Euclidean plane isometry
In geometry, a Euclidean plane isometry is an isometry of the Euclidean plane, or more informally, a way of transforming the plane that preserves geometrical properties such as length. There are four types: translations, rotations, reflections, and glide reflections (see below § Classification). The set of Euclidean plane isometries forms a group under composition: the Euclidean group in two dimensions. It is generated by reflections in lines, and every element of the Euclidean group is the composite of at most three distinct reflections.
Informal discussion
Informally, a Euclidean plane isometry is any way of transforming the plane without "deforming" it. For example, suppose that the Euclidean plane is represented by a sheet of transparent plastic sitting on a desk. Examples of isometries include:
- Shifting the sheet one inch to the right.
- Rotating the sheet by ten degrees around some marked point (which remains motionless).
- Turning the sheet over to look at it from behind. Notice that if a picture is drawn on one side of the sheet, then after turning the sheet over, we see the mirror image of the picture.
These are examples of translations, rotations, and reflections respectively. There is one further type of isometry, called a glide reflection (see below under classification of Euclidean plane isometries).
However, folding, cutting, or melting the sheet are not considered isometries. Neither are less drastic alterations like bending, stretching, or twisting.
Formal definition
An isometry of the Euclidean plane is a distance-preserving transformation of the plane. That is, it is a map
such that for any points p and q in the plane,
where d(p, q) is the usual Euclidean distance between p and q.
Classification
It can be shown that there are four types of Euclidean plane isometries. (Note: the notations for the types of isometries listed below are not completely standardised.)
Reflections

Reflections, or mirror isometries, denoted by Fc,v, where c is a point in the plane and v is a unit vector in R2. (F is for "flip".) have the effect of reflecting the point p in the line L that is perpendicular to v and that passes through c. The line L is called the reflection axis or the associated mirror. To find a formula for Fc,v, we first use the dot product to find the component t of p − c in the v direction,
and then we obtain the reflection of p by subtraction,
The combination of rotations about the origin and reflections about a line through the origin is obtained with all orthogonal matrices (i.e. with determinant 1 and −1) forming orthogonal group O(2). In the case of a determinant of −1 we have:
which is a reflection in the x-axis followed by a rotation by an angle θ, or equivalently, a reflection in a line making an angle of θ/2 with the x-axis. Reflection in a parallel line corresponds to adding a vector perpendicular to it.
Translations

Translations, denoted by Tv, where v is a vector in R2 have the effect of shifting the plane in the direction of v. That is, for any point p in the plane,
- or in terms of (x, y) coordinates,
A translation can be seen as a composite of two parallel reflections.
Rotations

Rotations, denoted by Rc,θ, where c is a point in the plane (the centre of rotation), and θ is the angle of rotation. In terms of coordinates, rotations are most easily expressed by breaking them up into two operations. First, a rotation around the origin is given by
These matrices are the orthogonal matrices (i.e. each is a square matrix G whose transpose is its inverse, i.e. ), with determinant 1 (the other possibility for orthogonal matrices is −1, which gives a mirror image, see below). They form the special orthogonal group SO(2).
A rotation around c can be accomplished by first translating c to the origin, then performing the rotation around the origin, and finally translating the origin back to c. That is,
or in other words,
Alternatively, a rotation around the origin is performed, followed by a translation:
A rotation can be seen as a composite of two non-parallel reflections.
Rigid transformations
The set of translations and rotations together form the rigid motions or rigid displacements. This set forms a group under composition, the group of rigid motions, a subgroup of the full group of Euclidean isometries.
Glide reflections
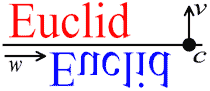
Glide reflections, denoted by Gc,v,w, where c is a point in the plane, v is a unit vector in R2, and w is non-null a vector perpendicular to v are a combination of a reflection in the line described by c and v, followed by a translation along w. That is,
or in other words,
(It is also true that
that is, we obtain the same result if we do the translation and the reflection in the opposite order.)
Alternatively we multiply by an orthogonal matrix with determinant −1 (corresponding to a reflection in a line through the origin), followed by a translation. This is a glide reflection, except in the special case that the translation is perpendicular to the line of reflection, in which case the combination is itself just a reflection in a parallel line.
The identity isometry, defined by I(p) = p for all points p is a special case of a translation, and also a special case of a rotation. It is the only isometry which belongs to more than one of the types described above.
In all cases we multiply the position vector by an orthogonal matrix and add a vector; if the determinant is 1 we have a rotation, a translation, or the identity, and if it is −1 we have a glide reflection or a reflection.
A "random" isometry, like taking a sheet of paper from a table and randomly laying it back, "almost surely" is a rotation or a glide reflection (they have three degrees of freedom). This applies regardless of the details of the probability distribution, as long as θ and the direction of the added vector are independent and uniformly distributed and the length of the added vector has a continuous distribution. A pure translation and a pure reflection are special cases with only two degrees of freedom, while the identity is even more special, with no degrees of freedom.
Isometries as reflection group
Reflections, or mirror isometries, can be combined to produce any isometry. Thus isometries are an example of a reflection group.
