Physics:Static forces and virtual-particle exchange
Static force fields are fields, such as a simple electric, magnetic or gravitational fields, that exist without excitations. The most common approximation method that physicists use for scattering calculations can be interpreted as static forces arising from the interactions between two bodies mediated by virtual particles, particles that exist for only a short time determined by the uncertainty principle.[1] The virtual particles, also known as force carriers, are bosons, with different bosons associated with each force.[2]:{{{1}}}
The virtual-particle description of static forces is capable of identifying the spatial form of the forces, such as the inverse-square behavior in Newton's law of universal gravitation and in Coulomb's law. It is also able to predict whether the forces are attractive or repulsive for like bodies.
The path integral formulation is the natural language for describing force carriers. This article uses the path integral formulation to describe the force carriers for spin 0, 1, and 2 fields. Pions, photons, and gravitons fall into these respective categories.
There are limits to the validity of the virtual particle picture. The virtual-particle formulation is derived from a method known as perturbation theory which is an approximation assuming interactions are not too strong, and was intended for scattering problems, not bound states such as atoms. For the strong force binding quarks into nucleons at low energies, perturbation theory has never been shown to yield results in accord with experiments,[3] thus, the validity of the "force-mediating particle" picture is questionable. Similarly, for bound states the method fails.[4] In these cases, the physical interpretation must be re-examined. As an example, the calculations of atomic structure in atomic physics or of molecular structure in quantum chemistry could not easily be repeated, if at all, using the "force-mediating particle" picture.[citation needed]
Use of the "force-mediating particle" picture (FMPP) is unnecessary in nonrelativistic quantum mechanics, and Coulomb's law is used as given in atomic physics and quantum chemistry to calculate both bound and scattering states. A non-perturbative relativistic quantum theory, in which Lorentz invariance is preserved, is achievable by evaluating Coulomb's law as a 4-space interaction using the 3-space position vector of a reference electron obeying Dirac's equation and the quantum trajectory of a second electron which depends only on the scaled time. The quantum trajectory of each electron in an ensemble is inferred from the Dirac current for each electron by setting it equal to a velocity field times a quantum density, calculating a position field from the time integral of the velocity field, and finally calculating a quantum trajectory from the expectation value of the position field. The quantum trajectories are of course spin dependent, and the theory can be validated by checking that Pauli's exclusion principle is obeyed for a collection of fermions.
Classical forces
The force exerted by one mass on another and the force exerted by one charge on another are strikingly similar. Both fall off as the square of the distance between the bodies. Both are proportional to the product of properties of the bodies, mass in the case of gravitation and charge in the case of electrostatics.
They also have a striking difference. Two masses attract each other, while two like charges repel each other.
In both cases, the bodies appear to act on each other over a distance. The concept of field was invented to mediate the interaction among bodies thus eliminating the need for action at a distance. The gravitational force is mediated by the gravitational field and the Coulomb force is mediated by the electromagnetic field.
Gravitational force
The gravitational force on a mass [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] exerted by another mass [math]\displaystyle{ M }[/math] is [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{F} = - G \frac{m M}{r^2} \, \hat\mathbf{r} = m \mathbf{g} \left ( \mathbf{r} \right ), }[/math] where G is the gravitational constant, r is the distance between the masses, and [math]\displaystyle{ \hat\mathbf{r} }[/math] is the unit vector from mass [math]\displaystyle{ M }[/math] to mass [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math].
The force can also be written [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{F} = m \mathbf{g} \left ( \mathbf{r} \right ), }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{g} \left ( \mathbf{r} \right ) }[/math] is the gravitational field described by the field equation [math]\displaystyle{ \nabla\cdot \mathbf{g} = -4\pi G\rho_m, }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \rho_m }[/math] is the mass density at each point in space.
Coulomb force
The electrostatic Coulomb force on a charge [math]\displaystyle{ q }[/math] exerted by a charge [math]\displaystyle{ Q }[/math] is (SI units) [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{F} = \frac{1}{4\pi\varepsilon_0}\frac{q Q}{r^2}\mathbf{\hat{r}}, }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \varepsilon_0 }[/math] is the vacuum permittivity, [math]\displaystyle{ r }[/math] is the separation of the two charges, and [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{\hat{r}} }[/math] is a unit vector in the direction from charge [math]\displaystyle{ Q }[/math] to charge [math]\displaystyle{ q }[/math].
The Coulomb force can also be written in terms of an electrostatic field: [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{F} = q \mathbf{E} \left ( \mathbf{r} \right ), }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \nabla \cdot \mathbf{E} = \frac {\rho_q}{\varepsilon _0}; }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \rho_q }[/math] being the charge density at each point in space.
Virtual-particle exchange
In perturbation theory, forces are generated by the exchange of virtual particles. The mechanics of virtual-particle exchange is best described with the path integral formulation of quantum mechanics. There are insights that can be obtained, however, without going into the machinery of path integrals, such as why classical gravitational and electrostatic forces fall off as the inverse square of the distance between bodies.
Path-integral formulation of virtual-particle exchange
A virtual particle is created by a disturbance to the vacuum state, and the virtual particle is destroyed when it is absorbed back into the vacuum state by another disturbance. The disturbances are imagined to be due to bodies that interact with the virtual particle’s field.
