Lomax distribution
|
Probability density function 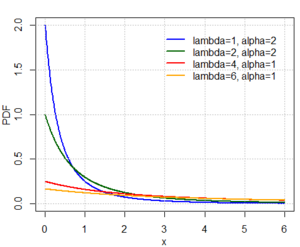 | |||
|
Cumulative distribution function 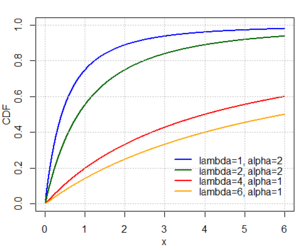 | |||
| Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | |||
| CDF | |||
| Quantile | |||
| Mean | ; undefined otherwise | ||
| Median | |||
| Mode | 0 | ||
| Variance | |||
| Skewness | |||
| Kurtosis | |||
| Entropy | |||
| MGF | |||
| CF | |||
The Lomax distribution, conditionally also called the Pareto Type II distribution, is a heavy-tail probability distribution used in business, economics, actuarial science, queueing theory and Internet traffic modeling.[1][2][3] It is named after K. S. Lomax. It is essentially a Pareto distribution that has been shifted so that its support begins at zero.[4]
Characterization
Probability density function
The probability density function (pdf) for the Lomax distribution is given by
with shape parameter and scale parameter . The density can be rewritten in such a way that more clearly shows the relation to the Pareto Type I distribution. That is:
Non-central moments
The th non-central moment exists only if the shape parameter strictly exceeds , when the moment has the value
Related distributions
Relation to the Pareto distribution
The Lomax distribution is a Pareto Type I distribution shifted so that its support begins at zero. Specifically:
The Lomax distribution is a Pareto Type II distribution with xm = λ and μ = 0:[5]
Relation to the generalized Pareto distribution
The Lomax distribution is a special case of the generalized Pareto distribution. Specifically:
Relation to the beta prime distribution
The Lomax distribution with scale parameter λ = 1 is a special case of the beta prime distribution. If X has a Lomax distribution, then .
Relation to the F distribution
The Lomax distribution with shape parameter α = 1 and scale parameter λ = 1 has density , the same distribution as an F(2,2) distribution. This is the distribution of the ratio of two independent and identically distributed random variables with exponential distributions.
Relation to the q-exponential distribution
The Lomax distribution is a special case of the q-exponential distribution. The q-exponential extends this distribution to support on a bounded interval. The Lomax parameters are given by:
Relation to the logistic distribution
The logarithm of a Lomax(shape = 1.0, scale = λ)-distributed variable follows a logistic distribution with location log(λ) and scale 1.0.
Gamma-exponential (scale-) mixture connection
The Lomax distribution arises as a mixture of exponential distributions where the mixing distribution of the rate is a gamma distribution. If λ | k,θ ~ Gamma(shape = k, scale = θ) and X | λ ~ Exponential(rate = λ) then the marginal distribution of X | k,θ is Lomax(shape = k, scale = 1/θ). Since the rate parameter may equivalently be reparameterized to a scale parameter, the Lomax distribution constitutes a scale mixture of exponentials (with the exponential scale parameter following an inverse-gamma distribution).
See also
- Power law
- Compound probability distribution
- Hyperexponential distribution (finite mixture of exponentials)
- Normal-exponential-gamma distribution (a normal scale mixture with Lomax mixing distribution)
References
- ↑ Lomax, K. S. (1954) "Business Failures; Another example of the analysis of failure data". Journal of the American Statistical Association, 49, 847–852. JSTOR 2281544
- ↑ Johnson, N. L.; Kotz, S.; Balakrishnan, N. (1994). "20 Pareto distributions". Continuous univariate distributions. 1 (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley. p. 573.
- ↑ J. Chen, J., Addie, R. G., Zukerman. M., Neame, T. D. (2015) "Performance Evaluation of a Queue Fed by a Poisson Lomax Burst Process", IEEE Communications Letters, 19, 3, 367–370.
- ↑ Van Hauwermeiren M and Vose D (2009). A Compendium of Distributions [ebook]. Vose Software, Ghent, Belgium. Available at www.vosesoftware.com.
- ↑ Kleiber, Christian; Kotz, Samuel (2003), Statistical Size Distributions in Economics and Actuarial Sciences, Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics, 470, John Wiley & Sons, p. 60, ISBN 9780471457169, https://books.google.com/books?id=7wLGjyB128IC&pg=PA60.
 |
