Physics:Airy wave theory
In fluid dynamics, Airy wave theory (often referred to as linear wave theory) gives a linearised description of the propagation of gravity waves on the surface of a homogeneous fluid layer. The theory assumes that the fluid layer has a uniform mean depth, and that the fluid flow is inviscid, incompressible and irrotational. This theory was first published, in correct form, by George Biddell Airy in the 19th century.[1]
Airy wave theory is often applied in ocean engineering and coastal engineering for the modelling of random sea states – giving a description of the wave kinematics and dynamics of high-enough accuracy for many purposes.[2][3] Further, several second-order nonlinear properties of surface gravity waves, and their propagation, can be estimated from its results.[4] Airy wave theory is also a good approximation for tsunami waves in the ocean, before they steepen near the coast.
This linear theory is often used to get a quick and rough estimate of wave characteristics and their effects. This approximation is accurate for small ratios of the wave height to water depth (for waves in shallow water), and wave height to wavelength (for waves in deep water).
Description
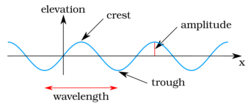
Airy wave theory uses a potential flow (or velocity potential) approach to describe the motion of gravity waves on a fluid surface. The use of (inviscid and irrotational) potential flow in water waves is remarkably successful, given its failure to describe many other fluid flows where it is often essential to take viscosity, vorticity, turbulence or flow separation into account. This is due to the fact that for the oscillatory part of the fluid motion, wave-induced vorticity is restricted to some thin oscillatory Stokes boundary layers at the boundaries of the fluid domain.[5]
Airy wave theory is often used in ocean engineering and coastal engineering. Especially for random waves, sometimes called wave turbulence, the evolution of the wave statistics – including the wave spectrum – is predicted well over not too long distances (in terms of wavelengths) and in not too shallow water. Diffraction is one of the wave effects which can be described with Airy wave theory. Further, by using the WKBJ approximation, wave shoaling and refraction can be predicted.[2]
Earlier attempts to describe surface gravity waves using potential flow were made by, among others, Laplace, Poisson, Cauchy and Kelland. But Airy was the first to publish the correct derivation and formulation in 1841.[1] Soon after, in 1847, the linear theory of Airy was extended by Stokes for non-linear wave motion – known as Stokes' wave theory – correct up to third order in the wave steepness.[6] Even before Airy's linear theory, Gerstner derived a nonlinear trochoidal wave theory in 1802, which however is not irrotational.[1]
Airy wave theory is a linear theory for the propagation of waves on the surface of a potential flow and above a horizontal bottom. The free surface elevation η(x,t) of one wave component is sinusoidal, as a function of horizontal position x and time t:
where
- a is the wave amplitude in metres,
- cos is the cosine function,
- k is the angular wavenumber in radians per metre, related to the wavelength λ by k = 2π/λ,
- ω is the angular frequency in radians per second, related to the period T and frequency f by ω = 2π/T = 2πf.
The waves propagate along the water surface with the phase speed cp:
The angular wavenumber k and frequency ω are not independent parameters (and thus also wavelength λ and period T are not independent), but are coupled. Surface gravity waves on a fluid are dispersive waves – exhibiting frequency dispersion – meaning that each wavenumber has its own frequency and phase speed.
Note that in engineering the wave height H – the difference in elevation between crest and trough – is often used:
valid in the present case of linear periodic waves.


Underneath the surface, there is a fluid motion associated with the free surface motion. While the surface elevation shows a propagating wave, the fluid particles are in an orbital motion. Within the framework of Airy wave theory, the orbits are closed curves: circles in deep water and ellipses in finite depth—with the circles dying out before reaching the bottom of the fluid layer, and the ellipses becoming flatter near the bottom of the fluid layer. So while the wave propagates, the fluid particles just orbit (oscillate) around their average position. With the propagating wave motion, the fluid particles transfer energy in the wave propagation direction, without having a mean velocity. The diameter of the orbits reduces with depth below the free surface. In deep water, the orbit's diameter is reduced to 4% of its free-surface value at a depth of half a wavelength.