The probability amplitude
Using natural units, [math]\displaystyle{ \hbar = c = 1 }[/math], the probability amplitude for the creation, propagation, and destruction of a virtual particle is given, in the path integral formulation by [math]\displaystyle{ Z \equiv \langle 0 | \exp\left ( -i \hat H T \right ) |0 \rangle = \exp\left ( -i E T \right ) = \int D\varphi \; \exp\left ( i \mathcal{S} [\varphi] \right )\; = \exp\left ( i W \right ) }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \hat H }[/math] is the Hamiltonian operator, [math]\displaystyle{ T }[/math] is elapsed time, [math]\displaystyle{ E }[/math] is the energy change due to the disturbance, [math]\displaystyle{ W = - E T }[/math] is the change in action due to the disturbance, [math]\displaystyle{ \varphi }[/math] is the field of the virtual particle, the integral is over all paths, and the classical action is given by [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{S} [\varphi] = \int \mathrm{d}^4x\; {\mathcal{L} [\varphi (x)]\,} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{L} [\varphi (x)] }[/math] is the Lagrangian density.
Here, the spacetime metric is given by [math]\displaystyle{ \eta_{\mu\nu} = \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & -1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix}. }[/math]
The path integral often can be converted to the form [math]\displaystyle{ Z = \int \exp\left[ i \int d^4x \left ( \frac 1 2 \varphi \hat O \varphi + J \varphi \right) \right ] D\varphi }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \hat O }[/math] is a differential operator with [math]\displaystyle{ \varphi }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ J }[/math] functions of spacetime. The first term in the argument represents the free particle and the second term represents the disturbance to the field from an external source such as a charge or a mass.
The integral can be written (see Common integrals in quantum field theory § Integrals with differential operators in the argument) [math]\displaystyle{ Z \propto \exp\left( i W\left ( J \right )\right) }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ W\left ( J \right ) = -\frac{1}{2} \iint d^4x \; d^4y \; J\left ( x \right ) D\left ( x-y \right ) J\left ( y \right ) }[/math] is the change in the action due to the disturbances and the propagator [math]\displaystyle{ D\left ( x-y \right ) }[/math] is the solution of [math]\displaystyle{ \hat O D\left ( x - y \right ) = \delta^4 \left ( x - y \right ). }[/math]
Energy of interaction
We assume that there are two point disturbances representing two bodies and that the disturbances are motionless and constant in time. The disturbances can be written [math]\displaystyle{ J(x) = \left( J_1 +J_2,0,0,0 \right) }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ J_1 = a_1 \delta^3\left ( \vec x - \vec x_1 \right ) }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ J_2 = a_2 \delta^3\left ( \vec x - \vec x_2 \right ) }[/math] where the delta functions are in space, the disturbances are located at [math]\displaystyle{ \vec x_1 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \vec x_2 }[/math], and the coefficients [math]\displaystyle{ a_1 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ a_2 }[/math] are the strengths of the disturbances.
If we neglect self-interactions of the disturbances then W becomes [math]\displaystyle{ W\left ( J \right ) = - \iint d^4x \; d^4y \; J_1\left ( x \right ) \frac{1}{2} \left [ D\left ( x-y \right ) + D\left ( y-x \right )\right ] J_2\left ( y \right ), }[/math]
which can be written [math]\displaystyle{ W\left ( J \right ) = - T a_1 a_2\int \frac{d^3k}{(2 \pi )^3} \; \; D\left ( k \right )\mid_{k_0=0} \; \exp\left ( i \vec k \cdot \left ( \vec x_1 - \vec x_2 \right ) \right ). }[/math]
Here [math]\displaystyle{ D\left ( k \right ) }[/math] is the Fourier transform of [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{2} \left [ D\left ( x-y \right ) + D\left ( y-x \right )\right ]. }[/math]
Finally, the change in energy due to the static disturbances of the vacuum is [math]\displaystyle{ E = - \frac{W}{T} = a_1 a_2\int \frac{d^3k}{(2 \pi )^3} \; \; D\left ( k \right )\mid_{k_0=0} \; \exp\left ( i \vec k \cdot \left ( \vec x_1 - \vec x_2 \right ) \right ). }[/math]
If this quantity is negative, the force is attractive. If it is positive, the force is repulsive.
Examples of static, motionless, interacting currents are the Yukawa potential, the Coulomb potential in a vacuum, and the Coulomb potential in a simple plasma or electron gas.
The expression for the interaction energy can be generalized to the situation in which the point particles are moving, but the motion is slow compared with the speed of light. Examples are the Darwin interaction in a vacuum and in a plasma.
Finally, the expression for the interaction energy can be generalized to situations in which the disturbances are not point particles, but are possibly line charges, tubes of charges, or current vortices. Examples include: two line charges embedded in a plasma or electron gas, Coulomb potential between two current loops embedded in a magnetic field, and the magnetic interaction between current loops in a simple plasma or electron gas. As seen from the Coulomb interaction between tubes of charge example, shown below, these more complicated geometries can lead to such exotic phenomena as fractional quantum numbers.
