Chemistry:Peroxide
From HandWiki

Short description: Chemical compounds with the structure R–O–O–R'
In chemistry, peroxides are a group of compounds with the structure R–O–O–R, where R is any element.[1][2] The O–O group in a peroxide is called the peroxide group or peroxy group (sometimes called peroxo group or peroxyl group). The nomenclature is somewhat variable,[3] and the term was introduced by Thomas Thomson in 1804 for an oxide with the greatest quantity of oxygen.[4]
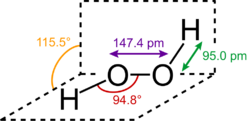
The most common peroxide is hydrogen peroxide (H
2O
2), colloquially known simply as "peroxide". It is marketed as solutions in water at various concentrations. Many organic peroxides are known as well.
In addition to hydrogen peroxide, some other major classes of peroxides are:
- Peroxy acids, the peroxy derivatives of many familiar acids, examples being peroxymonosulfuric acid and peracetic acid, and their salts, one example of which is potassium peroxydisulfate.
- Main group peroxides, compounds with the linkage E–O–O–E (E = main group element).
- Metal peroxides, examples being barium peroxide (BaO
2), sodium peroxide (Na
2O
2) and zinc peroxide (ZnO
2). - Organic peroxides, compounds with the linkage C–O–O–C or C–O–O–H. One example is tert-butylhydroperoxide.
References
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ↑ Smith, Michael B.; March, Jerry (2007), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (6th ed.), New York: Wiley-Interscience, ISBN 978-0-471-72091-1, https://books.google.com/books?id=JDR-nZpojeEC&printsec=frontcover
- ↑ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "peroxides". doi:10.1351/goldbook.P04510
- ↑ Harper, Douglas. "peroxide". Online Etymology Dictionary. https://www.etymonline.com/?term=peroxide.
 |