Chemistry:Trimethylsilylacetylene
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Ethynyltri(methyl)silane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | TMSA |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H10Si | |
| Molar mass | 98.220 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.69 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 53 °C (127 °F; 326 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H225, H315, H318, H319, H335 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P370+378, P403+233, P403+235, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
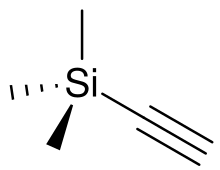
Trimethylsilylacetylene is the organosilicon compound with the formula (CH
3)
3SiC
2H. A colorless liquid, "tms acetylene", as it is also called, is used as a source of "HC2−" in organic synthesis.
Use
Trimethylsilylacetylene is used in Sonogashira couplings as the equivalent of acetylene. Using this protected alkyne, as opposed to acetylene itself, prevents further coupling reactions. The trimethylsilyl group can then be cleaved off with TBAF or DBU to form phenylacetylene derivatives.[1] Trimethylsilylacetylene is also used to synthesize diphenylacetylene derivatives in a one-pot Sonogashira coupling, in which the phenylacetylene derivative reacts with a second aryl halide after in-situ deprotection.[2] A less expensive alternative reagent is 2-methylbut-3-yn-2-ol, which after alkynylation is deprotected with base.
Trimethylsilylacetylene is commercially available. It may also be prepared in a manner similar to other silyl compounds: deprotonation of acetylene with a Grignard reagent, followed by reaction with trimethylsilyl chloride.[3]
Trimethylsilylacetylene is a precursor to 1,4-bis(trimethylsilyl)buta-1,3-diyne, a protected form of 1,3-butadiyne.[4]
History
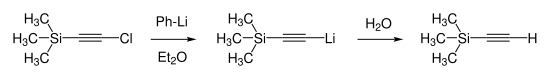
Trimethylsilylacetylene was first synthesized in 1959 by Heinz Günter Viehe. He reduced chloro(trimethylsilyl)acetylene by reaction with phenyllithium in diethyl ether and proceeded with subsequent hydrolysis.[5]
References
- ↑ Godson C. Nwokogu; Saskia Zemolka; Florian Dehme (2007). "Trimethylsilylacetylene". EROS. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rt288.pub2. ISBN 978-0-471-93623-7.
- ↑ Mio, Matthew J.; Kopel, Lucas C.; Braun, Julia B.; Gadzikwa, Tendai L.; Hull, Kami L.; Brisbois, Ronald G.; Markworth, Christopher J.; Grieco, Paul A. (2002). "One-Pot Synthesis of Symmetrical and Unsymmetrical Bisarylethynes by a Modification of the Sonogashira Coupling Reaction". Organic Letters 4 (19): 3199–3202. doi:10.1021/ol026266n. PMID 12227748.
- ↑ Andrew B. Holmes, Chris N. Sporikou (1987). "Trimethylsilylacetylene". Organic Syntheses: 61. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.065.0061.
- ↑ Graham E. Jones, David A. Kendrick, and Andrew B. Holmes (1987). "1,4-Bis(trimethylsilyl)buta-1,3-diyne". Organic Syntheses 65: 52. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.065.0052.
- ↑ H. G. Viehe (1959), "Heterosubstituierte Acetylene, III. Nucleophile Substitutionen und Halogen-Metall-Austauschreaktionen an Dreifachbindungen" (in German), Chemische Berichte 92 (12): pp. 3064–3075, doi:10.1002/cber.19590921209
 |