Chemistry:Fusafungine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Fusafungin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
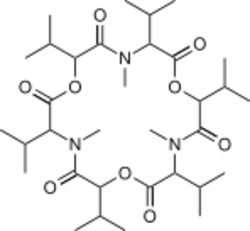
| Formula | C33H57N3O9 |
| Molar mass | 639.81 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 125 to 129 °C (257 to 264 °F) |
| |
| | |
Fusafungine (INN), also known as fusafungin, is an active agent used in antibiotics for treatment of nasal and throat infection. It also possesses anti-inflammatory properties. Fusafungine is a mixture of enniatin cyclohexadepsipeptides made up of alternating D-α-hydroxyvaleric acid and L-N-methylamino acid residues,[1] produced by the ascomycete Fusarium lateritium, and marketed by Servier under the trade names Locabiotal, Bioparox, and Locabiosol.
According to a pooled analysis study done in the UK for the efficacy of fusafungine in rhinopharingitis, it was found that the proportion of patients who showed an improvement in symptoms from Day 0 to Day 4 of infection was 61.5% with fusafungine vs. 46.8% when compared to a placebo.[2]
In February 2016, the European Medicines Agency recommended the withdrawal of fusafungine from the market due to rare but severe allergic reactions (mainly bronchospasms).[3]
References
- ↑ "Alkali cation transport through liposomes by the antimicrobial fusafungine and its constitutive enniatins". Biochemical Pharmacology 50 (12): 2105–7. December 1995. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(95)02045-4. PMID 8849339.
- ↑ "Efficacy of fusafungine in acute rhinopharyngitis: a pooled analysis". Rhinology 42 (4): 207–12. December 2004. PMID 15626253.
- ↑ "CMDh endorses revocation of authorisations for fusafungine sprays used to treat airway infections". European Medicines Agency. 17 September 2018. http://www.ema.europa.eu/ema/index.jsp?curl=pages/medicines/human/referrals/Fusafungine_for_oromucosal_and_nasal_use/human_referral_prac_000054.jsp&mid=WC0b01ac05805c516f.
 |

