Social:Khorasani Turkic language
| Khorasani Turkic | |
|---|---|
| خراسان تركچىسى | |
| Pronunciation | [xorɑsɑn tyrktʃesi] |
| Native to | Iran |
| Region | Greater Khorasan |
Native speakers | 400,000–886,000 [1] (2014)[2] |
Turkic
| |
| Persian alphabet | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | kmz |
| Glottolog | khor1269[3] |
Khorasani Turkic (Khorasani Turkic: خراسان تركچىسى, pronounced [xorɑsɑn tyrktʃesi]; Persian: زبان ترکی خراسانی, romanized: Zabân-e Torkī-ye Xorâsânī) is an Oghuz Turkic language spoken in the North Khorasan Province and the Razavi Khorasan Province in Iran. Nearly all Khorasani Turkic speakers are also bilingual in Persian.[4]
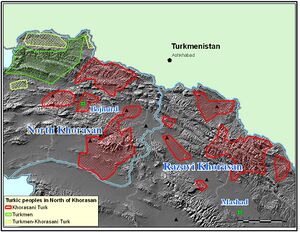
Geographic distribution
Khorasani Turkic is spoken in the Iranian provinces of North Khorasan near Bojnord and Razavi Khorasan near Sabzevar, Quchan. The Oghuz dialect spoken in Western Uzbekistan is sometimes considered a dialect of Khorasani Turkic.
Dialects
Khorasani Turkic is split into North, South and West dialects. The northern dialect is spoken in North Khorasan near Quchan; the southern in Soltanabad, near Sabzevar; the western, around Bojnord.
Khorasani Turkic belongs to the Oghuz group of Turkic languages, which also includes Turkish, Azerbaijani, Gagauz, Balkan Gagauz Turkish, Turkmen and Salar, as well as the Oghuz dialect spoken in Uzbekistan. Khorasani Turkic is most closely related to Oghuz Uzbek and Turkmen and is close to the Azerbaijani dialects spoken in Iran.[clarification needed]
Khorasani Turkic was first classified as a separate dialect by Iranian Azerbaijani linguist Javad Heyat in the book Tarikh-e zabān o lahcayā-ye Türki (History of the Turkic dialects).[5] According to some linguists, it should be considered intermediate linguistically between Azerbaijani and Turkmen, although it is sufficiently distinct not to be considered a dialect of either.[6]
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Glottal | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plosive | p | b | t | d | k | ɡ | q | |||||
| Affricate | t͡ʃ | d͡ʒ | ||||||||||
| Fricative | f | v | s | z | ʃ | ʒ | x | ɣ | h | |||
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | ŋ | ||||||||
| Flap | r | |||||||||||
| Lateral | l | |||||||||||
| Approximant | j | |||||||||||
Vowels
| Front | Back | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unrounded | Rounded | Unrounded | Rounded | |
| Close | i | y | ɯ | u |
| Mid | e | ø | o | |
| Open | æ | ɑ | ɒ | |
The open back vowel is rounded when followed by /u/ or /i/: muxabbat love /muxɒbbɑt/, insan human /insɒn/, but yoldaşlık friendship /joldɑʃlɯk/. It can also be rounded by a following long /o/. This may not happen for all speakers, and plurals never have any rounding.
Morphology
Nouns
Pluralization
Pluralization is marked on nouns with the suffix /-lar/, which has the two forms /-lar/ and /-lær/, depending on vowel harmony. Plural /ɑ/ is never rounded, even when it follows /u/ or /i/.
Case
Nouns in Khorasani Turkic take a number of case endings that change based on vowel harmony and whether they follow a vowel or a consonant:
| Case | After Vowels | After Consonants |
|---|---|---|
| Nominative | No Ending | |
| Genitive | niŋ/nin | iŋ/in |
| Dative | ja/jæ | a/æ |
| Accusative | ni/nɯ | i/ɯ |
| Locative | da/dæ | |
| Ablative | dan/dæn | |
| Instrumental | nan/næn | |
Possession
Possession is marked with a suffix on the possessed noun.
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| First Person | (I)m | (I)mIz |
| Second Person | (I)ŋ | (I)ŋIz |
| Third Person | (s)I | lArI |
Pronouns
Khorasani Turkic has six personal pronouns. Occasionally, personal pronouns take different case endings from regular nouns.
| Singular | Plural | |
|---|---|---|
| First Person | mæn | bɯz |
| Second Person | sæn | siz |
| Third Person | o | olar |
Verbs
Verbs are declined for tense, aspect, mood, person, and number. The infinitive form of the verb ends in -max.
Examples
- Excerpt from Tulu (1989) p. 90
| Translation | IPA | In Latin Alphabet | Arabic script (Iran) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thus, there was a padishah named Ziyad. | ɑl ɣəssa bir ziyæːd pæːdiʃæːhiː bæːɾɨdɨ | Al ğässa bir ziüäd pädişähi bärıdı | .ال غسا بیر زیود پدیشهی بـهریدی |
| Almighty God had given him no son. | xodɒːʷændi æːlæm ona hit͡ʃ ɔɣul ataː elæmɑmiʃdi | Xodavändi äläm ona hiç oğul ata elämamişdi. | .خوداوندی آلم اونا هیچ اوغول اتا ایلهمامیشدی |
| There he spoke to his vizier: "O Vizier, I have no son. What shall I do about it?" | bæːdæn vaziːɾæ dədi, ej vaziːɾ, mændæ ki ɔɣul joxdɨ, mæn næ t͡ʃaːɾæ eylem | Bädän vazirä dädi: "Ey vazir, mändä ki oğul yoxdı. Män nä çarä eylem?" | بدن وازیره دهدی: «ای وازیر, منده کی اوغول یوخدی. من نه چاره ایولیم»؟ |
| The vizier said: "Ruler of the whole world, what will you do with this possession?" | vaziːɾ dədi, pɒːdiʃaː-i ɢɨblæ-ji ɒːlæm, sæn bu mɒːlɨ-æmwɒːlɨ næjlijæsæn | Vazir dädi: "Padişai qıbläyi aläm, sän bu malıämvalı näyliyäsän?" | وازیر دهدی: «پادیشای قیبلنهیی آلم, سن بو مالیموالی نیلیسن»؟ |
References
- ↑ https://www.wycliffe.net/world?continent=ASI&country=IR&code=kmz
- ↑ Khorasani Turkish - Ethnologue
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds (2017). "Khorasan Turkic". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. http://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/khor1269.
- ↑ "Ethnologue report for Khorasani Turkic"
- ↑ [1] Horasan Türkçesi ne İlgili Folklor Çalışmaları
- ↑ "Sultan Tulu, “Horasan Türkçesi ile İlgili Folklor Çalışmaları”, Atatürk Üniversitesi Türkiyat Araştırmaları Enstitüsü Dergisi, Sayı 1, 1994, s. 48-51.". http://e-dergi.atauni.edu.tr/index.php/taed/article/viewFile/2091/2090.
Tulu, Sultan (1989). Chorasantürkische Materialien aus Kalāt bei Esfarāyen. Berlin: Klaus Schwarz Verlag. ISBN 3-922968-88-0.
Doerfer, Gerhard; Hesche, Wolfram (1993). Chorasantürkisch: Wörterlisten, Kurzgrammatiken, Indices. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz. ISBN 3-447-03320-7.
External links
| Khorasani Turkic language test of Wikipedia at Wikimedia Incubator |