Selected examples
The Yukawa potential: The force between two nucleons in an atomic nucleus
Consider the spin-0 Lagrangian density[2]:{{{1}}} [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{L} [\varphi (x)] = \frac{1}{2} \left [ \left ( \partial \varphi \right )^2 -m^2 \varphi^2 \right ]. }[/math]
The equation of motion for this Lagrangian is the Klein–Gordon equation [math]\displaystyle{ \partial^2 \varphi + m^2 \varphi =0. }[/math]
If we add a disturbance the probability amplitude becomes [math]\displaystyle{ Z = \int D\varphi \; \exp \left \{ i \int d^4x\; \left [ \frac{1}{2} \left ( \left ( \partial \varphi \right )^2 - m^2\varphi^2 \right ) + J\varphi \right ] \right \}. }[/math]
If we integrate by parts and neglect boundary terms at infinity the probability amplitude becomes [math]\displaystyle{ Z = \int D\varphi \; \exp \left \{ i \int d^4x\; \left [ -\frac{1}{2}\varphi \left ( \partial^2 + m^2\right )\varphi + J\varphi \right ] \right \}. }[/math]
With the amplitude in this form it can be seen that the propagator is the solution of [math]\displaystyle{ -\left ( \partial^2 + m^2\right ) D\left ( x-y \right ) = \delta^4\left ( x-y \right ). }[/math]
From this it can be seen that [math]\displaystyle{ D\left ( k \right )\mid_{k_0=0} \; = \; -\frac{1}{\vec k^2 + m^2}. }[/math]
The energy due to the static disturbances becomes (see Common integrals in quantum field theory § Yukawa Potential: The Coulomb potential with mass) [math]\displaystyle{ E =-\frac{a_1 a_2}{4 \pi r} \exp \left ( -m r \right ) }[/math] with [math]\displaystyle{ r^2 = \left (\vec x_1 - \vec x_2 \right )^2 }[/math] which is attractive and has a range of [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{m}. }[/math]
Yukawa proposed that this field describes the force between two nucleons in an atomic nucleus. It allowed him to predict both the range and the mass of the particle, now known as the pion, associated with this field.
Electrostatics
The Coulomb potential in a vacuum
Consider the spin-1 Proca Lagrangian with a disturbance[2]:{{{1}}}
[math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal{L} [\varphi (x)] = -\frac{1}{4} F_{\mu \nu} F^{\mu \nu} + \frac{1}{2} m^2 A_{\mu} A^{\mu} + A_{\mu} J^{\mu} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ F_{\mu \nu} = \partial_{\mu} A_{\nu} - \partial_{\nu} A_{\mu}, }[/math] charge is conserved [math]\displaystyle{ \partial_{\mu} J^{\mu} = 0, }[/math] and we choose the Lorenz gauge [math]\displaystyle{ \partial_{\mu} A^{\mu} = 0. }[/math]
Moreover, we assume that there is only a time-like component [math]\displaystyle{ J^0 }[/math] to the disturbance. In ordinary language, this means that there is a charge at the points of disturbance, but there are no electric currents.
If we follow the same procedure as we did with the Yukawa potential we find that [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} & -\frac{1}{4} \int d^4x F_{\mu \nu}F^{\mu \nu} = -\frac{1}{4}\int d^4x \left( \partial_{\mu} A_{\nu} - \partial_{\nu} A_{\mu} \right)\left( \partial^{\mu} A^{\nu} - \partial^{\nu} A^{\mu} \right) \\ = {} & \frac{1}{2}\int d^4x \; A_{\nu} \left( \partial^{2} A^{\nu} - \partial^{\nu} \partial_{\mu} A^{\mu} \right) = \frac{1}{2}\int d^4x \; A^{\mu} \left( \eta_{\mu \nu} \partial^{2} \right) A^{\nu}, \end{align} }[/math] which implies [math]\displaystyle{ \eta_{\mu \alpha} \left ( \partial^2 + m^2\right ) D^{\alpha \nu}\left ( x-y \right ) = \delta_{\mu}^{\nu} \delta^4\left ( x-y \right ) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ D_{\mu \nu}\left ( k \right )\mid_{k_0=0} \; = \; \eta_{\mu \nu}\frac{1}{- k^2 + m^2}. }[/math]
This yields [math]\displaystyle{ D\left( k \right)\mid_{k_0=0}\; = \; \frac{1}{\vec k^2 + m^2} }[/math] for the timelike propagator and [math]\displaystyle{ E = + \frac{a_1 a_2}{4 \pi r} \exp \left( -m r \right) }[/math] which has the opposite sign to the Yukawa case.
In the limit of zero photon mass, the Lagrangian reduces to the Lagrangian for electromagnetism [math]\displaystyle{ E = \frac{a_1 a_2}{4 \pi r}. }[/math]
Therefore the energy reduces to the potential energy for the Coulomb force and the coefficients [math]\displaystyle{ a_1 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ a_2 }[/math] are proportional to the electric charge. Unlike the Yukawa case, like bodies, in this electrostatic case, repel each other.
Coulomb potential in a simple plasma or electron gas
Plasma waves
The dispersion relation for plasma waves is[5]:{{{1}}} [math]\displaystyle{ \omega^2 = \omega_p^2 + \gamma\left( \omega \right) \frac{T_e}{m} \vec k^2. }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \omega }[/math] is the angular frequency of the wave, [math]\displaystyle{ \omega_p^2 = \frac{4\pi n e^2}{m} }[/math] is the plasma frequency, [math]\displaystyle{ e }[/math] is the magnitude of the electron charge, [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] is the electron mass, [math]\displaystyle{ T_e }[/math] is the electron temperature (Boltzmann's constant equal to one), and [math]\displaystyle{ \gamma\left( \omega \right) }[/math] is a factor that varies with frequency from one to three. At high frequencies, on the order of the plasma frequency, the compression of the electron fluid is an adiabatic process and [math]\displaystyle{ \gamma\left( \omega \right) }[/math] is equal to three. At low frequencies, the compression is an isothermal process and [math]\displaystyle{ \gamma\left( \omega \right) }[/math] is equal to one. Retardation effects have been neglected in obtaining the plasma-wave dispersion relation.