In a similar fashion, there is also a pressure oscillation underneath the free surface, with wave-induced pressure oscillations reducing with depth below the free surface – in the same way as for the orbital motion of fluid parcels.
Mathematical formulation of the wave motion
Flow problem formulation
The waves propagate in the horizontal direction, with coordinate x, and a fluid domain bound above by a free surface at z = η(x,t), with z the vertical coordinate (positive in the upward direction) and t being time.[7] The level z = 0 corresponds with the mean surface elevation. The impermeable bed underneath the fluid layer is at z = −h. Further, the flow is assumed to be incompressible and irrotational – a good approximation of the flow in the fluid interior for waves on a liquid surface – and potential theory can be used to describe the flow. The velocity potential Φ(x, z, t) is related to the flow velocity components ux and uz in the horizontal (x) and vertical (z) directions by:
Then, due to the continuity equation for an incompressible flow, the potential Φ has to satisfy the Laplace equation:
|
|
() |
Boundary conditions are needed at the bed and the free surface in order to close the system of equations. For their formulation within the framework of linear theory, it is necessary to specify what the base state (or zeroth-order solution) of the flow is. Here, we assume the base state is rest, implying the mean flow velocities are zero.
The bed being impermeable, leads to the kinematic bed boundary-condition:
|
|
() |
In case of deep water – by which is meant infinite water depth, from a mathematical point of view – the flow velocities have to go to zero in the limit as the vertical coordinate goes to minus infinity: z → −∞.
At the free surface, for infinitesimal waves, the vertical motion of the flow has to be equal to the vertical velocity of the free surface. This leads to the kinematic free-surface boundary-condition:
|
|
() |
If the free surface elevation η(x,t) was a known function, this would be enough to solve the flow problem. However, the surface elevation is an extra unknown, for which an additional boundary condition is needed. This is provided by Bernoulli's equation for an unsteady potential flow. The pressure above the free surface is assumed to be constant. This constant pressure is taken equal to zero, without loss of generality, since the level of such a constant pressure does not alter the flow. After linearisation, this gives the dynamic free-surface boundary condition:
|
|
() |
Because this is a linear theory, in both free-surface boundary conditions – the kinematic and the dynamic one, equations (3) and (4) – the value of Φ and ∂Φ/∂z at the fixed mean level z = 0 is used.
Solution for a progressive monochromatic wave
For a propagating wave of a single frequency – a monochromatic wave – the surface elevation is of the form:[7]
The associated velocity potential, satisfying the Laplace equation (1) in the fluid interior, as well as the kinematic boundary conditions at the free surface (2), and bed (3), is:
with sinh and cosh the hyperbolic sine and hyperbolic cosine function, respectively. But η and Φ also have to satisfy the dynamic boundary condition, which results in non-trivial (non-zero) values for the wave amplitude a only if the linear dispersion relation is satisfied:
with tanh the hyperbolic tangent. So angular frequency ω and wavenumber k – or equivalently period T and wavelength λ – cannot be chosen independently, but are related. This means that wave propagation at a fluid surface is an eigenproblem. When ω and k satisfy the dispersion relation, the wave amplitude a can be chosen freely (but small enough for Airy wave theory to be a valid approximation).
Table of wave quantities
In the table below, several flow quantities and parameters according to Airy wave theory are given.[7] The given quantities are for a bit more general situation as for the solution given above. Firstly, the waves may propagate in an arbitrary horizontal direction in the x = (x,y) plane. The wavenumber vector is k, and is perpendicular to the cams of the wave crests. Secondly, allowance is made for a mean flow velocity U, in the horizontal direction and uniform over (independent of) depth z. This introduces a Doppler shift in the dispersion relations. At an Earth-fixed location, the observed angular frequency (or absolute angular frequency) is ω. On the other hand, in a frame of reference moving with the mean velocity U (so the mean velocity as observed from this reference frame is zero), the angular frequency is different. It is called the intrinsic angular frequency (or relative angular frequency), denoted σ. So in pure wave motion, with U = 0, both frequencies ω and σ are equal. The wave number k (and wavelength λ) are independent of the frame of reference, and have no Doppler shift (for monochromatic waves).
