Helmert transformation
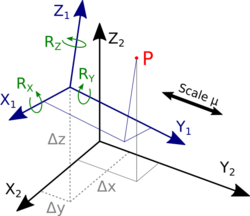
The Helmert transformation (named after Friedrich Robert Helmert, 1843–1917) is a geometric transformation method within a three-dimensional space. It is frequently used in geodesy to produce datum transformations between datums. The Helmert transformation is also called a seven-parameter transformation and is a similarity transformation.
Definition
It can be expressed as:
where
- XT is the transformed vector
- X is the initial vector
The parameters are:
- C – translation vector. Contains the three translations along the coordinate axes
- μ – scale factor, which is unitless; if it is given in ppm, it must be divided by 1,000,000 and added to 1.
- R – rotation matrix. Consists of three axes (small[clarification needed] rotations around each of the three coordinate axes) rx, ry, rz. The rotation matrix is an orthogonal matrix. The angles are given in either degrees or radians.
Variations
A special case is the two-dimensional Helmert transformation. Here, only four parameters are needed (two translations, one scaling, one rotation). These can be determined from two known points; if more points are available then checks can be made.
Sometimes it is sufficient to use the five parameter transformation, composed of three translations, only one rotation about the Z-axis, and one change of scale.
Restrictions
The Helmert transformation only uses one scale factor, so it is not suitable for:
- The manipulation of measured drawings and photographs
- The comparison of paper deformations while scanning old plans and maps.
In these cases, a more general affine transformation is preferable.
Application
The Helmert transformation is used, among other things, in geodesy to transform the coordinates of the point from one coordinate system into another. Using it, it becomes possible to convert regional surveying points into the WGS84 locations used by GPS.
For example, starting with the Gauss–Krüger coordinate, x and y, plus the height, h, are converted into 3D values in steps:
- Undo the map projection: calculation of the ellipsoidal latitude, longitude and height (W, L, H)
- Convert from geodetic coordinates to geocentric coordinates: Calculation of x, y and z relative to the reference ellipsoid of surveying
- 7-parameter transformation (where x, y and z almost always change by a few hundred metres at most, and distances by a few mm per km).
- Because of this, terrestrially measured positions can be compared with GPS data; these can then be brought into the surveying as new points – transformed in the opposite order.
The third step consists of the application of a rotation matrix, multiplication with the scale factor (with a value near 1) and the addition of the three translations, cx, cy, cz.
The coordinates of a reference system B are derived from reference system A by the following formula (position vector transformation convention and very small rotation angles simplification):[1]
or for each single parameter of the coordinate:
For the reverse transformation, each element is multiplied by −1.
The seven parameters are determined for each region with three or more "identical points" of both systems. To bring them into agreement, the small inconsistencies (usually only a few cm) are adjusted using the method of least squares – that is, eliminated in a statistically plausible manner.
Standard parameters
- Note: the rotation angles given in the table are in arcseconds and must be converted to radians before use in the calculation.
| EPSG Code | Region | Source datum | Target datum | Accuracy (metre) | cx (metre) | cy (metre) | cz (metre) | s (ppm) | rx (arcsecond) | ry (arcsecond) | rz (arcsecond) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8048 | Australia | GDA94 (EPSG:4283) | GDA2020 (EPSG:7844) | 0.01 | 0.06155 | -0.01087 | -0.04019 | -0.009994 | -0.0394924 | -0.0327221 | -0.0328979 |
| 9690 | Australia | WGS84 (EPSG:4326) | GDA2020 (EPSG:7844) | 3 | 0.06155 | -0.01087 | -0.04019 | -0.009994 | -0.0394924 | -0.0327221 | -0.0328979 |
| 1618 | Austria | MGI (EPSG:4312) | WGS84 (EPSG:4326) | 1.5 | 577.326 | 90.129 | 463.919 | 2.4232 | 5.137 | 1.474 | 5.297 |
| 1776 | Germany (West) | DHDN (EPSG:4314) | ETRS89 (EPSG:4258) | 3 | 598.1 | 73.7 | 418.2 | 6.7 | 0.202 | 0.045 | -2.455 |
| 1777 | Germany (West) | DHDN (EPSG:4314) | WGS84 (EPSG:4326) | 3 | 598.1 | 73.7 | 418.2 | 6.7 | 0.202 | 0.045 | -2.455 |
| 15869 | Germany (East) | DHDN (EPSG:4314) | WGS84 (EPSG:4326) | 2 | 612.4 | 77 | 440.2 | 2.55 | -0.054 | 0.057 | -2.797 |