For low frequencies, the dispersion relation becomes [math]\displaystyle{ \vec k^2 + \vec k_D^2 = 0 }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ k_D^2= \frac{4\pi n e^2}{T_e} }[/math] is the Debye number, which is the inverse of the Debye length. This suggests that the propagator is [math]\displaystyle{ D\left ( k \right )\mid_{k_0=0} \; = \; \frac{1}{\vec k^2 + k_D^2}. }[/math]
In fact, if the retardation effects are not neglected, then the dispersion relation is [math]\displaystyle{ -k_0^2 +\vec k^2 + k_D^2 -\frac{m}{T_e} k_0^2 = 0, }[/math] which does indeed yield the guessed propagator. This propagator is the same as the massive Coulomb propagator with the mass equal to the inverse Debye length. The interaction energy is therefore [math]\displaystyle{ E = \frac{a_1 a_2}{4 \pi r} \exp \left ( -k_D r \right ). }[/math] The Coulomb potential is screened on length scales of a Debye length.
Plasmons
In a quantum electron gas, plasma waves are known as plasmons. Debye screening is replaced with Thomas–Fermi screening to yield[6] [math]\displaystyle{ E = \frac{a_1 a_2}{4 \pi r} \exp \left ( -k_s r \right ) }[/math] where the inverse of the Thomas–Fermi screening length is [math]\displaystyle{ k_s^2 = \frac{6\pi n e^2}{\varepsilon_F} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \varepsilon_F }[/math] is the Fermi energy [math]\displaystyle{ \varepsilon_F = \frac{\hbar^2}{2m} \left( {3 \pi^2 n} \right)^{2/3} . }[/math]
This expression can be derived from the chemical potential for an electron gas and from Poisson's equation. The chemical potential for an electron gas near equilibrium is constant and given by [math]\displaystyle{ \mu = -e\varphi + \varepsilon_F }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \varphi }[/math] is the electric potential. Linearizing the Fermi energy to first order in the density fluctuation and combining with Poisson's equation yields the screening length. The force carrier is the quantum version of the plasma wave.
Two line charges embedded in a plasma or electron gas
We consider a line of charge with axis in the z direction embedded in an electron gas [math]\displaystyle{ J_1\left( x\right) = \frac{a_1}{L_B} \frac{1}{2 \pi r} \delta^2\left( r \right) }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ r }[/math] is the distance in the xy-plane from the line of charge, [math]\displaystyle{ L_B }[/math] is the width of the material in the z direction. The superscript 2 indicates that the Dirac delta function is in two dimensions. The propagator is [math]\displaystyle{ D\left ( k \right )\mid_{k_0=0}\; = \; \frac{1}{\vec k^2 + k_{Ds}^2} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ k_{Ds} }[/math] is either the inverse Debye–Hückel screening length or the inverse Thomas–Fermi screening length.
The interaction energy is [math]\displaystyle{ E = \left( \frac{a_1\, a_2}{2 \pi L_B}\right) \int_0^{\infty} \frac{k\,dk}{k^2 + k_{Ds}^2} \mathcal J_0 ( kr_{12} ) = \left( \frac{a_1\, a_2}{2 \pi L_B}\right) K_0 \left( k_{Ds} r_{12} \right) }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal J_n ( x ) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ K_0 ( x ) }[/math] are Bessel functions and [math]\displaystyle{ r_{12} }[/math] is the distance between the two line charges. In obtaining the interaction energy we made use of the integrals (see Common integrals in quantum field theory § Integration of the cylindrical propagator with mass) [math]\displaystyle{ \int_0^{2 \pi} \frac{d\varphi}{2 \pi} \exp\left( i p \cos\left( \varphi \right) \right) = \mathcal J_0 ( p ) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \int_0^{\infty} \frac{k\,dk}{k^2 + m^2} \mathcal J_0 (kr) = K_0 (mr). }[/math]
For [math]\displaystyle{ k_{Ds} r_{12} \ll 1 }[/math], we have [math]\displaystyle{ K_0 \left( k_{Ds} r_{12} \right) \rightarrow -\ln \left(\frac{k_{Ds} r_{12}}{2}\right) + 0.5772. }[/math]
Coulomb potential between two current loops embedded in a magnetic field
Interaction energy for vortices
We consider a charge density in tube with axis along a magnetic field embedded in an electron gas [math]\displaystyle{ J_1\left( x\right) = \frac{a_1}{L_b} \frac{1}{2 \pi r} \delta^2{\left( r - r_{B1}\right)} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ r }[/math] is the distance from the guiding center, [math]\displaystyle{ L_B }[/math] is the width of the material in the direction of the magnetic field [math]\displaystyle{ r_{B1} = \frac{\sqrt{4 \pi} m_1 v_1}{a_1 B} = \sqrt{\frac{2 \hbar}{m_1 \omega_c}} }[/math] where the cyclotron frequency is (Gaussian units) [math]\displaystyle{ \omega_c = \frac{a_1 B}{\sqrt{4 \pi} m_1 c} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ v_1 = \sqrt {\frac{2 \hbar \omega_c}{m_1}} }[/math] is the speed of the particle about the magnetic field, and B is the magnitude of the magnetic field. The speed formula comes from setting the classical kinetic energy equal to the spacing between Landau levels in the quantum treatment of a charged particle in a magnetic field.