Mirror combinations
In the Euclidean plane, we have the following possibilities.
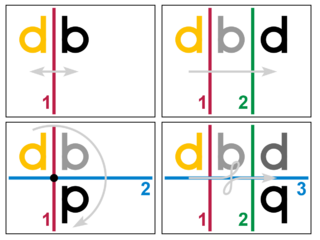
- [d ] Identity
- Two reflections in the same mirror restore each point to its original position. All points are left fixed. Any pair of identical mirrors has the same effect.
- [db] Reflection
- As Alice found through the looking-glass, a single mirror causes left and right hands to switch. (In formal terms, topological orientation is reversed.) Points on the mirror are left fixed. Each mirror has a unique effect.
- [dp] Rotation
- Two distinct intersecting mirrors have a single point in common, which remains fixed. All other points rotate around it by twice the angle between the mirrors. Any two mirrors with the same fixed point and same angle give the same rotation, so long as they are used in the correct order.
- [dd] Translation
- Two distinct mirrors that do not intersect must be parallel. Every point moves the same amount, twice the distance between the mirrors, and in the same direction. No points are left fixed. Any two mirrors with the same parallel direction and the same distance apart give the same translation, so long as they are used in the correct order.
- [dq] Glide reflection
- Three mirrors. If they are all parallel, the effect is the same as a single mirror (slide a pair to cancel the third). Otherwise we can find an equivalent arrangement where two are parallel and the third is perpendicular to them. The effect is a reflection combined with a translation parallel to the mirror. No points are left fixed.
Three mirrors suffice
Adding more mirrors does not add more possibilities (in the plane), because they can always be rearranged to cause cancellation.
An isometry is completely determined by its effect on three independent (not collinear) points. So suppose p1, p2, p3 map to q1, q2, q3; we can generate a sequence of mirrors to achieve this as follows. If p1 and q1 are distinct, choose their perpendicular bisector as mirror. Now p1 maps to q1; and we will pass all further mirrors through q1, leaving it fixed. Call the images of p2 and p3 under this reflection p2′ and p3′. If q2 is distinct from p2′, bisect the angle at q1 with a new mirror. With p1 and p2 now in place, p3 is at p3″; and if it is not in place, a final mirror through q1 and q2 will flip it to q3. Thus at most three reflections suffice to reproduce any plane isometry. Q.E.D.
Recognition
We can recognize which of these isometries we have according to whether it preserves hands or swaps them, and whether it has at least one fixed point or not, as shown in the following table (omitting the identity).
| Preserves hands? | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | ||
| Fixed point? | Yes | Rotation | Reflection |
| No | Translation | Glide reflection | |
Group structure
Isometries requiring an odd number of mirrors — reflection and glide reflection — always reverse left and right. The even isometries — identity, rotation, and translation — never do; they correspond to rigid motions, and form a normal subgroup of the full Euclidean group of isometries. Neither the full group nor the even subgroup are abelian; for example, reversing the order of composition of two parallel mirrors reverses the direction of the translation they produce.
The identity is an isometry; nothing changes, so distance cannot change. And if one isometry cannot change distance, neither can two (or three, or more) in succession; thus the composition of two isometries is again an isometry, and the set of isometries is closed under composition. The identity isometry is also an identity for composition, and composition is associative; therefore isometries satisfy the axioms for a semigroup. For a group, we must also have an inverse for every element. To cancel a reflection, we merely compose it with itself (Reflections are involutions). And since every isometry can be expressed as a sequence of reflections, its inverse can be expressed as that sequence reversed. Notice that the cancellation of a pair of identical reflections reduces the number of reflections by an even number, preserving the parity of the sequence; also notice that the identity has even parity. Therefore all isometries form a group, and even isometries a subgroup. (Odd isometries do not include the identity, so are not a subgroup). This subgroup is a normal subgroup, because sandwiching an even isometry between two odd ones yields an even isometry. Q.E.D.
Since the even subgroup is normal, it is the kernel of a homomorphism to a quotient group, where the quotient is isomorphic to a group consisting of a reflection and the identity. However the full group is not a direct product, but only a semidirect product, of the even subgroup and the quotient group.
Composition
Composition of isometries mixes kinds in assorted ways. We can think of the identity as either two mirrors or none; either way, it has no effect in composition. And two reflections give either a translation or a rotation, or the identity (which is both, in a trivial way). Reflection composed with either of these could cancel down to a single reflection; otherwise it gives the only available three-mirror isometry, a glide reflection. A pair of translations always reduces to a single translation; so the challenging cases involve rotations. We know a rotation composed with either a rotation or a translation must produce an even isometry. Composition with translation produces another rotation (by the same amount, with shifted fixed point), but composition with rotation can yield either translation or rotation. It is often said that composition of two rotations produces a rotation, and Euler proved a theorem to that effect in 3D; however, this is only true for rotations sharing a fixed point.
Translation, rotation, and orthogonal subgroups
We thus have two new kinds of isometry subgroups: all translations, and rotations sharing a fixed point. Both are subgroups of the even subgroup, within which translations are normal. Because translations are a normal subgroup, we can factor them out leaving the subgroup of isometries with a fixed point, the orthogonal group.
