Medicine:Transrectal ultrasonography
From HandWiki
| Transrectal ultrasonography | |
|---|---|
| Medical diagnostics | |
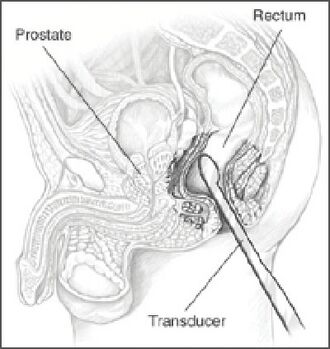 A probe inserted in the rectum emits sound waves in order to image the prostate | |
| ICD-9-CM | 88.74 |
| OPS-301 code | 3-058 |
Transrectal ultrasonography, or TRUS in short, is a method of creating an image of organs in the pelvis, most commonly used to perform an ultrasound-guided needle biopsy evaluation of the prostate gland in men with elevated prostate-specific antigen or prostatic nodules on digital rectal exam. TRUS--guided biopsy may reveal prostate cancer, benign prostatic hypertrophy, or prostatitis. TRUS may also detect other diseases of the lower rectum and can be used to stage primary rectal cancer.[1][2][3]
References
- ↑ "Genitourinary imaging: current and emerging applications". J Postgrad Med 56 (2): 131–9. 2010. doi:10.4103/0022-3859.65291. PMID 20622393. http://www.jpgmonline.com/article.asp?issn=0022-3859;year=2010;volume=56;issue=2;spage=131;epage=139;aulast=O'.
- ↑ Shetty, Sugandh (4 August 2016). "Transrectal Ultrasonography of the Prostate". https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/457757-overview.(Subscription content?)
- ↑ Kim, Min Ju (2014-11-19). "Transrectal ultrasonography of anorectal diseases: advantages and disadvantages" (in English). Ultrasonography 34 (1): 19–31. doi:10.14366/usg.14051. ISSN 2288-5919. PMID 25492891. PMC 4282231. http://www.e-ultrasonography.org/journal/view.php?number=63.
 |