In this geometry, the interaction energy can be written [math]\displaystyle{ E = \left( \frac{a_1\, a_2}{2 \pi L_B}\right) \int_0^{\infty} {k\;dk \;} D\left( k \right) \mid_{k_0=k_B=0} \mathcal J_0 \left ( kr_{B1} \right) \mathcal J_0 \left ( kr_{B2} \right) \mathcal J_0 \left ( kr_{12} \right) }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ r_{12} }[/math] is the distance between the centers of the current loops and [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal J_n ( x ) }[/math] is a Bessel function of the first kind. In obtaining the interaction energy we made use of the integral [math]\displaystyle{ \int_0^{2 \pi} \frac{d\varphi}{2 \pi} \exp\left( i p \cos(\varphi) \right) = \mathcal J_0 ( p ) . }[/math]
Electric field due to a density perturbation
The chemical potential near equilibrium, is given by [math]\displaystyle{ \mu = -e\varphi + N\hbar \omega_c = N_0\hbar \omega_c }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ -e\varphi }[/math] is the potential energy of an electron in an electric potential and [math]\displaystyle{ N_0 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ N }[/math] are the number of particles in the electron gas in the absence of and in the presence of an electrostatic potential, respectively.
The density fluctuation is then [math]\displaystyle{ \delta n = \frac{e \varphi}{\hbar \omega_c A_M L_B} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ A_M }[/math] is the area of the material in the plane perpendicular to the magnetic field.
Poisson's equation yields [math]\displaystyle{ \left( k^2 + k_B^2 \right) \varphi = 0 }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ k_B^2 = \frac{4 \pi e^2}{\hbar \omega_c A_M L_B}. }[/math]
The propagator is then [math]\displaystyle{ D\left( k \right) \mid_{k_0=k_B=0} = \frac{1}{k^2 + k_B^2} }[/math] and the interaction energy becomes [math]\displaystyle{ E = \left( \frac{a_1\, a_2}{2 \pi L_B}\right) \int_0^{\infty} \frac{k\;dk \;}{k^2 + k_B^2} \mathcal J_0 \left ( kr_{B1} \right) \mathcal J_0 \left ( kr_{B2} \right) \mathcal J_0 \left ( kr_{12} \right) = \left( \frac{2 e^2}{L_B}\right) \int_0^{\infty} \frac{k\;dk \;}{k^2 + k_B^2 r_B^2} \mathcal J_0^2 \left ( k \right) \mathcal J_0 \left ( k\frac{r_{12}}{r_B} \right) }[/math] where in the second equality (Gaussian units) we assume that the vortices had the same energy and the electron charge.
In analogy with plasmons, the force carrier is the quantum version of the upper hybrid oscillation which is a longitudinal plasma wave that propagates perpendicular to the magnetic field.
Currents with angular momentum
Delta function currents
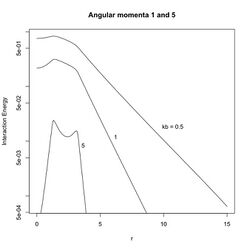
Unlike classical currents, quantum current loops can have various values of the Larmor radius for a given energy.[7]:{{{1}}} Landau levels, the energy states of a charged particle in the presence of a magnetic field, are multiply degenerate. The current loops correspond to angular momentum states of the charged particle that may have the same energy. Specifically, the charge density is peaked around radii of [math]\displaystyle{ r_{l} = \sqrt{l}\;r_B\; \; \; l=0,1,2, \ldots }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ l }[/math] is the angular momentum quantum number. When [math]\displaystyle{ l = 1 }[/math] we recover the classical situation in which the electron orbits the magnetic field at the Larmor radius. If currents of two angular momentum [math]\displaystyle{ l \gt 0 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ l' \ge l }[/math] interact, and we assume the charge densities are delta functions at radius [math]\displaystyle{ r_{l} }[/math], then the interaction energy is [math]\displaystyle{ E = \left( \frac{2 e^2}{L_B}\right) \int_0^{\infty} \frac{k\;dk \;}{k^2 + k_B^2 r_{l}^2} \;\mathcal J_0 \left ( k \right) \;\mathcal J_0 \left ( \sqrt{\frac{l'}{l}} \;k \right) \;\mathcal J_0 \left ( k \frac{r_{12}}{r_{l}} \right). }[/math]
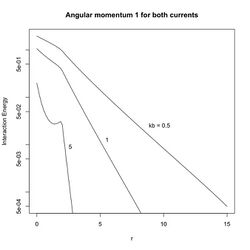
The interaction energy for [math]\displaystyle{ l= l' }[/math] is given in Figure 1 for various values of [math]\displaystyle{ k_B r_{l} }[/math]. The energy for two different values is given in Figure 2.
Quasiparticles
For large values of angular momentum, the energy can have local minima at distances other than zero and infinity. It can be numerically verified that the minima occur at [math]\displaystyle{ r_{12} = r_{l l'} = \sqrt{l + l'} \; r_B. }[/math]
This suggests that the pair of particles that are bound and separated by a distance [math]\displaystyle{ r_{l l'} }[/math] act as a single quasiparticle with angular momentum [math]\displaystyle{ l + l' }[/math].
