Chemistry:Luteolinidin
From HandWiki
Short description: Ion
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
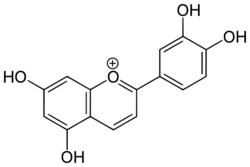
3′,4′,5,7-Tetrahydroxyflavylium
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-1λ4-benzopyran-1-ylium | |
| Other names
2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxychromenylium
2-(3,4-Dihydroxy-phenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-chromenylium | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H11O5+ | |
| Molar mass | 271.24 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Luteolinidin is a member of the 3-deoxyanthocyanidins. It is a cation with ill-defined anions. This orange species that can be found in Sorghum bicolor.[1][2]
Luteolinidin was shown to inhibit CD38 with relatively high potency compared with previously used inhibitors[3][4]
Glycosides
Luteolinidin 5-O-β-D-[3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-2-O-acetylglucopyranoside] (a 3-deoxyanthocyanidin laminaribioside) can be found in the fern Parablechnum novae-zelandiae (syn. Blechnum novae-zelandiae).[5]
See also
- List of compounds with carbon number 15
References
- ↑ Nielsen, Kirsten A.; Gotfredsen, Charlotte H.; Buch-Pedersen, Morten J.; Ammitzbøll, Henriette; Mattsson, Ole; Duus, Jens Ø.; Nicholson, Ralph L. (2004). "Inclusions of flavonoid 3-deoxyanthocyanidins in Sorghum bicolor self-organize into spherical structures". Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology 65 (4): 187–196. doi:10.1016/j.pmpp.2005.02.001.
- ↑ Dykes, Linda; Rooney, Lloyd W. (2006). "Sorghum and millet phenols and antioxidants". Journal of Cereal Science 44 (3): 236–251. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2006.06.007.
- ↑ Kellenberger, Esther; Kuhn, Isabelle; Schuber, Francis; Muller-Steffner, Hélène (2011). "Flavonoids as inhibitors of human CD38". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 21 (13): 3939–3942. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.05.022. PMID 21641214.
- ↑ Boslett, James; Hemann, Craig; Zhao, Yong Juan; Lee, Hon-Cheung; Zweier, Jay L. (2017). "Luteolinidin protects the postischemic heart through CD38 inhibition with preservation of NAD(P)(H)". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 361 (1): 99–108. doi:10.1124/jpet.116.239459. PMID 28108596.
- ↑ Swinny, Ewald E. (2001). "A novel acetylated 3-deoxyanthocyanidin laminaribioside from the fern Blechnum novae-zelandiae". Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C: Biosciences 56 (3–4): 177–180. doi:10.1515/znc-2001-3-402. PMID 11371005.
 |

