate; 3β-Acetoxy-5,16-pregnadien-20-one
| |
| Identifiers | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H32O3 | |
| Molar mass | 356.506 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 171–172 °C (340–342 °F; 444–445 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
16-Dehydropregnenolone acetate (16-DPA) is a chemical compound used as an intermediate or synthon in the production of many semisynthetic steroids. As 7-ACA is for cephalosporins and 6-APA is for penicillins, 16-DPA is for steroids. While it is not easy to synthesize, it is a convenient intermediate which can be made from other more available materials, and which can then be modified to produce the desired target compound.
Upstream sources
16-DPA can be produced from a variety of steroidal sapogenins. Industrially useful sources are diosgenin in mexican yams[1][2] and solasodine from certain nightshades. These two sapogenins can be used in a one-pot synthesis.[3] Solanidine in potato greens, an alkaloid sapogenin, is also a key source material.[4]
Downstream products
Compounds derived from 16-DPA include:
- Corticosteroids (mainly of a C22 pregnane backbone): hydrocortisone*, betamethasone*, dexamethasone*, beclometasone*, fluticasone, and prednicarbate;[5]
- Progestogen (mainly of a C22 pregnane backbone): pregnenolone, progesterone*,[6] various synthetic derivatives such as medroxyprogesterone acetate* and levonorgestrel*;
- Androgens (mainly of a C19 androstane, 17-keto backbone): testosterone*[7] and esters, various synthetic derivatives;
- Estrogens (mainly of a C18 estrane, 17-hydroxy backbone): estradiol[7] and esters such as estradiol cypionate*, various synthetic derivatives such as ethinylestradiol*.
Those marked with a * appear on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, some as part of a compound medication. The list is by no means complete due to the central role of 16-DPA in steroid production.
Pharmacology
There are no current medical uses of 16-DPA. Studies in male hamsters show that the related chemical 16-DHP acts as an farnesoid X receptor (FXR) antagonist, consequently up-regulating CYP7A1 and lowering serum cholesterol. The CSIR-CDRI holds a patent over 16-DHP for prospective lipid-lowering use.[8]
History
Production of substantial quantities of steroids was not achieved until the Marker degradation in the late 1930s, a synthesis route converting diosgenin into the related compound 16-dehydropregnenolone (16-DP or 16-DHP). This reaction established Mexico as a world center of steroid production.[9] 16-DPA was produced in a variant of Marker degradation published in 1940.[6]
The earliest PubChem patent record for 16-DPA is US2656364A of 1951, describing its conversion into 17-ketosteroids.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ Pritish Kumar Chowdhury, "Process for the production of 16-Dehydropregenolone acetate form diosgenin", us patent 5808117, issued 15-09-1998
- ↑ Baruah, Diganta; Das, Ram Nath; Konwar, Dilip (2015). "Facile green synthesis of 16-dehydropregnenolone acetate (16-DPA) from diosgenin". Synthetic Communications 46 (1): 79–84. doi:10.1080/00397911.2015.1121280. https://figshare.com/articles/journal_contribution/1609791.
- ↑ Goswami, Amrit; Kotoky, Rumi; Rastogi, Romesh C.; Ghosh, Anil C. (1 May 2003). "A One-Pot Efficient Process for 16-Dehydropregnenolone Acetate". Organic Process Research & Development 7 (3): 306–308. doi:10.1021/op0200625. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/234671756.pdf.
- ↑ Vronen, Patrick J.E.; Koval, Nadeshda; de Groot, Aede (2003). "The synthesis of 16-dehydropregnenolone acetate (DPA) from potato glycoalkaloids". Arkivoc 2004 (2): 24–50. doi:10.3998/ark.5550190.0005.203. http://www.arkat-usa.org/get-file/19135/.
- ↑ "13.4.7 The Crystal Structure of Dehydropregnolone Acetate: A Pregnane". Chemistry and Pharmacology of Naturally Occurring Bioactive Compounds. CRC Press. p. 308.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Sterols. CXII. Sapogenins. XLI. The Preparation of Trillin and its Conversion to Progesterone". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 62 (12): 3349–3350. 1940. doi:10.1021/ja01869a023.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Hershberg, Emanuel B.; Oliveto, Eugene P. (20 October 1953). "Process for the manufacture of 17-keto steroids". https://patents.google.com/patent/US2656364A.
- ↑ Ramakrishna, Rachumallu; Kumar, Durgesh; Bhateria, Manisha; Gaikwad, Anil Nilkanth; Bhatta, Rabi Sankar (1 April 2017). "16-Dehydropregnenolone lowers serum cholesterol by up-regulation of CYP7A1 in hyperlipidemic male hamsters". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 168: 110–117. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.02.013. PMID 28232149.
- ↑ "Russell Marker and the Mexican Steroid Hormone Industry". American Chemical Society. https://www.acs.org/content/acs/en/education/whatischemistry/landmarks/progesteronesynthesis.html. Retrieved June 5, 2012.
 |

