Chemistry:2-Chloro-6-fluorobenzaldehyde
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-chloro-6-fluorobenzaldehyde
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H4ClFO | |
| Molar mass | 158.56 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 32–35 °C (89.6-95 °F; 305–308 K) |
| Boiling point | 104–105 °C (219–221 °F; 377–378 K) |
| Insoluble in water | |
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol, ethanol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335, H401 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P321, P362+364Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 101 °C (214 °F; 374 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
2-Chloro-6-fluorobenzaldoxime Chlorobenzaldehyde Fluorobenzaldehyde |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
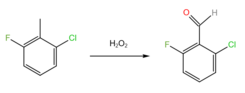
2-Chloro-6-fluorobenzaldehyde is a halogenated benzaldehyde derivative with the formula C6H3ClFCHO. It is an intermediate in the synthesis of other halogenated heterocyclic compounds.[1][2]
Uses and preparation
2-Chloro-6-fluorobenzaldehyde is a synthetic intermediate in the production of dicloxacillin and flucloxacillin. In addition it is used in the production of pesticides.
2-Chloro-6-fluorobenzaldehyde is prepared by oxidation of 2-chloro-6-fluorotolulene by hydrogen peroxide.[3]
References
- ↑ Daniewski, Andrzej R.; Liu, Wen; Püntener, Kurt; Scalone, Michelangelo (2002-05-01). "Two Efficient Methods for the Preparation of 2-Chloro-6-methylbenzoic Acid" (in en). Organic Process Research & Development 6 (3): 220–224. doi:10.1021/op0102363. ISSN 1083-6160. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/op0102363.
- ↑ Naveen, S.; Kavitha, Chandagirikoppal V.; Sarala, G.; Anandalwar, SridharM.; Prasad, J. Shashidhara; Rangappa, Kanchugarakoppal S. (2006). "Crystal Structure of 3-(2-Chloro-6-fluorophenyl)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-acrylonitrile" (in en). Analytical Sciences: X-ray Structure Analysis Online 22: X291–X292. doi:10.2116/analscix.22.x291. ISSN 1348-2238. http://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/analscix/22/0/22_0_x291/_article.
- ↑ Bunnett, J. F.; Miles, J. H.; Nahabedian, K. V. (1961). "Kinetics and Mechanism of the Alkali Cleavage of 2,6-Dihalobenzaldehydes 1" (in en). Journal of the American Chemical Society 83 (11): 2512–2516. doi:10.1021/ja01472a022. ISSN 0002-7863. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ja01472a022.
 |