If we scale the lengths as [math]\displaystyle{ r_{l l'} }[/math], then the interaction energy becomes [math]\displaystyle{ E = \frac{2 e^2}{L_B} \int_0^{\infty} \frac{k\,dk}{k^2 + k_B^2 r_{l l'}^2} \;\mathcal J_0 \left ( \cos \theta \, k \right) \;\mathcal J_0 ( \sin \theta \,k ) \;\mathcal J_0{\left( k \frac{r_{12}}{r_{l l'}} \right)} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \tan \theta = \sqrt{\frac{l}{l'}}. }[/math]
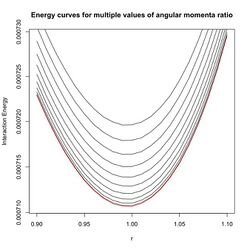
The value of the [math]\displaystyle{ r_{12} }[/math] at which the energy is minimum, [math]\displaystyle{ r_{12} = r_{l l'} }[/math], is independent of the ratio [math]\displaystyle{ \tan \theta = \sqrt{{l}/{l'}} }[/math]. However the value of the energy at the minimum depends on the ratio. The lowest energy minimum occurs when [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{l}{l'} = 1. }[/math]
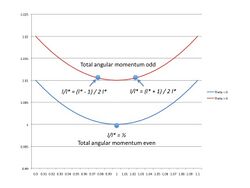
When the ratio differs from 1, then the energy minimum is higher (Figure 3). Therefore, for even values of total momentum, the lowest energy occurs when (Figure 4) [math]\displaystyle{ l = l' = 1 }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{l}{l^*} = \frac{1}{2} }[/math] where the total angular momentum is written as [math]\displaystyle{ l^* = l + l'. }[/math]
When the total angular momentum is odd, the minima cannot occur for [math]\displaystyle{ l = l' . }[/math] The lowest energy states for odd total angular momentum occur when [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{l}{l^*} = \; \frac{l^*\pm 1}{2l^*} }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{l}{l^*} = \frac{1}{3}, \frac{2}{5}, \frac{3}{7}, \text{etc.,} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{l}{l^*} = \frac{2}{3}, \frac{3}{5}, \frac{4}{7}, \text{etc.,} }[/math] which also appear as series for the filling factor in the fractional quantum Hall effect.
Charge density spread over a wave function
The charge density is not actually concentrated in a delta function. The charge is spread over a wave function. In that case the electron density is[7]:189 [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{\pi r_B^2 L_B} \frac{1}{n!} \left( \frac{r}{r_B} \right)^{2l} \exp \left( -\frac{r^2}{r_B^2} \right). }[/math]
The interaction energy becomes [math]\displaystyle{ E = \left( \frac{2 e^2}{L_B}\right) \int_0^{\infty} \frac{k\;dk \;}{k^2 + k_B^2 r_{B}^2} \; M {\left ( l + 1, 1, -\frac{k^2}{4} \right)} \;M {\left ( l' + 1, 1, -\frac{k^2}{4} \right)} \;\mathcal J_0 {\left ( k \frac{r_{12}}{r_{B}} \right)} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ M }[/math] is a confluent hypergeometric function or Kummer function. In obtaining the interaction energy we have used the integral (see Common integrals in quantum field theory § Integration over a magnetic wave function)
[math]\displaystyle{ \frac{2}{n!} \int_0^{\infty} dr \;r^{2n+1}\exp\left( -r^2\right) J_0(kr) = M\left( n+1, 1, -\frac{k^2}{4}\right). }[/math]
As with delta function charges, the value of [math]\displaystyle{ r_{12} }[/math] in which the energy is a local minimum only depends on the total angular momentum, not on the angular momenta of the individual currents. Also, as with the delta function charges, the energy at the minimum increases as the ratio of angular momenta varies from one. Therefore, the series [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{l}{l^*} = \frac{1}{3}, \frac{2}{5}, \frac{3}{7}, \text{etc.,} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{l}{l^*} = \frac{2}{3}, \frac{3}{5}, \frac{4}{7}, \text{etc.,} }[/math]
appear as well in the case of charges spread by the wave function.
The Laughlin wavefunction is an ansatz for the quasiparticle wavefunction. If the expectation value of the interaction energy is taken over a Laughlin wavefunction, these series are also preserved.
Magnetostatics
Darwin interaction in a vacuum
A charged moving particle can generate a magnetic field that affects the motion of another charged particle. The static version of this effect is called the Darwin interaction. To calculate this, consider the electrical currents in space generated by a moving charge [math]\displaystyle{ \vec J_1{\left( \vec x \right)} = a_1 \vec v_1 \delta^3 {\left( \vec x - \vec x_1 \right)} }[/math] with a comparable expression for [math]\displaystyle{ \vec J_2 }[/math].
The Fourier transform of this current is [math]\displaystyle{ \vec J_1{\left( \vec k \right)} = a_1 \vec v_1 \exp\left( i \vec k \cdot \vec x_1 \right). }[/math]
The current can be decomposed into a transverse and a longitudinal part (see Helmholtz decomposition). [math]\displaystyle{ \vec J_1{\left( \vec k \right)} = a_1 \left[ 1 - \hat k \hat k \right ] \cdot \vec v_1 \exp\left( i \vec k \cdot \vec x_1 \right) + a_1 \left[ \hat k \hat k \right ] \cdot \vec v_1 \exp\left( i \vec k \cdot \vec x_1 \right). }[/math]
The hat indicates a unit vector. The last term disappears because [math]\displaystyle{ \vec k \cdot \vec J = -k_0 J^0 \rightarrow 0, }[/math] which results from charge conservation. Here [math]\displaystyle{ k_0 }[/math] vanishes because we are considering static forces.
