Chemistry:Tantalum pentafluoride
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
tantalum pentafluoride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| TaF5 | |
| Molar mass | 275.95 g/mol |
| Appearance | white powder |
| Density | 4.74 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 96.8 °C (206.2 °F; 369.9 K) |
| Boiling point | 229.5 °C (445.1 °F; 502.6 K) |
| decomposes | |
| +795.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| 0 D | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | HF source |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H302, H314 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P301+330+331, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P321, P322, P330, P363, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
TaCl5 NbCl5 WF6 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tantalum(V) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula TaF5. It is one of the principal molecular compounds of tantalum. Characteristic of some other pentafluorides, the compound is volatile but exists as an oligomer in the solid state.
Preparation and structure
It is prepared by treating tantalum metal with fluorine gas.[2] NbF5 is prepared similarly.
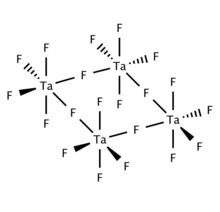
Solid and molten TaF5 is tetrameric, consisting of four TaF6 centers linked via bridging fluoride centers. Gaseous TaF5 adopts the trigonal pyramidal structure with D3h symmetry.[3]
Reactions and derivatives
The tendency of TaF5 to form clusters in the solid state indicates the Lewis acidity of the monomer. Indeed, TaF5 reacts with fluoride sources to give the ions [TaF6]−, [TaF7]2−, and [TaF8]3−. With neutral Lewis bases, such as diethyl ether TaF5 forms adducts.
TaF5 is used in combination with HF as a catalyst for the alkylation of alkanes and alkenes and for the protonation of aromatic compounds. The TaF5–HF system is stable in reducing environments, unlike SbF5–HF.[4] In the presence of fluoride, tantalum pentafluoride forms the anions [TaF8]3−, [TaF7]2−, or [TaF6]−, depending on the nature of the counterion and the concentration of HF. High concentrations of HF favor the hexafluoride by virtue of the formation of HF−2:[5]
- [TaF7]2− + HF ⇌ [TaF6]− + HF−2
The salts M3TaF8 have been crystallized. For K+ = M+, the crystals consist of [TaF7]2− anions together with fluoride that does not coordinate to Ta(V).[6] For M+ = M+, the crystals features [TaF8]3−.[7]
Relevance to separation of Ta and Nb
In the Marignac process, Nb and Ta are separated by fractional crystallization of K2TaF7 from solutions of hydrofluoric acid. Under these conditions, niobium forms K2NbOF5, which is more soluble than K2TaF7. Reduction of K2TaF7 with sodium gives metallic Ta.[8]
References
- ↑ "Tantalum pentafluoride" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/82218#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ Priest, H. F. (1950). Anhydrous Metal Fluorides" Inorganic Syntheses. 3. p. 171-183. doi:10.1002/9780470132340.ch47.
- ↑ Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. "Inorganic Chemistry" Academic Press: San Diego, 2001. ISBN:0-12-352651-5.
- ↑ Arpad Molnar; G. K. Surya Prakash; Jean Sommer (2009). Superacid Chemistry (2nd ed.). Wiley-Interscience. p. 60. ISBN 978-0-471-59668-4.
- ↑ Anatoly Agulyanski (2004). The chemistry of tantalum and niobium fluoride compounds. Amsterdam: Elsevier. p. 134. ISBN 0-444-51604-2. https://archive.org/details/chemistrytantalu00agul.
- ↑ Ľubomír Smrčok, Radovan Černý, Miroslav Boča, Iveta Macková, Blanka Kubíková (2010). "K3TaF8 from Laboratory X-ray powder data". Acta Crystallographica C 66 (2): pi16–pi18. doi:10.1107/S0108270109055140. PMID 20124670. https://archive-ouverte.unige.ch/unige:35441/ATTACHMENT01.
- ↑ Langer, V.; Smrčok, L.; Boča, M. (2010). "Redetermination of Na3TaF8". Acta Crystallographica C 66 (9): pi85–pi86. doi:10.1107/S0108270110030556. PMID 20814090.
- ↑ Klaus Andersson, Karlheinz Reichert, Rüdiger Wolf "Tantalum and Tantalum Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH. Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a26_071


