Engineering:Orbital Maneuvering System
 The underside of a left OMS/RCS pod on Space Shuttle Endeavour | |
| Manufacturer | Aerojet |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | United States |
| Used on | Space Shuttle/Orion European Service Module |
| General characteristics | |
| Length | 21.8 feet (6.6 m) |
| Width |
|
| Launch history | |
| Status | Pod Retired/Engines Active |
| Total launches | 135 Space Shuttle/ 1 Orion |
| Successes (stage only) | 134 Space Shuttle/ 1 Orion |
| Lower stage failed | 1 (STS-51-L) |
| First flight | STS-1 (12 April 1981) |
| Last flight | |
| OMS Engine | |
| Engines | 1 AJ10-190 |
| Thrust | 26.7 kilonewtons (6,000 lbf) |
| Specific impulse | 316 seconds (vacuum) |
| Burn time |
|
| Fuel | MMH/N2O4 |
| Aft Primary RCS | |
| Engines | Primary RCS engines |
| Thrust | 3.87 kilonewtons (870 lbf) |
| Burn time |
|
| Fuel | MMH/N2O4 |
| Aft Vernier RCS | |
| Engines | Vernier RCS engines |
| Thrust | 106 newtons (24 lbf) |
| Burn time | 1–125 seconds (each burn) |
| Fuel | MMH/N2O4 |
The Orbital Maneuvering System (OMS) is a system of hypergolic liquid-propellant rocket engines used on the Space Shuttle and the Orion MPCV. Designed and manufactured in the United States by Aerojet,[1] the system allowed the orbiter to perform various orbital maneuvers according to requirements of each mission profile: orbital injection after main engine cutoff, orbital corrections during flight, and the final deorbit burn for reentry.[2] From STS-90 onwards the OMS were typically ignited part-way into the Shuttle's ascent for a few minutes to aid acceleration to orbital insertion. Notable exceptions were particularly high-altitude missions such as those supporting the Hubble Space Telescope (STS-31) or those with unusually heavy payloads such as Chandra (STS-93). An OMS dump burn also occurred on STS-51-F, as part of the Abort to Orbit procedure.[3]
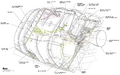
The OMS consists of two pods mounted on the orbiter's aft fuselage, on either side of the vertical stabilizer.[2] Each pod contains a single AJ10-190 engine,[4] based on the Apollo Service Module's Service Propulsion System engine,[5] which produces 26.7 kilonewtons (6,000 lbf) of thrust with a specific impulse (Isp) of 316 seconds.[4] The oxidizer-to-fuel ratio is 1.65-to-1, The expansion ratio of the nozzle exit to the throat is 55-to-1, and the chamber pressure of the engine is 8.6 bar.[2] The dry weight of each engine is 118kg (260lb). Each engine could be reused for 100 missions and was capable of a total of 1,000 starts and 15 hours of burn time.[2]
These pods also contained the Orbiter's aft set of reaction control system (RCS) engines, and so were referred to as OMS/RCS pods. The OM engine and RCS both burned monomethylhydrazine (MMH) as fuel, which was oxidized with MON-3 (mixed oxides of nitrogen, 3% nitric acid), with the propellants being stored in tanks within the OMS/RCS pod, alongside other fuel and engine management systems.[6] When full, the pods together carried around 4,087 kilograms (9,010 lb) of MMH and 6,743 kilograms (14,866 lb) of MON-3, allowing the OMS to produce a total delta-v of around 305 metres per second (1,000 ft/s) with a 29,000-kilogram (64,000 lb) payload.[6][7]
-
Diagram of OMS pod components
-
An OMS pod detached from an orbiter for maintenance
Proposed OMS Payload Bay Kit
It was never built, but to augment the OMS an OMS Payload Bay Kit was proposed.[8] It would have used one, two or three sets of OMS tanks, installed in the payload bay, to provide an extra 150 m/s, 300 m/s or 450 m/s( (500 ft, 1000 ft/s or 1500 ft/s) of delta-V to the orbiter.[8] The orbiter control panels had related switches and gauges but they were nonfunctional.[9]: 1–2
Orion ESM Main Engine

Following the retirement of the Shuttle, these engines were repurposed for use on the Orion spacecraft's service module.[10] This variant uses Monomethylhydrazine as fuel, with MON-3 Mixed Oxides of Nitrogen as oxidizer.[11] It is planned to be used for the first six flights of the Artemis program, afterwards it would be replaced by a new "Orion Main Engine" starting Artemis 7.[12]
References
- ↑ D. Craig Judd (1992). "Capability and flight record of the versatile space shuttle OMS engine". Space Technology and Science (NASA): 107. Bibcode: 1992spte.symp..107J.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "Orbital Maneuvering System". NASA. 1998. http://science.ksc.nasa.gov/shuttle/technology/sts-newsref/sts-oms.html.
- ↑ Legler R. D. and Bennett F. V. (2011). "Space Shuttle Missions Summary, NASA TM-2011-216142". NASA. https://spaceflight.nasa.gov/outreach/SignificantIncidents/assets/space-shuttle-missions-summary.pdf.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Encyclopedia Astronautica (2009). "OME". Encyclopedia Astronautica. http://www.astronautix.com/o/ome.html.
- ↑ Gibson, C.; Humphrles, C.. Orbital Maneuvering System Design Evolution (Report). NASA NTRS. https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/19850008634/downloads/19850008634.pdf. Retrieved December 6, 2022.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 NASA (1998). "Propellant Storage and Distribution". NASA. http://spaceflight.nasa.gov/shuttle/reference/shutref/orbiter/oms/storage.html.
- ↑ David Palmer, Allie Cliffe and Tim Kallman (9 May 1997). "Spacecraft Fuel". NASA. http://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/ask_astro/answers/970509c.html.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 SHUTTLE PERFORMANCE ENHANCEMENTS USING AN OMS PAYLOAD BAY KIT 1991
- ↑ Orbital Maneuvering System Workbook 2006
- ↑ Bergin, Chris (20 June 2015). "Plum Brook prepped for EM-1 Orion Service Module testing". NASASpaceFlight.com. http://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2015/06/plum-brook-orion-service-module-testing/.
- ↑ "Aerojet Rocketdyne - In-Space Propulsion Data Sheets". https://www.rocket.com/sites/default/files/documents/In-Space%20Data%20Sheets%209.13.19.pdf.
- ↑ "Aerojet Rocketdyne Awarded NASA Contract for Orion Spacecraft Main Engine | Aerojet Rocketdyne". https://www.rocket.com/article/aerojet-rocketdyne-awarded-nasa-contract-orion-spacecraft-main-engine.
 |