Concyclic points
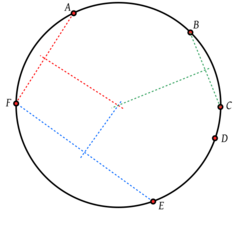
In geometry, a set of points are said to be concyclic (or cocyclic) if they lie on a common circle. A polygon whose vertices are concyclic is called a cyclic polygon, and the circle is called its circumscribing circle or circumcircle. All concyclic points are equidistant from the center of the circle.
Three points in the plane that do not all fall on a straight line are concyclic, so every triangle is a cyclic polygon, with a well-defined circumcircle. However, four or more points in the plane are not necessarily concyclic. After triangles, the special case of cyclic quadrilaterals has been most extensively studied.
Perpendicular bisectors
In general the centre O of a circle on which points P and Q lie must be such that OP and OQ are equal distances. Therefore O must lie on the perpendicular bisector of the line segment PQ.[1] For n distinct points there are n(n − 1)/2 bisectors, and the concyclic condition is that they all meet in a single point, the centre O.
Triangles
The vertices of every triangle fall on a circle called the circumcircle. (Because of this, some authors define "concyclic" only in the context of four or more points on a circle.)[2] Several other sets of points defined from a triangle are also concyclic, with different circles; see Nine-point circle[3] and Lester's theorem.[4]
The radius of the circle on which lie a set of points is, by definition, the radius of the circumcircle of any triangle with vertices at any three of those points. If the pairwise distances among three of the points are a, b, and c, then the circle's radius is
The equation of the circumcircle of a triangle, and expressions for the radius and the coordinates of the circle's center, in terms of the Cartesian coordinates of the vertices are given here.
Other concyclic points
In any triangle all of the following nine points are concyclic on what is called the nine-point circle: the midpoints of the three edges, the feet of the three altitudes, and the points halfway between the orthocenter and each of the three vertices.
Lester's theorem states that in any scalene triangle, the two Fermat points, the nine-point center, and the circumcenter are concyclic.
If lines are drawn through the Lemoine point parallel to the sides of a triangle, then the six points of intersection of the lines and the sides of the triangle are concyclic, in what is called the Lemoine circle.
The van Lamoen circle associated with any given triangle contains the circumcenters of the six triangles that are defined inside by its three medians.
A triangle's circumcenter, its Lemoine point, and its first two Brocard points are concyclic, with the segment from the circumcenter to the Lemoine point being a diameter.[5]
Cyclic quadrilaterals

A quadrilateral ABCD with concyclic vertices is called a cyclic quadrilateral; this happens if and only if (the inscribed angle theorem) which is true if and only if the opposite angles inside the quadrilateral are supplementary.[6] A cyclic quadrilateral with successive sides a, b, c, d and semiperimeter s = (a + b + c + d) / 2 has its circumradius given by[7][8]
an expression that was derived by the Indian mathematician Vatasseri Parameshvara in the 15th century.
By Ptolemy's theorem, if a quadrilateral is given by the pairwise distances between its four vertices A, B, C, and D in order, then it is cyclic if and only if the product of the diagonals equals the sum of the products of opposite sides:
If two lines, one containing segment AC and the other containing segment BD, intersect at X, then the four points A, B, C, D are concyclic if and only if[9]
The intersection X may be internal or external to the circle. This theorem is known as power of a point.
A convex quadrilateral is orthodiagonal (has perpendicular diagonals) if and only if the midpoints of the sides and the feet of the four altitudes are eight concyclic points, on what is called the eight-point circle.
Cyclic polygons
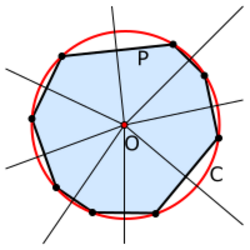
More generally, a polygon in which all vertices are concyclic is called a cyclic polygon. A polygon is cyclic if and only if the perpendicular bisectors of its edges are concurrent.[10] Every regular polygon is a cyclic polygon.
For a cyclic polygon with an odd number of sides, all angles are equal if and only if the polygon is regular. A cyclic polygon with an even number of sides has all angles equal if and only if the alternate sides are equal (that is, sides 1, 3, 5, ... are equal, and sides 2, 4, 6, ... are equal).[11]
A cyclic pentagon with rational sides and area is known as a Robbins pentagon. In all known cases, its diagonals also have rational lengths, though whether this is true for all possible Robbins pentagons is an unsolved problem.[12]
In any cyclic n-gon with even n, the sum of one set of alternate angles (the first, third, fifth, etc.) equals the sum of the other set of alternate angles. This can be proven by induction from the n = 4 case, in each case replacing a side with three more sides and noting that these three new sides together with the old side form a quadrilateral which itself has this property; the alternate angles of the latter quadrilateral represent the additions to the alternate angle sums of the previous n-gon.
