Chemistry:Lead stearate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Lead(2+) octadecanoate, lead(II) stearate, lead distearate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C36H70PbO4 | |
| Molar mass | 774.14 |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Density | 1.4 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 115.7 °C (240.3 °F; 388.8 K) |
| Boiling point | 359.4 °C (678.9 °F; 632.5 K) |
| Slightly soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H302, H332, H360, H373 | |
| P260, P261, P281, P304, P340, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
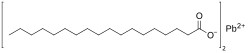
Lead stearate is a metal-organic compound, a salt of lead and stearic acid with the chemical formula C36H70PbO4.[1] The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid.[2] The compound is toxic.
Synthesis
The compound can be prepared by reacting stearic acid, lead(II) oxide, and a catalyst acetic acid.[3]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathrm{2 \ C_{17}H_{35}COOH + PbO \longrightarrow (C_{17}H_{35}COO)_{2}Pb + \ H_2O} }[/math]
Also, an exchange reaction between lead(II) acetate and sodium stearate:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathsf{ Pb(CH_3COO)_2 + 2NaC_{18}H_{35}O_2 \ \xrightarrow{}\ Pb(C_{18}H_{35}O_2)_2\downarrow + 2 CH_3COONa } }[/math]
Physical properties
White powder with a slight fatty odor. Sinks in water.[4] Hygroscopic in air.
Slightly soluble in water.[1] Soluble in hot ethanol.
Uses
The compound is used as a drier in oil paints and varnishes to speed the polymerization and oxidation processes. Also used as a lubricant and stabilizer in vinyl polymers and as a corrosion inhibitor in petroleum products.[5][6][7]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Lead Stearate". American Elements. https://www.americanelements.com/lead-stearate-1072-35-1.
- ↑ "T3DB: Lead stearate". t3db.ca. http://www.t3db.ca/toxins/T3D1324.
- ↑ "Preparation process of lead stearate based on melting method". 18 December 2013. https://patents.google.com/patent/CN103450003A/en.
- ↑ "LEAD STEARATE | CAMEO Chemicals | NOAA". cameochemicals.noaa.gov. https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/3746.
- ↑ "Lead Stearate » Waldies Co. Ltd.". Waldies Co. Ltd.. https://www.waldies.com/products/lead-stearate-ls/.
- ↑ (in en) Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology: Fuel resources to heat stabilizers. Wiley. 1991. p. 1074. ISBN 978-0-471-52669-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=WPBTAAAAMAAJ&q=lead+stearate. Retrieved 7 March 2023.
- ↑ Titow, M. V. (6 December 2012) (in en). PVC Technology. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 269. ISBN 978-94-009-5614-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=aYPtCAAAQBAJ&dq=lead+stearate&pg=PA269. Retrieved 7 March 2023.
 |