| 1641 | Ireland | TM65 (EPSG:4299) | WGS84 (EPSG:4326) | 1 | 482.5 | -130.6 | 564.6 | 8.15 | -1.042 | -0.214 | -0.631 |
| 1953 | Ireland | TM75 (EPSG:4300) | ETRS89 (EPSG:4258) | 1 | 482.5 | -130.6 | 564.6 | 8.15 | -1.042 | -0.214 | -0.631 |
| 1954 | Ireland | TM75 (EPSG:4300) | WGS84 (EPSG:4326) | 1 | 482.5 | -130.6 | 564.6 | 8.15 | -1.042 | -0.214 | -0.631 |
| 8689 | Slovenia | MGI 1901 (EPSG:3906) | Slovenia 1996 (EPSG:4765) | 1 | 476.08 | 125.947 | 417.81 | 9.896638 | -4.610862 | -2.388137 | 11.942335 |
| 1314 | United Kingdom | OSGB36 (EPSG:4247) | WGS84 (EPSG:4326) | 2 | 446.448 | -125.157 | 542.06 | -20.489 | 0.15 | 0.247 | 0.842 |
| 1315 | United Kingdom | OSGB36 (EPSG:4247) | ED50 (EPSG:4230) | 2 | 535.948 | -31.357 | 665.16 | -21.689 | 0.15 | 0.247 | 0.998 |
| 1901 | United States | NAD83(HARN) (EPSG:4152) | WGS84 (EPSG:4326) | 1 | -0.991 | 1.9072 | 0.5129 | 0 | 1.25033×10−7 | 4.6785×10−8 | 5.6529×10−8 |
These are standard parameter sets for the 7-parameter transformation (or data transformation) between two datums. For a transformation in the opposite direction, inverse transformation parameters should be calculated or inverse transformation should be applied (as described in paper "On geodetic transformations"[2]). The translations cx, cy, cz are sometimes described as tx, ty, tz, or dx, dy, dz. The rotations rx, ry, and rz are sometimes also described as , and .[who?] In the United Kingdom the prime interest is the transformation between the OSGB36 datum used by the Ordnance survey for Grid References on its Landranger and Explorer maps to the WGS84 implementation used by GPS technology. The Gauss–Krüger coordinate system used in Germany normally refers to the Bessel ellipsoid. A further datum of interest was ED50 (European Datum 1950) based on the Hayford ellipsoid. ED50 was part of the fundamentals of the NATO coordinates up to the 1980s, and many national coordinate systems of Gauss–Krüger are defined by ED50.
The earth does not have a perfect ellipsoidal shape, but is described as a geoid. Instead, the geoid of the earth is described by many ellipsoids. Depending upon the actual location, the "locally best aligned ellipsoid" has been used for surveying and mapping purposes. The standard parameter set gives an accuracy of about 7 m for an OSGB36/WGS84 transformation. This is not precise enough for surveying, and the Ordnance Survey supplements these results by using a lookup table of further translations in order to reach 1 cm accuracy.
Estimating the parameters
If the transformation parameters are unknown, they can be calculated with reference points (that is, points whose coordinates are known before and after the transformation. Since a total of seven parameters (three translations, one scale, three rotations) have to be determined, at least two points and one coordinate of a third point (for example, the Z-coordinate) must be known. This gives a system with seven equations and seven unknowns, which can be solved.
For transformations between conformal map projections near an arbitrary point, the Helmert transformation parameters can be calculated exactly from the Jacobian matrix of the transformation function.
In practice, it is best to use more points. Through this correspondence, more accuracy is obtained, and a statistical assessment of the results becomes possible. In this case, the calculation is adjusted with the Gaussian least squares method.
A numerical value for the accuracy of the transformation parameters is obtained by calculating the values at the reference points, and weighting the results relative to the centroid of the points.
While the method is mathematically rigorous, it is entirely dependent on the accuracy of the parameters that are used. In practice, these parameters are computed from the inclusion of at least three known points in the networks. However the accuracy of these will affect the following transformation parameters, as these points will contain observation errors. Therefore, a "real-world" transformation will only be a best estimate and should contain a statistical measure of its quality.
See also
References
- ↑ "Equations Used for Datum Transformations" (in en-NZ). https://www.linz.govt.nz/data/geodetic-system/coordinate-conversion/geodetic-datum-conversions/equations-used-datum.
- ↑ On geodetic transformations, Bo-Gunnar Reit, 2009 https://www.lantmateriet.se/contentassets/4a728c7e9f0145569edd5eb81fececa7/rapport_reit_eng.pdf
External links
- Helmert transform in PROJ coordinate transformation software
- Computing Helmert Transformations
 |