With the current in this form the energy of interaction can be written [math]\displaystyle{ E = a_1 a_2\int \frac{d^3k}{(2 \pi )^3} \; \; D\left ( k \right )\mid_{k_0=0} \; \vec v_1 \cdot \left[ 1 - \hat k \hat k \right ] \cdot \vec v_2 \; \exp\left ( i \vec k \cdot \left ( x_1 - x_2 \right ) \right ) . }[/math]
The propagator equation for the Proca Lagrangian is [math]\displaystyle{ \eta_{\mu \alpha} \left ( \partial^2 + m^2\right ) D^{\alpha \nu}\left ( x-y \right ) = \delta_{\mu}^{\nu} \delta^4\left ( x-y \right ). }[/math]
The spacelike solution is [math]\displaystyle{ D\left ( k \right )\mid_{k_0=0}\; = \; -\frac{1}{\vec k^2 + m^2}, }[/math] which yields [math]\displaystyle{ E = - a_1 a_2 \int \frac{d^3k}{(2 \pi )^3} \; \; \frac{\vec v_1 \cdot \left[ 1 - \hat k \hat k \right ] \cdot \vec v_2}{\vec k^2 + m^2} \; \exp\left ( i \vec k \cdot \left ( x_1 - x_2 \right ) \right ) }[/math] which evaluates to (see Common integrals in quantum field theory § Transverse potential with mass)
[math]\displaystyle{ E = - \frac{1}{2} \frac{a_1 a_2}{4 \pi r} e^{ - m r} \left\{ \frac{2}{\left( mr \right)^2} \left( e^{mr} -1 \right) - \frac{2}{mr} \right \} \vec v_1 \cdot \left[ 1 + {\hat r} {\hat r}\right]\cdot \vec v_2 }[/math] which reduces to [math]\displaystyle{ E = - \frac{1}{2} \frac{a_1 a_2}{4 \pi r} \vec v_1 \cdot \left[ 1 + {\hat r} {\hat r}\right] \cdot \vec v_2 }[/math] in the limit of small m. The interaction energy is the negative of the interaction Lagrangian. For two like particles traveling in the same direction, the interaction is attractive, which is the opposite of the Coulomb interaction.
Darwin interaction in a plasma
In a plasma, the dispersion relation for an electromagnetic wave is[5]:{{{1}}} ([math]\displaystyle{ c = 1 }[/math]) [math]\displaystyle{ k_0^2 = \omega_p^2 +\vec k^2, }[/math] which implies [math]\displaystyle{ D\left ( k \right )\mid_{k_0=0}\; = \; -\frac{1}{\vec k^2 + \omega_p^2}. }[/math]
Here [math]\displaystyle{ \omega_p }[/math] is the plasma frequency. The interaction energy is therefore [math]\displaystyle{ E = - \frac{1}{2} \frac{a_1 a_2}{4 \pi r} \vec v_1 \cdot \left[ 1 + {\hat r} {\hat r}\right]\cdot \vec v_2 \; e^{ - \omega_p r } \left\{ \frac{2}{\left( \omega_p r \right)^2} \left( e^{\omega_p r} -1 \right) - \frac{2}{\omega_p r} \right \}. }[/math]
Magnetic interaction between current loops in a simple plasma or electron gas
The interaction energy
Consider a tube of current rotating in a magnetic field embedded in a simple plasma or electron gas. The current, which lies in the plane perpendicular to the magnetic field, is defined as [math]\displaystyle{ \vec J_1( \vec x) = a_1 v_1 \frac{1}{2 \pi r L_B} \; \delta^ 2 {\left( r - r_{B1} \right)} \left( \hat b \times \hat r \right) }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ r_{B1} = \frac{\sqrt{4 \pi}m_1 v_1}{a_1 B} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \hat b }[/math] is the unit vector in the direction of the magnetic field. Here [math]\displaystyle{ L_B }[/math] indicates the dimension of the material in the direction of the magnetic field. The transverse current, perpendicular to the wave vector, drives the transverse wave.
The energy of interaction is [math]\displaystyle{ E = \left( \frac{a_1\, a_2}{2 \pi L_B}\right) v_1\, v_2\, \int_0^{\infty} {k\;dk \;} D\left( k \right) \mid_{k_0=k_B=0} \mathcal J_1 {\left ( kr_{B1} \right)} \mathcal J_1 {\left ( kr_{B2} \right)} \mathcal J_0 {\left ( kr_{12} \right)} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ r_{12} }[/math] is the distance between the centers of the current loops and [math]\displaystyle{ \mathcal J_n ( x ) }[/math] is a Bessel function of the first kind. In obtaining the interaction energy we made use of the integrals [math]\displaystyle{ \int_0^{2 \pi} \frac{d\varphi}{2 \pi} \exp\left( i p \cos\left( \varphi \right) \right) = \mathcal J_0 \left( p \right) }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \int_0^{2 \pi} \frac{d\varphi}{2 \pi} \cos\left( \varphi \right) \exp\left( i p \cos\left( \varphi \right) \right) = i\mathcal J_1 \left( p \right) . }[/math]
See Common integrals in quantum field theory § Angular integration in cylindrical coordinates.
A current in a plasma confined to the plane perpendicular to the magnetic field generates an extraordinary wave.[5]:{{{1}}} This wave generates Hall currents that interact and modify the electromagnetic field. The dispersion relation for extraordinary waves is[5]:112 [math]\displaystyle{ -k_0^2 +\vec k^2 + \omega_p^2 \frac{k_0^2 - \omega_p^2}{k_0^2- \omega_H^2} =0, }[/math] which gives for the propagator [math]\displaystyle{ D\left( k \right) \mid_{k_0=k_B=0}\;= \;-\left( \frac{1}{\vec k^2 + k_X^2}\right) }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ k_X \equiv \frac{\omega_p^2}{\omega_H} }[/math] in analogy with the Darwin propagator. Here, the upper hybrid frequency is given by [math]\displaystyle{ \omega_H^2 = \omega_p^2 + \omega_c^2, }[/math] the cyclotron frequency is given by (Gaussian units) [math]\displaystyle{ \omega_c = \frac{e B}{m c}, }[/math] and the plasma frequency (Gaussian units) [math]\displaystyle{ \omega_p^2 = \frac{4\pi n e^2}{m}. }[/math]
Here n is the electron density, e is the magnitude of the electron charge, and m is the electron mass.
