Chemistry:Triethyl phosphate
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Triethyl phosphate | |
| Other names
Phosphoric acid triethyl ester
Phosphoric ester (archaic) Flame retardant TEP[2] Tris(ethyl) phosphate Triethoxyphosphine oxide Ethyl phosphate (neutral) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | TEP, Et3PO4 |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H15O4P | |
| Molar mass | 182.15 g/mol |
| Density | 1.072 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −56.5 °C (−69.7 °F; 216.7 K) |
| Boiling point | 215 °C (419 °F; 488 K) |
| Miscible | |
| -125.3·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | http://www.sciencelab.com/msds.php?msdsId=9925320 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 107 °C (225 °F; 380 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
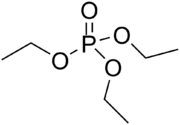
Triethyl phosphate is an organic chemical compound with the formula (C2H5)3PO4 or OP(OEt)3. It is a colorless liquid. It is the triester of ethanol and phosphoric acid and can be called "phosphoric acid, triethyl ester".
Its primary uses are as an industrial catalyst (in acetic anhydride synthesis), a polymer resin modifier, and a plasticizer (e.g. for unsaturated polyesters). In smaller scale it is used as a solvent for e.g. cellulose acetate, flame retardant, an intermediate for pesticides and other chemicals, stabilizer for peroxides, a strength agent for rubber and plastic including vinyl polymers and unsaturated polyesters, etc.[3]
History
It was studied for the first time by France chemist Jean Louis Lassaigne in the early 19th century.
See also
- Franz Anton Voegeli
References
- ↑ "Zhangjiagang Shunchang Chemical Co., Ltd". Triethylphosphate. Archived from the original on December 17, 2004. https://web.archive.org/web/20041217051620/http://www.shunchangchem.com/template/produe90.htm. Retrieved June 13, 2009.
- ↑ "Triethyl phosphate". https://pubchem.ncbi.nih.gov/compound/6535.
- ↑ Triethylphosphate, International Programme on Chemical Safety
 |

