Chemistry:Neodymium tantalate
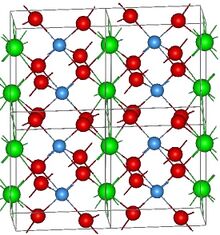 The structure of Neodymium tanatalate. Atoms are: O(red), Ta(blue) and Nd(green)
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| NdTaO4 | |
| Molar mass | 389.19 |
| Appearance | gray-purple solid[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Neodymium tantalate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NdTaO4. It is prepared by reacting neodymium oxide and tantalum pentoxide at 1200 °C.[1] It reacts with a mixture of tantalum pentoxide and chlorine gas at high temperature to obtain Nd2Ta2O7Cl2.[2] It is ammonolyzed at high temperature to obtain oxynitrides of Nd-Ta.[3]
Properties
Neodymium tantalate forms violet crystals of the monoclinic system, with space group I 2/a, cell parameters a = 0.55153 nm, b = 1.12388 nm, c = 0.51184 nm, β = 95.731°, Z = 4.[4]
There is a metastable high-pressure phase of the monoclinic system, space group P 21/c, cell parameters a = 0.75920 nm, b = 0.54673 nm, c = 0.77022 nm, β = 100.032°, Z = 4.[5]
Neodymium tantalate is insoluble in water.[citation needed]
See also
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 Krylov, E. I.; Strelina, M. M. Praseodymium and neodymium orthotantalates. Zhurnal Neorganicheskoi Khimii, 1961. 6: 235-235. ISSN 0044-457X.
- ↑ U. Schaffrath, R. Gruehn (1988-12-01). "Nd7,33Ta8O28CI6 — ein Zwischenprodukt des thermischen Abbaus von Nd2Ta2O7Cl2: Präparation, Struktur und magnetische Eigenschaften / Nd7,33Ta8O28Cl6 — an Intermediate Product of the Thermal Decomposition of Nd2Ta2O7Cl2: Preparation, Crystal Structure and Magnetic Properties". Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B 43 (12): 1567–1574. doi:10.1515/znb-1988-1208. ISSN 1865-7117.
- ↑ Pascal Maillard, Franck Tessier, Emmanuelle Orhan, François Cheviré, Roger Marchand (January 2005). "Thermal Ammonolysis Study of the Rare-Earth Tantalates RTaO 4" (in en). Chemistry of Materials 17 (1): 152–156. doi:10.1021/cm040131p. ISSN 0897-4756. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/cm040131p. Retrieved 2021-06-06.
- ↑ Kaijie Ning, Qingli Zhang, Deming Zhang, Jintai Fan, Dunlu Sun, Xiaofei Wang, Yin Hang (2014). "Crystal growth, characterization of NdTaO4: A new promising stoichiometric neodymium laser material". Journal of Crystal Growth 388: 83–86. doi:10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2013.10.030. Bibcode: 2014JCrGr.388...83N.
- ↑ Titov Yu. A., Sych A. M., Sokolov A. N., Kapshuk A. A., Markiv V. Ya., Belyavina N. M. (2000). Crystal structure of the high-pressure modification of NdTaO4. 311 (Journal of alloys and compounds ed.). pp. 252–255. http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=1506065.
External links
- Patrick N. Walsh, Harold W. Goldstein, David White (May 1960). "Vaporization of Rare-Earth Oxides" (in en). Journal of the American Ceramic Society 43 (5): 229–233. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1960.tb14589.x. ISSN 0002-7820. http://doi.wiley.com/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1960.tb14589.x. Retrieved 2021-06-06.
 |

