Chemistry:Vincamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Oxybral SR |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
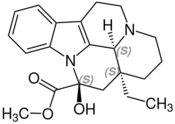
| Formula | C21H26N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 354.450 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Vincamine is a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid found in the leaves of Vinca minor (lesser periwinkle), comprising about 25–65% of its indole alkaloids by weight. It can also be synthesized from related alkaloids.[1]
Uses
Vincamine is sold in Europe as a prescription medicine for the treatment of primary degenerative and vascular dementia.[citation needed] In the United States, it is permitted to be sold as a dietary supplement when labeled for use in adults for six months or less.[2] Most common preparations are in the sustained release tablet forms.
Chemistry
Synthesis
Tabersonine can be used for semi-synthesis of vincamine.[3]
Derivatives
Vinpocetine is a synthetic derivative of vincamine used for cerebrovascular diseases and as dietary supplement.[4] Vincamine derivatives have been also studied as anti addictive[5] and antidiabetic[6] agents.
Research
It may have nootropic effects.[3] It has been investigated as novel anticancer drug.[7]
Concerns over long-term use have been documented by the US National Toxicology Program.[8]
See also
References
- ↑ "Indole Alkaloids". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry (Fifth ed.). Wiley-VCH. 1985. p. 393. ISBN 3-527-20100-9.
- ↑ "Summary of Data for Chemical Selection: Vincamine". National Toxicology Program. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/htdocs/chem_background/exsumpdf/vincamine_508.pdf.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Voacanga, (Apocynaceae), a review of taxonomy, phytochemistry, ethnobotany and pharmacology". Agricultural University Wageningen papers 85 (3). 1985. ISSN 0169-345X. https://www.erowid.org/plants/voacanga_africana/voacanga_africana_info1.shtml.
- ↑ "Vinpocetine in Dietary Supplements". FDA. 2019-06-03. https://www.fda.gov/Food/DietarySupplements/ProductsIngredients/ucm518478.htm.
- ↑ "Preventing Morphine-Seeking Behavior through the Re-Engineering of Vincamine's Biological Activity". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 63 (10): 5119–5138. May 2020. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01924. PMID 31913038.
- ↑ "Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of vincamine derivatives as potential pancreatic β-cells protective agents for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus". European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 188: 111976. February 2020. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111976. PMID 31918073.
- ↑ "Vincamine, a safe natural alkaloid, represents a novel anticancer agent". Bioorganic Chemistry 107: 104626. February 2021. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104626. PMID 33450545.
- ↑ "Vincamine Dietary Supplements 1617-90-9 - National Toxicology Program". https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/sites/default/files/ntp/htdocs/chem_background/exsumpdf/vincamine_508.pdf.
External links
- "Vincamine MSDS". http://www.mpbio.com/includes/msds/ansi/en/158295-EN-ANSI.pdf.
- Chemical Selection Working Group. "Vincamine - 1617-90-9". Summary of Data for Chemical Selection. NIH - United States National Institutes of Health. https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/htdocs/chem_background/exsumpdf/vincamine_508.pdf.
 |