The table only gives the oscillatory parts of flow quantities – velocities, particle excursions and pressure – and not their mean value or drift. The oscillatory particle excursions ξx and ξz are the time integrals of the oscillatory flow velocities ux and uz respectively.
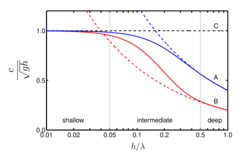
Water depth is classified into three regimes:[8]
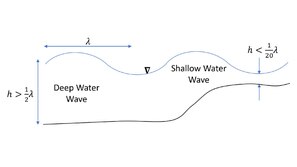
- deep water – for a water depth larger than half the wavelength, h > 1/2λ, the phase speed of the waves is hardly influenced by depth (this is the case for most wind waves on the sea and ocean surface),[9]
- shallow water – for a water depth smaller than 5% of the wavelength, h < 1/20λ, the phase speed of the waves is only dependent on water depth, and no longer a function of period or wavelength;[10] and
- intermediate depth – all other cases, 1/20λ < h < 1/2λ, where both water depth and period (or wavelength) have a significant influence on the solution of Airy wave theory.
In the limiting cases of deep and shallow water, simplifying approximations to the solution can be made. While for intermediate depth, the full formulations have to be used.
| Properties of gravity waves on the surface of deep water, shallow water and at intermediate depth, according to Airy wave theory[7] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| quantity | symbol | units | deep water (h > 1/2λ) |
shallow water (h < 1/20λ) |
intermediate depth (all λ and h) |
| surface elevation | m | ||||
| wave phase | rad | ||||
| observed angular frequency | rad·s−1 | ||||
| intrinsic angular frequency | rad·s−1 | ||||
| unit vector in the wave propagation direction | – | ||||
| dispersion relation | rad·s−1 | ||||
| phase speed | m·s−1 | ||||
| group speed | m·s−1 | ||||
| ratio | – | ||||
| horizontal velocity | m·s−1 | ||||
| vertical velocity | m·s−1 | ||||
| horizontal particle excursion | m | ||||
| vertical particle excursion | m | ||||
| pressure oscillation | N·m−2 | ||||
Surface tension effects
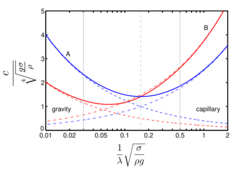
Blue lines (A): phase velocity cp, Red lines (B): group velocity cg.
Drawn lines: gravity–capillary waves.
Dashed lines: gravity waves.
Dash-dot lines: pure capillary waves.
Note: σ is surface tension in this graph.
Due to surface tension, the dispersion relation changes to:[11]
with γ the surface tension in newtons per metre. All above equations for linear waves remain the same, if the gravitational acceleration g is replaced by[12]
As a result of surface tension, the waves propagate faster. Surface tension only has influence for short waves, with wavelengths less than a few decimeters in case of a water–air interface. For very short wavelengths – 2 mm or less, in case of the interface between air and water – gravity effects are negligible. Note that surface tension can be altered by surfactants.
The group velocity ∂Ω/∂k of capillary waves – dominated by surface tension effects – is greater than the phase velocity Ω/k. This is opposite to the situation of surface gravity waves (with surface tension negligible compared to the effects of gravity) where the phase velocity exceeds the group velocity.[13]
Interfacial waves
Surface waves are a special case of interfacial waves, on the interface between two fluids of different density.
Two layers of infinite depth
Consider two fluids separated by an interface, and without further boundaries. Then their dispersion relation ω2 = Ω2(k) is given through[11][14][15]
where ρ and ρ′ are the densities of the two fluids, below (ρ) and above (ρ′) the interface, respectively. Further γ is the surface tension on the interface.