A tangential polygon is one having an inscribed circle tangent to each side of the polygon; these tangency points are thus concyclic on the inscribed circle. Let one n-gon be inscribed in a circle, and let another n-gon be tangential to that circle at the vertices of the first n-gon. Then from any point P on the circle, the product of the perpendicular distances from P to the sides of the first n-gon equals the product of the perpendicular distances from P to the sides of the second n-gon.[13]
Point on the circumcircle
Let a cyclic n-gon have vertices A1 , ..., An on the unit circle. Then for any point M on the minor arc A1An, the distances from M to the vertices satisfy[14]
For a regular n-gon, if are the distances from any point M on the circumcircle to the vertices Ai, then [15]
Polygon circumscribing constant

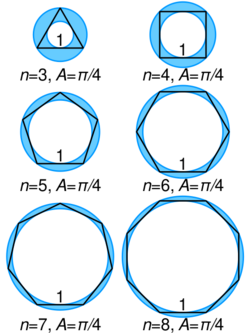
Any regular polygon is cyclic. Consider a unit circle, then circumscribe a regular triangle such that each side touches the circle. Circumscribe a circle, then circumscribe a square. Again circumscribe a circle, then circumscribe a regular pentagon, and so on. The radii of the circumscribed circles converge to the so-called polygon circumscribing constant
(sequence A051762 in the OEIS). The reciprocal of this constant is the Kepler–Bouwkamp constant.
Variations
In contexts where lines are taken to be a type of generalised circle with infinite radius, collinear points (points along a single line) are considered to be concyclic. This point of view is helpful, for instance, when studying inversion through a circle or more generally Möbius transformations (geometric transformations generated by reflections and circle inversions), as these transformations preserve the concyclicity of points only in this extended sense.[16]
In the complex plane (formed by viewing the real and imaginary parts of a complex number as the x and y Cartesian coordinates of the plane), concyclicity has a particularly simple formulation: four points in the complex plane are either concyclic or collinear if and only if their cross-ratio is a real number.[17]
Integer area and side lengths
Some cyclic polygons have the property that their area and all of their side lengths are positive integers. Triangles with this property are called Heronian triangles; cyclic quadrilaterals with this property (and that the diagonals that connect opposite vertices have integer length) are called Brahmagupta quadrilaterals; cyclic pentagons with this property are called Robbins pentagons. More generally, versions of these cyclic polygons scaled by a rational number will have area and side lengths that are rational numbers.
Let θ1 be the angle spanned by one side of the cyclic polygon as viewed from the center of the circumscribing circle. Similarly define the central angles θ2, ..., θn for the remaining n − 1 sides. Every Heronian triangle and every Brahmagupta quadrilateral has a rational value for the tangent of the quarter angle, tan θk/4, for every value of k. Every known Robbins pentagon (has diagonals that have rational length and) has this property, though it is an unsolved problem whether every possible Robbins pentagon has this property.
The reverse is true for all cyclic polygons with any number of sides; if all such central angles have rational tangents for their quarter angles then the implied cyclic polygon circumscribed by the unit circle will simultaneously have rational side lengths and rational area. Additionally, each diagonal that connects two vertices, whether or not the two vertices are adjacent, will have a rational length. Such a cyclic polygon can be scaled so that its area and lengths are all integers.
This reverse relationship gives a way to generate cyclic polygons with integer area, sides, and diagonals. For a polygon with n sides, let 0 < c1 < ... < cn−1 < +∞ be rational numbers. These are the tangents of one quarter of the cumulative angles θ1, θ1 + θ2, ..., θ1 + ... + θn−1. Let q1 = c1, let qn = 1 / cn−1, and let qk = (ck − ck−1) / (1 + ckck−1) for k = 2, ..., n−1. These rational numbers are the tangents of the individual quarter angles, using the formula for the tangent of the difference of angles. Rational side lengths for the polygon circumscribed by the unit circle are thus obtained as sk = 2 sin θk/2 = 4qk / (1 + qk2). The rational area is A = Σk sin θk/2 cos θk/2 = Σk 2qk(1 − qk2) / (1 + qk2)2. These can be made into integers by scaling the side lengths by a shared constant.
Other properties
A set of five or more points is concyclic if and only if every four-point subset is concyclic.[18] This property can be thought of as an analogue for concyclicity of the Helly property of convex sets.
Minimum bounding circle
A related notion is the one of a minimum bounding circle, which is the smallest circle that completely contains a set of points. Every set of points in the plane has a unique minimum bounding circle, which may be constructed by a linear time algorithm.[19]
Even if points from a set are concyclic, their circumscribing circle may be different from their minimum bounding circle. For example, for an obtuse triangle, the minimum bounding circle has the longest side as diameter and does not pass through the opposite vertex.
