Chemistry:Cyclopentadienyltungsten tricarbonyl dimer
From HandWiki
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
bis(tricarbonyl[η5-cyclopentadienyl]
| |
| Other names
cyclopentadienyl tungsten
carbonyl dimer
Bis(tricarbonylcyclopentadienyltungsten) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H10O6W2 | |
| Molar mass | 665.93 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | red solid |
| Density | 2.738 g/cm3 |
| insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | flammable |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
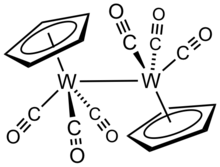
Cyclopentadienyltungsten tricarbonyl dimer is the organotungsten compound with the formula Cp2W2(CO)6, where Cp is C5H5. A dark red crystalline solid, it is the subject of research, although it has no or few practical uses.
Structure and synthesis
The molecule exists in two rotamers, gauche and anti.[1] The six CO ligands are terminal, and the W-W bond distance is 3.222 Å.[2] The compound is prepared by treatment of tungsten hexacarbonyl with sodium cyclopentadienide followed by oxidation of the resulting NaW(CO)3(C5H5).[3]
Related compounds
References
- ↑ Brian Mann (1997-01-06). "Fluxionality of Cp2Mo2(CO)6". University of Sheffield. http://brian-mann.staff.shef.ac.uk/Cp2Mo2CO6.html.
- ↑ R. D. Adams, D. M. Collins, and F. A. Cotton (1974). "Molecular Structures and Barriers to Internal Rotation in Bis(η5 -cyclopentadienyl)hexacarbonylditungsten and Its Molybdenum Analog". Inorg. Chem. 13 (5): 1086–1090. doi:10.1021/ic50135a015.
- ↑ Manning, A. R.; Hacket, Paul; Birdwhistell, Ralph (1990). "Hexacarbonylbis(η5-Cyclopentadienyl)Dichromium, Molybdenum, and Tungsten and their Analogs, M2(η5-C5H4R)2(CO)6 (M = Cr, Mo, and W; R = H, Me or PhCH2)". Inorganic Syntheses 28: 148–149. doi:10.1002/9780470132593.ch39. ISBN 9780470132593.
 |
