Chemistry:Terazosin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Hytrin, Zayasel, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a693046 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 90–94% |
| Elimination half-life | 12 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
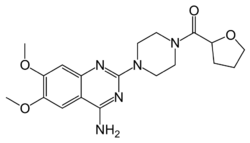
| Formula | C19H25N5O4 |
| Molar mass | 387.440 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Terazosin, sold under the brand name Hytrin among others, is a medication used to treat symptoms of an enlarged prostate and high blood pressure.[1] For high blood pressure, it is a less preferred option.[1] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects include dizziness, headache, tiredness, swelling, nausea, and low blood pressure with standing.[1] Severe side effects may include priapism and low blood pressure.[1] Prostate cancer should be ruled out before starting treatment.[1] It is an alpha-1 blocker and works by relaxing blood vessels and the opening of the bladder.[1]
Terazosin was patented in 1975 and came into medical use in 1985.[2] It is available as a generic medication.[3] In 2020, it was the 211th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2 million prescriptions.[4][5]
A study by researchers from the University of Edinburgh and the University of Oxford, published in 2022, suggested that terazosin may have the potential to confer neuroprotection upon motor neurons in motor neuron disease, as a result of its ability to activate PGK1.[6]
Synthesis
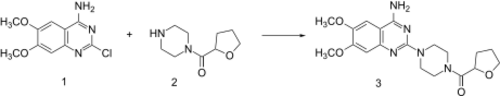
Reaction of piperazine with 2-furoyl chloride followed by catalytic hydrogenation of the furan ring leads to 2. This, when heated in the presence of 2-chloro-6,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4-amine (1) undergoes direct alkylation to terazosin (3).
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 "Terazosin Hydrochloride Monograph for Professionals" (in en). American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. https://www.drugs.com/monograph/terazosin-hydrochloride.html.
- ↑ (in en) Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. 2006. p. 455. ISBN 9783527607495. https://books.google.com/books?id=FjKfqkaKkAAC&pg=PA455.
- ↑ British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. pp. 768. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ↑ "The Top 300 of 2020". https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Top300Drugs.aspx.
- ↑ "Terazosin - Drug Usage Statistics". https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Drugs/Terazosin.
- ↑ "Targeting phosphoglycerate kinase 1 with terazosin improves motor neuron phenotypes in multiple models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis". EBioMedicine 83: 104202. September 2022. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104202. PMID 35963713.
- ↑ Winn M, Kyncl J, Dunnigan DA, Jones PH, US patent 4026894, issued 31 May 1977, assigned to Abbott
{{Navbox
| name = Drugs used in benign prostatic hypertrophy | title = Drugs used in [[Medicine:Benign prostatic hyperpbenign prostatic hyperplasia (G04C) | state = collapsed | listclass = hlist
| group1 = 5α-Reductase inhibitors | list1 =
| group2 = Alpha-1 blockers | list2 =
| group3 = Steroidal antiandrogens | list3 =
| group4 = Herbal products | list4 =
| group5 = Others | list5 =
}}
 |
