Software:Xenko
| File:Xenko Logo.png | |
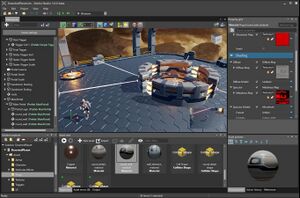 Screenshot of Xenko GameStudio | |
| Stable release | 3.0.0.3
/ 8 August 2018 |
|---|---|
| Written in | C# |
| Operating system | Creation
|
| Available in | English |
| Type | Game engine |
| License | MIT License (as of Xenko 3.0); GNU GPLv3 and proprietary (engine and editor, respectively, prior to Xenko 3.0) |
| Website | xenko |
Xenko is a free and open source 2D and 3D cross-platform game engine originally developed by Silicon Studio. It can be used to create video games for PC and mobile devices,[1] and virtual reality.[2][3]
Xenko's game engine was originally made available by Silicon Studio under a dual-license model, available to anyone under GNU GPLv3, with alternative, for-pay license terms available for those for whom the GPL's copyleft terms are a barrier to adoption.[4] However, on August 2, 2018, developer Virgile Bello announced on the Xenko blog that Silicon Studio has dropped support of the project and relicensed Xenko 3.0 under the MIT License. Unlike the prior dual-license arrangement where the engine was available as free and open source software but the editor remained proprietary, under the new arrangement both the engine and the editor are available under the MIT License.[5]
Functionality
Xenko is a C# suite of tools to create games. It is also a full game engine with a customizable shader system intended for virtual reality game development. Its main tool is the Game Studio, a fully integrated environment that allows you to import assets, create and arrange scenes using an Entity component system, assign scripts, build and run games. The game engine features a Physically-Based Rendering (PBR) layered material editor, photorealistic post effects such as a particle editor, a scene streaming system, a full tool-chain a Sprites editor, a scripting editor and an UI engine. Additionally, it supports a nested prefab and archetype systems scaling along all editors and assets. Xenko is also a cross-platform runtime supporting iOS, Android, Windows UWP, Linux, and PlayStation 4. It creates Visual Studio projects, allowing for easy scripting and debugging.
At release time, expect the following:
|
History
Xenko was formerly known as Paradox. Xenko first public mention was in September 2014. It went open-source on GitHub in October 2014.[6] Scene editor and Physically Based Rendering (PBR) material editor were announced in March 2015[7] and released in April 2015.[8]
Xenko beta version 1.8x was then released finally out of beta in February 2017.[9]
On March 1, 2017, Microsoft announced that Xenko would be included in their Xbox Creators Program[10] and newsite Major Nelson reporting that Xenko would be one of the supported game engines with "out of the box" support for UWP.[11]
In April 2017, Silicon Studio launched Xenko version 2.0 under a commercial proprietary license.[4]
In August 2018, Silicon Studio launched Xenko version 3.0 and announced the end of their support for the engine[5]
References
- ↑ "Bravely Default developer Silicon Studio moves into game engines with open-source Xenko platform". 2017-04-25. https://venturebeat.com/2017/04/24/japanese-game-publisher-silicon-studio-moves-into-game-engines-with-open-source-xenko-platform/.
- ↑ "Xenko Game Engine: A New Way To Develop Better VR Games" (in en-US). VRFocus. https://www.vrfocus.com/2017/04/xenko-game-engine-a-new-way-to-develop-better-vr-games/.
- ↑ "Xenko Game Engine Launches with Free Edition" (in en-US). VRFocus. https://www.vrfocus.com/2017/04/xenko-game-engine-launches-with-free-edition/.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Silicon Studio launches mobile and VR game engine Xenko after two years in beta". pocketgamer.biz. http://www.pocketgamer.biz/asia/news/65594/silicon-studio-launches-xenko/.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Virgile Bello. "Xenko Game Engine - Xenko 3.0 is now free and open-source!". https://xenko.com/blog/xenko-opensource-mit/.
- ↑ "Xenko is going Open Source!". 17 October 2014. http://xenko.com/blog/new-version-open-sourcing/. Retrieved 18 March 2016.
- ↑ "Scene Editor and New Advanced Rendering presented at GDC". 5 March 2015. http://xenko.com/blog/gdc-2015-scene-editor-new-rendering/. Retrieved 18 March 2016.
- ↑ "Xenko 1.1.0β: Scene Editor, PBR and PostFX". 28 April 2015. http://xenko.com/blog/new-version-1-1-0-beta-physically-based-rendering-and-scene-editor/. Retrieved 18 March 2016.
- ↑ 2017-02-24-silicon-studio-releasing-xenko-engine on gamesindustry.biz
- ↑ "Xbox Live Creators Program". 10 March 2017. https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/games/xbox/xboxlive/creator. Retrieved 10 March 2017.
- ↑ "New Investments For Xbox Developers And Gamers Kick Off GDC 2017". Major Nelson. 2017-03-10. https://majornelson.com/2017/03/01/new-investments-for-xbox-developers-and-gamers-kick-off-gdc-2017/.
External links
