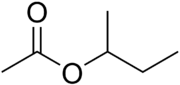
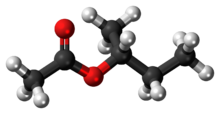
Chemistry:Sec-Butyl acetate
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Butan-2-yl acetate[1] | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12O2 | |
| Molar mass | 116.160 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear, liquid |
| Odor | Fruity[2] |
| Density | 0.87 g/cm3, liquid |
| Melting point | −99 °C (−146 °F; 174 K) |
| Boiling point | 112 °C (234 °F; 385 K) |
| 0.80 g/100 mL | |
| Vapor pressure | 10 mmHg[2] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Flammable |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| Flash point | 17 °C; 62 °F; 290 K[2] |
| Explosive limits | 1.7–9.8%[2] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 200 ppm (950 mg/m3)[2] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 200 ppm (950 mg/m3)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
1700 ppm[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
sec-Butyl acetate, or s-butyl acetate, is an ester commonly used as a solvent in lacquers and enamels, where it is used in the production of acyclic polymers, vinyl resins, and nitrocellulose.[3] It is a clear flammable liquid with a sweet smell.[4]
sec-Butyl acetate has three isomers that are also acetate esters: n-butyl acetate, isobutyl acetate, and tert-butyl acetate.
History
The first method of production of sec-butyl acetate was the esterification of sec-butanol and acetic anhydride[5] It was experimentally determined and published in 1946 by Rolf Altschul.[6]
Toxicology
The -1">50 for rats is 13 g/kg.[7] Exposure in humans to significant quantities of sec-butyl acetate can cause irritation to the eyes, mouth, throat, nose, and skin.[8] Ingestion and inhalation of sec-butyl acetate can cause central nervous system depression producing symptoms of dizziness and disorientation.[8]
Nomenclature
sec-Butyl acetate is chiral. It has one stereocenter, carbon 2 in the sec-butyl group. The names of the two enantiomers are:
- [(2S)-butan-2-yl] acetate, (+)-sec-butyl acetate
- [(2R)-butan-2-yl] acetate, (-)-sec-butyl acetate
References
- ↑ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 370. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0073". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0073.html.
- ↑ "Acetic acid", Ullman's encyclopedia of industrial chemistry (2003, 6th ed., Vol. 1, pp. 170–171). Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH.
- ↑ Howard, H. H. (1993). sec-Butyl acetate. In Handbook of environmental fate and exposure data for organic chemists (Vol. 5, pp. 60–65). Chelsea, MI: Lewis.
- ↑ Altschul, R. (1946). "The Reversible Esterification of Carboxylic Acids with Isobutene and Trimethylethylene. Quantitative Studies and Synthetic Applications", Journal of the American Chemical Society, 68(12), 2605–2609.
- ↑ Template:Cite Merck Index
- ↑ Canadian Center for Occupational Health and Safety. (1996). 2-Butyl acetate. Retrieved February 20, 2009, from CHEMINFO database.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 International Programme on Chemical Safety. (2003). sec-Butyl acetate. Retrieved February 20, 2009, from INCHEM database.
External links
 |