For interfacial waves to exist, the lower layer has to be heavier than the upper one, ρ > ρ′. Otherwise, the interface is unstable and a Rayleigh–Taylor instability develops.
Two layers between horizontal rigid planes
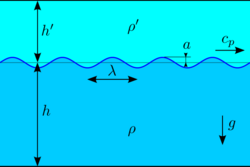
For two homogeneous layers of fluids, of mean thickness h below the interface and h′ above – under the action of gravity and bounded above and below by horizontal rigid walls – the dispersion relationship ω2 = Ω2(k) for gravity waves is provided by:[16]
where again ρ and ρ′ are the densities below and above the interface, while coth is the hyperbolic cotangent function. For the case ρ′ is zero this reduces to the dispersion relation of surface gravity waves on water of finite depth h.
Two layers bounded above by a free surface
In this case the dispersion relation allows for two modes: a barotropic mode where the free surface amplitude is large compared with the amplitude of the interfacial wave, and a baroclinic mode where the opposite is the case – the interfacial wave is higher than and in antiphase with the free surface wave. The dispersion relation for this case is of a more complicated form.[17]
Second-order wave properties
Several second-order wave properties, ones that are quadratic in the wave amplitude a, can be derived directly from Airy wave theory. They are of importance in many practical applications, such as forecasts of wave conditions.[18] Using a WKBJ approximation, second-order wave properties also find their applications in describing waves in case of slowly varying bathymetry, and mean-flow variations of currents and surface elevation. As well as in the description of the wave and mean-flow interactions due to time and space-variations in amplitude, frequency, wavelength and direction of the wave field itself.
Table of second-order wave properties
In the table below, several second-order wave properties – as well as the dynamical equations they satisfy in case of slowly varying conditions in space and time – are given. More details on these can be found below. The table gives results for wave propagation in one horizontal spatial dimension. Further on in this section, more detailed descriptions and results are given for the general case of propagation in two-dimensional horizontal space.
| Second-order quantities and their dynamics, using results of Airy wave theory | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| quantity | symbol | units | formula |
| mean wave-energy density per unit horizontal area | J·m−2 | ||
| radiation stress or excess horizontal momentum flux due to the wave motion | N·m−1 | ||
| wave action | J·s·m−2 | ||
| mean mass-flux due to the wave motion or the wave pseudo-momentum | kg·m−1·s−1 | ||
| mean horizontal mass-transport velocity | m·s−1 | ||
| Stokes drift | m·s−1 | ||
| wave-energy propagation | J·m−2·s−1 | ||
| wave action conservation | J·m−2 | ||
| wave-crest conservation | rad·m−1·s−1 | ||
| mean mass conservation | kg·m−2·s−1 | ||
| mean horizontal-momentum evolution | N·m−2 | ||
The last four equations describe the evolution of slowly varying wave trains over bathymetry in interaction with the mean flow, and can be derived from a variational principle: Whitham's averaged Lagrangian method.[19] In the mean horizontal-momentum equation, d(x) is the still water depth, that is, the bed underneath the fluid layer is located at z = −d. Note that the mean-flow velocity in the mass and momentum equations is the mass transport velocity Ũ, including the splash-zone effects of the waves on horizontal mass transport, and not the mean Eulerian velocity (for example, as measured with a fixed flow meter).
Wave energy density
Wave energy is a quantity of primary interest, since it is a primary quantity that is transported with the wave trains.[20] As can be seen above, many wave quantities like surface elevation and orbital velocity are oscillatory in nature with zero mean (within the framework of linear theory). In water waves, the most used energy measure is the mean wave energy density per unit horizontal area. It is the sum of the kinetic and potential energy density, integrated over the depth of the fluid layer and averaged over the wave phase. Simplest to derive is the mean potential energy density per unit horizontal area Epot of the surface gravity waves, which is the deviation of the potential energy due to the presence of the waves:[21]
The overbar denotes the mean value (which in the present case of periodic waves can be taken either as a time average or an average over one wavelength in space).
