Angular frequency
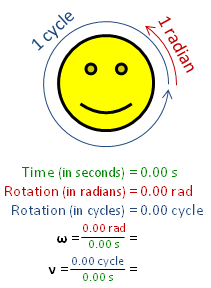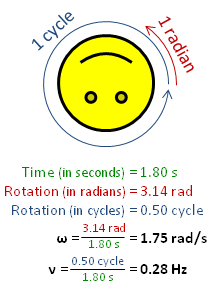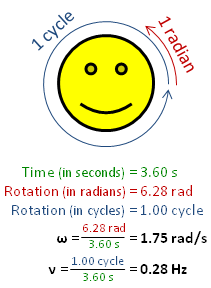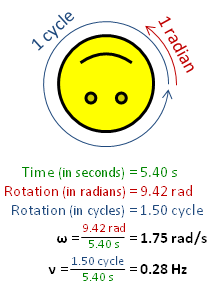
In physics, angular frequency "ω" (also referred to by the terms angular speed and angular rate) is a scalar measure of the angular displacement per unit time (for example, in rotation) or the rate of change of the phase of a sinusoidal waveform (for example, in oscillations and waves), or as the rate of change of the argument of the sine function. Angular frequency (or angular speed) is the magnitude of the pseudovector quantity angular velocity.[1]
One turn is equal to 2π radians, hence[1][2]
[math]\displaystyle{ \omega = \frac{2 \pi}{T} = {2 \pi f} , }[/math] where:
- ω is the angular frequency (unit: radians per second),
- T is the period (unit: seconds),
- f is the ordinary frequency (unit: hertz) (sometimes ν).
Units
In SI units, angular frequency is normally presented in radians per second, even when it does not express a rotational value. The unit hertz (Hz) is dimensionally equivalent, but by convention it is only used for frequency f, never for angular frequency ω. This convention is used to help avoid the confusion[3] that arises when dealing with quantities such as frequency and angular quantities because the units of measure (such as cycle or radian) are considered to be one and hence may be omitted when expressing quantities in SI units.[4][5]
In digital signal processing, the frequency may be normalized by the sampling rate, yielding the normalized frequency.
Examples
Circular motion
In a rotating or orbiting object, there is a relation between distance from the axis, [math]\displaystyle{ r }[/math], tangential speed, [math]\displaystyle{ v }[/math], and the angular frequency of the rotation. During one period, [math]\displaystyle{ T }[/math], a body in circular motion travels a distance [math]\displaystyle{ vT }[/math]. This distance is also equal to the circumference of the path traced out by the body, [math]\displaystyle{ 2\pi r }[/math]. Setting these two quantities equal, and recalling the link between period and angular frequency we obtain: [math]\displaystyle{ \omega = v/r. }[/math]
Oscillations of a spring
| Part of a series on |
| Classical mechanics |
|---|
| [math]\displaystyle{ \textbf{F} = \frac{d}{dt} (m\textbf{v}) }[/math] |
An object attached to a spring can oscillate. If the spring is assumed to be ideal and massless with no damping, then the motion is simple and harmonic with an angular frequency given by[6] [math]\displaystyle{ \omega = \sqrt{\frac{k}{m}}, }[/math] where
- k is the spring constant,
- m is the mass of the object.
ω is referred to as the natural angular frequency (sometimes be denoted as ω0).
As the object oscillates, its acceleration can be calculated by [math]\displaystyle{ a = -\omega^2 x, }[/math] where x is displacement from an equilibrium position.
Using standard frequency f, this equation would be [math]\displaystyle{ a = -(2 \pi f)^2 x. }[/math]
LC circuits
The resonant angular frequency in a series LC circuit equals the square root of the reciprocal of the product of the capacitance (C measured in farads) and the inductance of the circuit (L, with SI unit henry):[7] [math]\displaystyle{ \omega = \sqrt{\frac{1}{LC}}. }[/math]
Adding series resistance (for example, due to the resistance of the wire in a coil) does not change the resonant frequency of the series LC circuit. For a parallel tuned circuit, the above equation is often a useful approximation, but the resonant frequency does depend on the losses of parallel elements.
Terminology
Angular frequency is often loosely referred to as frequency, although these two quantities differ by a factor of 2π leading to potential confusion when the distinction is not clear.
See also
- Cycle per second
- Radian per second
- Degree (angle)
- Mean motion
- Orders of magnitude (angular velocity)
- Simple harmonic motion
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Cummings, Karen; Halliday, David (2007). Understanding physics. New Delhi: John Wiley & Sons, authorized reprint to Wiley – India. pp. 449, 484, 485, 487. ISBN 978-81-265-0882-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=rAfF_X9cE0EC.(UP1)
- ↑ Holzner, Steven (2006). Physics for Dummies. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley Publishing. pp. 201. ISBN 978-0-7645-5433-9. https://archive.org/details/physicsfordummie00holz. "angular frequency."
- ↑ Lerner, Lawrence S. (1996-01-01). Physics for scientists and engineers. p. 145. ISBN 978-0-86720-479-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=eJhkD0LKtJEC&pg=PA145.
- ↑ Mohr, J. C.; Phillips, W. D. (2015). "Dimensionless Units in the SI". Metrologia 52 (1): 40–47. doi:10.1088/0026-1394/52/1/40. Bibcode: 2015Metro..52...40M.
- ↑ "SI units need reform to avoid confusion". Nature 548 (7666): 135. 7 August 2011. doi:10.1038/548135b. PMID 28796224.
- ↑ Serway, Raymond A.; Jewett, John W. (2006). Principles of physics (4th ed.). Belmont, CA: Brooks / Cole – Thomson Learning. pp. 375, 376, 385, 397. ISBN 978-0-534-46479-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=1DZz341Pp50C&q=angular+frequency&pg=PA376.
- ↑ Nahvi, Mahmood; Edminister, Joseph (2003). Schaum's outline of theory and problems of electric circuits. McGraw-Hill Companies (McGraw-Hill Professional). pp. 214, 216. ISBN 0-07-139307-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=nrxT9Qjguk8C&q=angular+frequency&pg=PA103. (LC1)
Related Reading:
- Olenick, Richard P.; Apostol, Tom M.; Goodstein, David L. (2007). The Mechanical Universe. New York City: Cambridge University Press. pp. 383–385, 391–395. ISBN 978-0-521-71592-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=xMWwTpn53KsC&q=angular+frequency&pg=RA1-PA383.
ca:Freqüència angular fr:Vitesse angulaire he:תדירות זוויתית
 |