Chemistry:Fisetinidin
From HandWiki
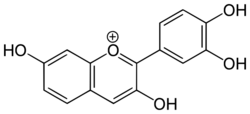
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)chromenylium-3,7-diol chloride
| |
| Other names
Fisetinidin chloride
3,3',4',7-Tetrahydroxyflavylium chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H11O5+ (Cl−) | |
| Molar mass | 306.69 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Fisetinidin is an anthocyanidin. It has been obtained from the heartwood of Acacia mearnsii,[1] from the bark of Rhizophora apiculata[2] and can also be synthesized.[3] Fisetinidin is very similar in structure to fisetin,[3] which itself differs in structure from quercetin only by an additional hydroxyl group on the latter.
An assay of twenty flavonoids showed fisetinidin to be the least effective in inhibition of CD38 enzyme.[4]
Tannins
Fisetinidin can compose tannins.[1] The polymers are then called profisetinidin (Porter, 1992).[2]
See also
- Leuco-fisetinidin
- List of compounds with carbon number 15
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 D. G. Roux; E. Paulus (February 1962). "Condensed tannins. 12. Polymeric leuco-fisetinidin tannins from the heartwood of Acacia mearnsii". Biochem. J. 82 (2): 320–324. doi:10.1042/bj0820320. PMID 14494576.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Afidah A. Rahim; Emmanuel Rocca; Jean Steinmetz; M. Jain Kassim; M. Sani Ibrahim; Hasnah Osman (2008). "Antioxidant activities of mangrove Rhizophora apiculata bark extracts". Food Chemistry 107 (1): 200–207. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.08.005.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 M. Gábor; E. EperJessy (10 December 1966). "Antibacterial Effect of Fisetin and Fisetinidin". Nature 212 (1273): 1273. doi:10.1038/2121273a0. PMID 21090477.
- ↑ "Flavonoids as inhibitors of human CD38". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 21 (13): 3939-3942. 2011. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.05.022. PMID 21641214.
 |

