Chemistry:Primulin (anthocyanin)
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
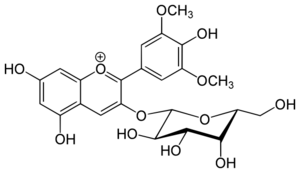
(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-2-[5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)chromenylium-3-yl]oxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol chloride
| |
| Other names
Malvidin 3-galactoside
Malvidin-3-galactoside chloride Malvidin-3-O-galactoside Malvidin-3-O-galactoside chloride 3-(Galactosyloxy)-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-benzopyrylium chloride Primulin Yellow[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H25ClO12 C23H25O12+ | |
| Molar mass | 528.89 g/mol (chloride) 493.43 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Primulin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-galactoside of malvidin. It can be found in Primula sinensis.[2]
The first crystalline form of this pigment was prepared by Rose Scott-Moncrieff in about 1930. This was the first crystalline anthrocyanine pigment ever identified. This was possible because of her insight into linking genetics with chemistry.[3]
References
- ↑ Primulin Yellow on chemicalregister.com
- ↑ J. B. Harborne; H. S. A. Sherratt (1961). "Plant Polyphenols: 3. Flavonoids in genotypes of Primula sinensis". Biochem. J. 78 (2): 298–306. doi:10.1042/bj0780298. PMID 13711452. PMC 1205266. http://www.biochemj.org/bj/078/0298/0780298.pdf.
- ↑ Rose Scott-Moncrieff and the dawn of (Bio) Chemical Genetics, Cathie Martin, April 2016, Biochemical classics, Biochemist.org, Retrieved 5 July 2016