The interaction energy becomes, for like currents, [math]\displaystyle{ E = - \left( \frac{a^2}{2 \pi L_B}\right) v^2\, \int_0^{\infty} \frac{k\;dk}{\vec k^2 + k_X^2} \mathcal J_1^2 \left ( kr_{B} \right) \mathcal J_0 \left ( kr_{12} \right) }[/math]
Limit of small distance between current loops
In the limit that the distance between current loops is small, [math]\displaystyle{ E = - E_0 \; I_1 \left( \mu \right) K_1 \left( \mu \right) }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ E_0 = \left( \frac{a^2}{2 \pi L_B}\right) v^2 }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ \mu =\frac{\omega_p^2 r_B}{\omega_H}= k_X \;r_B }[/math] and I and K are modified Bessel functions. we have assumed that the two currents have the same charge and speed.
We have made use of the integral (see Common integrals in quantum field theory § Integration of the cylindrical propagator with mass) [math]\displaystyle{ \int_o^{\infty} \frac{k\; dk}{k^2 +m^2} \mathcal J_1^2 \left( kr \right) = I_1 \left( mr \right)K_1 \left( mr \right) . }[/math]
For small mr the integral becomes [math]\displaystyle{ I_1 \left( mr \right)K_1 \left( mr \right) \rightarrow \frac{1}{2}\left[ 1- \frac{1}{8}\left( mr \right)^2 \right] . }[/math]
For large mr the integral becomes [math]\displaystyle{ I_1 \left( mr \right)K_1 \left( mr \right) \rightarrow \frac{1}{2}\;\left( \frac{1}{mr}\right) . }[/math]
Relation to the quantum Hall effect
The screening wavenumber can be written (Gaussian units) [math]\displaystyle{ \mu = \frac{\omega_p^2 r_B}{\omega_H c} = \left( \frac{2e^2r_B}{L_B \hbar c}\right) \frac{\nu}{\sqrt{1+\frac{\omega_p^2}{\omega_c^2}}} = 2 \alpha \left( \frac{r_B}{L_B}\right) \left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{1+\frac{\omega_p^2}{\omega_c^2}}}\right) \nu }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha }[/math] is the fine-structure constant and the filling factor is [math]\displaystyle{ \nu = \frac{2\pi N \hbar c}{eBA} }[/math] and N is the number of electrons in the material and A is the area of the material perpendicular to the magnetic field. This parameter is important in the quantum Hall effect and the fractional quantum Hall effect. The filling factor is the fraction of occupied Landau states at the ground state energy.
For cases of interest in the quantum Hall effect, [math]\displaystyle{ \mu }[/math] is small. In that case the interaction energy is [math]\displaystyle{ E = - \frac{E_0}{2} \left[ 1- \frac{1}{8}\mu^2\right] }[/math] where (Gaussian units) [math]\displaystyle{ E_0 = {4\pi}\frac{e^2}{L_B}\frac{v^2}{c^2} = {8\pi}\frac{e^2}{L_B}\left( \frac{\hbar \omega_c}{m c^2}\right) }[/math] is the interaction energy for zero filling factor. We have set the classical kinetic energy to the quantum energy [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{2} m v^2 = \hbar \omega_c. }[/math]
Gravitation
A gravitational disturbance is generated by the stress–energy tensor [math]\displaystyle{ T^{\mu \nu} }[/math]; consequently, the Lagrangian for the gravitational field is spin-2. If the disturbances are at rest, then the only component of the stress–energy tensor that persists is the [math]\displaystyle{ 00 }[/math] component. If we use the same trick of giving the graviton some mass and then taking the mass to zero at the end of the calculation the propagator becomes [math]\displaystyle{ D\left ( k \right )\mid_{k_0=0}\; = \; - \frac{4}{3} \frac{1}{\vec k^2 + m^2} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ E = -\frac{4}{3}\frac{a_1 a_2}{4 \pi r} \exp \left ( -m r \right ), }[/math] which is once again attractive rather than repulsive. The coefficients are proportional to the masses of the disturbances. In the limit of small graviton mass, we recover the inverse-square behavior of Newton's Law.[2]:{{{1}}}
Unlike the electrostatic case, however, taking the small-mass limit of the boson does not yield the correct result. A more rigorous treatment yields a factor of one in the energy rather than 4/3.[2]:35
References
- ↑ Jaeger, Gregg (2019). "Are virtual particles less real?". Entropy 21 (2): 141. doi:10.3390/e21020141. PMID 33266857. Bibcode: 2019Entrp..21..141J.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Zee, A. (2003). Quantum Field Theory in a Nutshell. Princeton University. ISBN 0-691-01019-6.
- ↑ "High Energy Physics Group - Hadronic Physics". Archived from the original on 2011-07-17. https://web.archive.org/web/20110717002648/http://www.hep.phy.cam.ac.uk/theory/research/hadronic.html. Retrieved 2010-08-31.
- ↑ "Time-Independent Perturbation Theory". virginia.edu. http://galileo.phys.virginia.edu/classes/752.mf1i.spring03/Time_Ind_PT.htm.
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Chen, Francis F. (1974). Introduction to Plasma Physics. Plenum Press. ISBN 0-306-30755-3.
- ↑ C. Kittel (1976). Introduction to Solid State Physics (Fifth ed.). John Wiley and Sons. ISBN 0-471-49024-5. pp. 296-299.
- ↑ Jump up to: 7.0 7.1 Ezewa, Zyun F. (2008). Quantum Hall Effects: Field Theoretical Approach And Related Topics (Second ed.). World Scientific. ISBN 978-981-270-032-2.
 |