The mean kinetic energy density per unit horizontal area Ekin of the wave motion is similarly found to be:[21]
with σ the intrinsic frequency, see the table of wave quantities. Using the dispersion relation, the result for surface gravity waves is:
As can be seen, the mean kinetic and potential energy densities are equal. This is a general property of energy densities of progressive linear waves in a conservative system.[22][23] Adding potential and kinetic contributions, Epot and Ekin, the mean energy density per unit horizontal area E of the wave motion is:
In case of surface tension effects not being negligible, their contribution also adds to the potential and kinetic energy densities, giving[22]
so
with γ the surface tension.
Wave action, wave energy flux and radiation stress
In general, there can be an energy transfer between the wave motion and the mean fluid motion. This means, that the wave energy density is not in all cases a conserved quantity (neglecting dissipative effects), but the total energy density – the sum of the energy density per unit area of the wave motion and the mean flow motion – is. However, there is for slowly varying wave trains, propagating in slowly varying bathymetry and mean-flow fields, a similar and conserved wave quantity, the wave action A = E/σ:[19][24][25]
with (U + cg) A the action flux and cg = cgek the group velocity vector. Action conservation forms the basis for many wind wave models and wave turbulence models.[26] It is also the basis of coastal engineering models for the computation of wave shoaling.[27] Expanding the above wave action conservation equation leads to the following evolution equation for the wave energy density:[28]
with:
- (U + cg)E is the mean wave energy density flux,
- S is the radiation stress tensor and
- ∇U is the mean-velocity shear rate tensor.
In this equation in non-conservation form, the Frobenius inner product S : (∇U) is the source term describing the energy exchange of the wave motion with the mean flow. Only in the case that the mean shear-rate is zero, ∇U = 0, the mean wave energy density E is conserved. The two tensors S and ∇U are in a Cartesian coordinate system of the form:[29]
with kx and ky the components of the wavenumber vector k and similarly Ux and Uy the components in of the mean velocity vector U.
Wave mass flux and wave momentum
The mean horizontal momentum per unit area M induced by the wave motion – and also the wave-induced mass flux or mass transport – is:[30]
which is an exact result for periodic progressive water waves, also valid for nonlinear waves.[31] However, its validity strongly depends on the way how wave momentum and mass flux are defined. Stokes already identified two possible definitions of phase velocity for periodic nonlinear waves:[6]
- Stokes first definition of wave celerity (S1) – with the mean Eulerian flow velocity equal to zero for all elevations z' below the wave troughs, and
- Stokes second definition of wave celerity (S2) – with the mean mass transport equal to zero.
The above relation between wave momentum M and wave energy density E is valid within the framework of Stokes' first definition.
However, for waves perpendicular to a coast line or in closed laboratory wave channel, the second definition (S2) is more appropriate. These wave systems have zero mass flux and momentum when using the second definition.[32] In contrast, according to Stokes' first definition (S1), there is a wave-induced mass flux in the wave propagation direction, which has to be balanced by a mean flow U in the opposite direction – called the undertow.
So in general, there are quite some subtleties involved. Therefore also the term pseudo-momentum of the waves is used instead of wave momentum.[33]
Mass and momentum evolution equations
For slowly varying bathymetry, wave and mean-flow fields, the evolution of the mean flow can de described in terms of the mean mass-transport velocity Ũ defined as:[34]
Note that for deep water, when the mean depth h goes to infinity, the mean Eulerian velocity U and mean transport velocity Ũ become equal.
The equation for mass conservation is:[19][34]
where h(x,t) is the mean water depth, slowly varying in space and time.
Similarly, the mean horizontal momentum evolves as:[19][34]
with d the still-water depth (the sea bed is at z = –d), S is the wave radiation-stress tensor, I is the identity matrix and ⊗ is the dyadic product:
Note that mean horizontal momentum is only conserved if the sea bed is horizontal (the still-water depth d is a constant), in agreement with Noether's theorem.