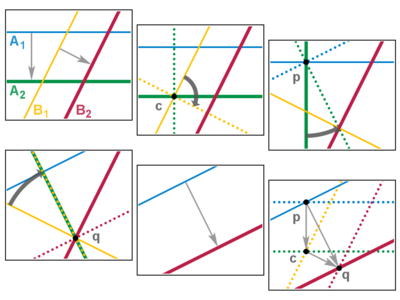
If two rotations share a fixed point, then we can swivel the mirror pair of the second rotation to cancel the inner mirrors of the sequence of four (two and two), leaving just the outer pair. Thus the composition of two rotations with a common fixed point produces a rotation by the sum of the angles about the same fixed point.
If two translations are parallel, we can slide the mirror pair of the second translation to cancel the inner mirror of the sequence of four, much as in the rotation case. Thus the composition of two parallel translations produces a translation by the sum of the distances in the same direction. Now suppose the translations are not parallel, and that the mirror sequence is A1, A2 (the first translation) followed by B1, B2 (the second). Then A2 and B1 must cross, say at c; and, reassociating, we are free to pivot this inner pair around c. If we pivot 90°, an interesting thing happens: now A1 and A2′ intersect at a 90° angle, say at p, and so do B1′ and B2, say at q. Again reassociating, we pivot the first pair around p to make B2″ pass through q, and pivot the second pair around q to make A1″ pass through p. The inner mirrors now coincide and cancel, and the outer mirrors are left parallel. Thus the composition of two non-parallel translations also produces a translation. Also, the three pivot points form a triangle whose edges give the head-to-tail rule of vector addition: 2(p c) + 2(c q) = 2(p q). Q.E.D.
Nested group construction
The subgroup structure suggests another way to compose an arbitrary isometry:
- Pick a fixed point, and a mirror through it.
- If the isometry is odd, use the mirror; otherwise do not.
- If necessary, rotate around the fixed point.
- If necessary, translate.
This works because translations are a normal subgroup of the full group of isometries, with quotient the orthogonal group; and rotations about a fixed point are a normal subgroup of the orthogonal group, with quotient a single reflection.
Discrete subgroups
The subgroups discussed so far are not only infinite, they are also continuous (Lie groups). Any subgroup containing at least one non-zero translation must be infinite, but subgroups of the orthogonal group can be finite. For example, the symmetries of a regular pentagon consist of rotations by integer multiples of 72° (360° / 5), along with reflections in the five mirrors which perpendicularly bisect the edges. This is a group, D5, with 10 elements. It has a subgroup, C5, of half the size, omitting the reflections. These two groups are members of two families, Dn and Cn, for any n > 1. Together, these families constitute the rosette groups.
Translations do not fold back on themselves, but we can take integer multiples of any finite translation, or sums of multiples of two such independent translations, as a subgroup. These generate the lattice of a periodic tiling of the plane.
We can also combine these two kinds of discrete groups — the discrete rotations and reflections around a fixed point and the discrete translations — to generate the frieze groups and wallpaper groups. Curiously, only a few of the fixed-point groups are found to be compatible with discrete translations. In fact, lattice compatibility imposes such a severe restriction that, up to isomorphism, we have only 7 distinct frieze groups and 17 distinct wallpaper groups. For example, the pentagon symmetries, D5, are incompatible with a discrete lattice of translations. (Each higher dimension also has only a finite number of such crystallographic groups, but the number grows rapidly; for example, 3D has 230 groups and 4D has 4783.)
Isometries in the complex plane
In terms of complex numbers, the isometries of the plane are either of the form
or of the form
for some complex numbers a and ω with |ω| = 1. This is easy to prove: if a = f(0) and ω = f(1) − f(0) and if one defines
then g is an isometry, g(0) = 0, and g(1) = 1. It is then easy to see that g is either the identity or the conjugation, and the statement being proved follows from this and from the fact that f(z) = a + ωg(z).
This is obviously related to the previous classification of plane isometries, since:
- functions of the type z → a + z are translations;
- functions of the type z → ωz are rotations (when |ω| = 1);
- the conjugation is a reflection.
Note that a rotation about complex point p is obtained by complex arithmetic with
where the last expression shows the mapping equivalent to rotation at 0 and a translation. Therefore, given direct isometry one can solve to obtain as the center for an equivalent rotation, provided that , that is, provided the direct isometry is not a pure translation. As stated by Cederberg, "A direct isometry is either a rotation or a translation."[1]
See also
- Beckman–Quarles theorem, a characterization of isometries as the transformations that preserve unit distances
- Congruence (geometry)
- Coordinate rotations and reflections
- Hjelmslev's theorem, the statement that the midpoints of corresponding pairs of points in an isometry of lines are collinear
References
- ↑ Cederberg, Judith N. (2001). A Course in Modern Geometries. pp. 136–164. ISBN 978-0-387-98972-3. https://archive.org/details/coursemoderngeom00cede., quote from page 151
External links
 |