References
- ↑ Libeskind, Shlomo (2008), Euclidean and Transformational Geometry: A Deductive Inquiry, Jones & Bartlett Learning, p. 21, ISBN 9780763743666, https://books.google.com/books?id=6YUUeO-RjU0C&pg=PA21/
- ↑ Elliott, John (1902), Elementary Geometry, Swan Sonnenschein & co., p. 126, https://books.google.com/books?id=9psBAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA126.
- ↑ Isaacs, I. Martin (2009), Geometry for College Students, Pure and Applied Undergraduate Texts, 8, American Mathematical Society, p. 63, ISBN 9780821847947, https://books.google.com/books?id=0ahK8UneO3kC&pg=PA63.
- ↑ Yiu, Paul (2010), "The circles of Lester, Evans, Parry, and their generalizations", Forum Geometricorum 10: 175–209, http://forumgeom.fau.edu/FG2010volume10/FG201020.pdf.
- ↑ Scott, J. A. "Some examples of the use of areal coordinates in triangle geometry", Mathematical Gazette 83, November 1999, 472–477.
- ↑ Pedoe, Dan (1997), Circles: A Mathematical View, MAA Spectrum (2nd ed.), Cambridge University Press, p. xxii, ISBN 9780883855188, https://books.google.com/books?id=rlbQTxbutA4C&pg=PR22.
- ↑ Alsina, Claudi; Nelsen, Roger B. (2007), "On the diagonals of a cyclic quadrilateral", Forum Geometricorum 7: 147–9, http://forumgeom.fau.edu/FG2007volume7/FG200720.pdf
- ↑ Hoehn, Larry (March 2000), "Circumradius of a cyclic quadrilateral", Mathematical Gazette 84 (499): 69–70, doi:10.2307/3621477
- ↑ Bradley, Christopher J. (2007), The Algebra of Geometry: Cartesian, Areal and Projective Co-Ordinates, Highperception, p. 179, ISBN 978-1906338008, OCLC 213434422
- ↑ Byer, Owen; Lazebnik, Felix (2010), Methods for Euclidean Geometry, Mathematical Association of America, p. 77, ISBN 9780883857632, https://books.google.com/books?id=W4acIu4qZvoC&pg=PA77.
- ↑ De Villiers, Michael (March 2011). "95.14 Equiangular cyclic and equilateral circumscribed polygons". The Mathematical Gazette 95 (532): 102–107. doi:10.1017/S0025557200002461.
- ↑ Buchholz, Ralph H.; MacDougall, James A. (2008). "Cyclic polygons with rational sides and area". Journal of Number Theory 128 (1): 17–48. doi:10.1016/j.jnt.2007.05.005.
- ↑ Johnson, Roger A. (1929). Modern Geometry: An Elementary Treatise on the Geometry of the Triangle and the Circle. Houghton Mifflin Co.. p. 72. Republished by Dover Publications as Advanced Euclidean Geometry, 1960 and 2007.
- ↑ "Inequalities proposed in Crux Mathematicorum". The IMO Compendium. p. 190, #332.10. http://www.imomath.com/othercomp/Journ/ineq.pdf.
- ↑ Meskhishvili, Mamuka (2020). "Cyclic Averages of Regular Polygons and Platonic Solids". Communications in Mathematics and Applications 11: 335–355. doi:10.26713/cma.v11i3.1420. https://www.rgnpublications.com/journals/index.php/cma/article/view/1420/1065.
- ↑ Zwikker, C. (2005), The Advanced Geometry of Plane Curves and Their Applications, Courier Dover Publications, p. 24, ISBN 9780486442761, https://books.google.com/books?id=25tMEYTik-AC&pg=PA24.
- ↑ Hahn, Liang-shin (1996), Complex Numbers and Geometry, MAA Spectrum (2nd ed.), Cambridge University Press, p. 65, ISBN 9780883855102, https://books.google.com/books?id=s3nMMkPEvqoC&pg=PA65.
- ↑ Pedoe, Dan (1988), Geometry: A Comprehensive Course, Courier Dover Publications, p. 431, ISBN 9780486658124, https://books.google.com/books?id=s7DDxuoNr_0C&pg=PA431.
- ↑ Megiddo, N. (1983). "Linear-time algorithms for linear programming in R3 and related problems". SIAM Journal on Computing 12 (4): 759–776. doi:10.1137/0212052.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W.. "Concyclic". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Concyclic.html.
- Four Concyclic Points by Michael Schreiber, The Wolfram Demonstrations Project.
 |