The system of equations is closed through the description of the waves. Wave energy propagation is described through the wave-action conservation equation (without dissipation and nonlinear wave interactions):[19][24]
The wave kinematics are described through the wave-crest conservation equation:[35]
with the angular frequency ω a function of the (angular) wavenumber k, related through the dispersion relation. For this to be possible, the wave field must be coherent. By taking the curl of the wave-crest conservation, it can be seen that an initially irrotational wavenumber field stays irrotational.
Stokes drift
When following a single particle in pure wave motion (U = 0), according to linear Airy wave theory, a first approximation gives closed elliptical orbits for water particles.[36] However, for nonlinear waves, particles exhibit a Stokes drift for which a second-order expression can be derived from the results of Airy wave theory (see the table above on second-order wave properties).[37] The Stokes drift velocity ūS, which is the particle drift after one wave cycle divided by the period, can be estimated using the results of linear theory:[38]
so it varies as a function of elevation. The given formula is for Stokes first definition of wave celerity. When ρūS is integrated over depth, the expression for the mean wave momentum M is recovered.[38]
See also
- Boussinesq approximation (water waves) – nonlinear theory for waves in shallow water.
- Capillary wave – surface waves under the action of surface tension
- Cnoidal wave – nonlinear periodic waves in shallow water, solutions of the Korteweg–de Vries equation
- Mild-slope equation – refraction and diffraction of surface waves over varying depth
- Ocean surface wave – real water waves as seen in the ocean and sea
- Stokes wave – nonlinear periodic waves in non-shallow water
- Wave power – using ocean and sea waves for power generation.
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Craik, Alex (2004). "The Origins of Water Wave Theory". Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics 36: 1-28. doi:10.1146/annurev.fluid.36.050802.122118.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Goda, Y. (2000). Random Seas and Design of Maritime Structures. Advanced Series on Ocean Engineering. 15. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Company. ISBN 978-981-02-3256-6. OCLC 45200228.
- ↑ Dean & Dalrymple (1991).
- ↑ Phillips (1977), §3.2, pp. 37–43 and §3.6, pp. 60–69.
- ↑ Lighthill, M. J. (1986). "Fundamentals concerning wave loading on offshore structures". J. Fluid Mech. 173: 667–681. doi:10.1017/S0022112086001313. Bibcode: 1986JFM...173..667L.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Stokes (1847).
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 For the equations, solution and resulting approximations in deep and shallow water, see Dingemans (1997), Part 1, §2.1, pp. 38–45. Or: Phillips (1977), pp. 36–45.
- ↑ Dean & Dalrymple (1991) pp. 64–65
- ↑ The error in the phase speed is less than 0.2% if depth h is taken to be infinite, for h > 1/2λ.
- ↑ The error in the phase speed is less than 2% if wavelength effects are neglected for h < 1/20λ.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Phillips (1977), p. 37.
- ↑ Lighthill (1978), p. 223.
- ↑ Phillips (1977), p. 175.
- ↑ Lamb, H. (1994), §267, page 458–460.
- ↑ Dingemans (1997), Section 2.1.1, p. 45.
- ↑ Turner, J. S. (1979), Buoyancy effects in fluids, Cambridge University Press, p. 18, ISBN 978-0521297264
- ↑ Apel, J. R. (1987), Principles of ocean physics, Academic Press, pp. 231–239, ISBN 9780080570747
- ↑ See for example: the High seas forecasts of NOAA's National Weather service.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 19.3 19.4 Whitham, G.B. (1974). Linear and nonlinear waves. Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 978-0-471-94090-6. OCLC 815118., p. 559.
- ↑ Phillips (1977), p. 23–25.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Phillips (1977), p. 39.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Phillips (1977), p. 38.
