Chemistry:Hexafluoropropylene oxide
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
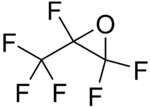
| IUPAC name
2,2,3-Trifluoro-3-(trifluoromethyl)oxirane
| |
| Other names
trifluoro(trifluoromethyl)oxirane
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | HFPO |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3F6O | |
| Molar mass | 166.02 g/mol |
| Appearance | colourless gas |
| Density | 1300kg/m3 at 25 °C |
| Melting point | −144 °C (−227 °F; 129 K) |
| Boiling point | −27.4 °C (−17.3 °F; 245.8 K) |
| Solubility | nonpolar solvents |
| Vapor pressure | 660kPa at 25 °C |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Hexafluoropropylene oxide (HFPO) is an intermediate used in industrial organofluorine chemistry; specifically it is a monomer for fluoropolymers. This colourless gas is the epoxide of hexafluoropropylene, which is a fluorinated analog of propylene oxide, HFPO is produced by DuPont and 3M and as a precursor to the lubricant Krytox and related materials. It is generated by oxidation of perfluoropropylene, e.g. with oxygen as well as other oxidants.[1]
Reactivity
Fluoride catalyzes the formation of perfluorinated polyethers such as Krytox. The initial step entails nucleophilic attack at the middle carbon to give the perfluoropropoxide anion, which in turn attacks another monomer. This process generates a polymer terminated by an acyl fluoride, which is hydrolyzed to the carboxylic acid which is decarboxylated with fluorine. [2] The net polymerization reaction can be represented as:
- n+2 CF3CFCF2O → CF3CF2CF2O(CF(CF3)CF2O)nCF2CF3 + CO
Upon heating above 150 °C, HFPO decomposes to trifluoroacetyl fluoride and difluorocarbene:
- CF3CFCF2O → CF3C(O)F + CF2
The epoxide of tetrafluoroethylene is even more unstable with respect to trifluoroacetyl fluoride.
In the presence of Lewis acids the compound rearranges to hexafluoroacetone, another important chemical intermediate. This rearrangement can be of concern during storage as the rearrangement be catalyzed by the material of the storage cylinder's walls and leads to unwanted formation of HFA during storage. As a result of this, 3M recommends using all HFPO shipped in carbon-steel containers within 90 days of shipping.[3]
Methanolysis affords methyl trifluoropyruvate, a reagent useful in organic synthesis:[4]
- CF3CFCF2O + 2 MeOH → CF3C(O)CO2Me + MeF + 2 HF
References
- ↑ Siegemund, Günter; Schwertfeger, Werner; Feiring, Andrew; Smart, Bruce; Behr, Fred; Vogel, Herward; McKusick, Blaine; Kirsch, Peer (2016-01-28). Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. ed (in en). Fluorine Compounds, Organic. Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. pp. 1–56. doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_349.pub2. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14356007.a11_349.pub2.
- ↑ https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/844#
- ↑ https://multimedia.3m.com/mws/mediawebserver?SSSSSuUn_zu8l00xlYtG4x2G4v70k17zHvu9lxtD7SSSSSS
- ↑ Ruth Figueroa; Richard P. Hsung; Gang Li; Jin Haek Yang (2007). "Methyltrifluoropyruvate". e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn00769. ISBN 978-0-471-93623-7.
External links
 |