- ↑ Lord Rayleigh (J. W. Strutt) (1877). "On progressive waves". Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society 9: 21–26. doi:10.1112/plms/s1-9.1.21. https://zenodo.org/record/1447762. Reprinted as Appendix in: Theory of Sound 1, MacMillan, 2nd revised edition, 1894.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Phillips (1977), p. 26.
- ↑ Bretherton, F. P.; Garrett, C. J. R. (1968). "Wavetrains in inhomogeneous moving media". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series A 302 (1471): 529–554. doi:10.1098/rspa.1968.0034. Bibcode: 1968RSPSA.302..529B.
- ↑ Phillips (1977), pp. 179–183.
- ↑ Phillips (1977), pp. 70–74.
- ↑ Phillips (1977), p. 66.
- ↑ Phillips (1977), p. 68.
- ↑ Phillips (1977), pp. 39–40 & 61.
- ↑ Phillips (1977), p. 40.
- ↑ Phillips (1977), p. 70.
- ↑ McIntyre, M. E. (1978). "On the 'wave-momentum' myth". Journal of Fluid Mechanics 106: 331–347. doi:10.1017/S0022112081001626. Bibcode: 1981JFM...106..331M.
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 34.2 Phillips (1977), pp. 61–63.
- ↑ Phillips (1977), p. 23.
- ↑ LeBlond, P.H.; Mysak, L.A. (1981). Waves in the Ocean. Elsevier Oceanography Series. 20. Elsevier. pp. 85 & 110–111. ISBN 978-0-444-41926-2.
- ↑ Craik, A.D.D. (1988). Wave interactions and fluid flows. Cambridge University Press. p. 105. ISBN 978-0-521-36829-2.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 Phillips (1977), p. 44.
References
Historical
- Airy, G. B. (1841). "Tides and waves". in Hugh James Rose. Encyclopædia Metropolitana. Mixed Sciences. 3. 1817–1845. Also: "Trigonometry, On the Figure of the Earth, Tides and Waves", 396 pp.
- Stokes, G. G. (1847). "On the theory of oscillatory waves". Transactions of the Cambridge Philosophical Society 8: 441–455.
Reprinted in: Stokes, G. G. (1880). Mathematical and Physical Papers, Volume I. Cambridge University Press. pp. 197–229. https://archive.org/details/mathphyspapers01stokrich.
Further reading
- Craik, A. D. D. (2004). "The origins of water wave theory". Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics 36: 1–28. doi:10.1146/annurev.fluid.36.050802.122118. Bibcode: 2004AnRFM..36....1C.
- Dean, R. G.; Dalrymple, R. A. (1991). Water wave mechanics for engineers and scientists. Advanced Series on Ocean Engineering. 2. Singapore: World Scientific. ISBN 978-981-02-0420-4. OCLC 22907242.
- Dingemans, M. W. (1997). Water wave propagation over uneven bottoms. Advanced Series on Ocean Engineering. 13. Singapore: World Scientific. ISBN 978-981-02-0427-3. OCLC 36126836. Two parts, 967 pages.
- Lamb, H. (1994). Hydrodynamics (6th ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-45868-9. OCLC 30070401. Originally published in 1879, the 6th extended edition appeared first in 1932.
- Landau, L. D.; Lifschitz, E. M. (1986). Fluid mechanics. Course of Theoretical Physics. 6 (2nd revised ed.). Pergamon Press. ISBN 978-0-08-033932-0. OCLC 15017127.
- Lighthill, M. J. (1978). Waves in fluids. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-29233-7. OCLC 2966533. 504 pp.
- Phillips, O. M. (1977). The dynamics of the upper ocean (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-29801-8. OCLC 7319931.
- Wehausen, J. V.; Laitone, E. V. (1960), Flügge, S.; Truesdell, C., eds., "Surface Waves", Encyclopaedia of Physics (Springer Verlag) 9: 653–667, §27, OCLC 612422741, http://coe.berkeley.edu/SurfaceWaves/, retrieved 2013-05-05
External links
- Linear theory of ocean surface waves on WikiWaves.
- Water waves at MIT.
 |