Chemistry:Tetrarhodium dodecacarbonyl
| |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
tri-μ-carbonyl-1:2κ2C;1:3κ2C;2:3κ2C-nonacarbonyl-
1κ2C,2κ2C,3κ2C,4κ3C-[Td-(13)-Δ4-closo]-
| |
| Other names
rhodium(0) carbonyl; rhodium carbonyl; rhodium dodecacarbonyl
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Rh4(CO)12 | |
| Molar mass | 747.743 g/mol |
| Appearance | Red crystals |
| Solubility | Chlorocarbons, toluene, tetrahydrofuran |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H312, H332 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P312, P322, P330, P363, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Tetracobalt dodecacarbonyl, Tetrairidium dodecacarbonyl |
Related compounds
|
Rhodium(III) chloride, Rh6(CO)16, Rh2(CO)4Cl2 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tetrarhodium dodecacarbonyl is the chemical compound with the formula Rh4(CO)12. This dark-red crystalline solid is the smallest binary rhodium carbonyl that can be handled as a solid under ambient conditions. It is used as a catalyst in organic synthesis.
Structure, synthesis, reactions
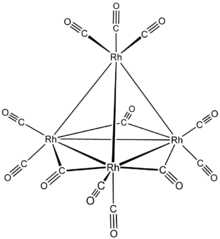
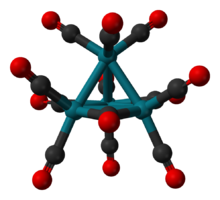
According to X-ray crystallography, Rh
4(CO)
12 features a tetrahedral array of four Rh atoms with nine terminal CO ligands and three bridging CO ligands. The structure can be expressed as Rh4(CO)9(µ-CO)3.[1]
Rh
4(CO)
12 is prepared by treatment of an aqueous solution of rhodium trichloride with activated copper metal under an atmosphere of CO.[2]
- 4 RhCl3(H2O)3 + 8 Cu + 22 CO → Rh
4(CO)
12 + 2 CO2 + 8 Cu(CO)Cl + 4 HCl + 10 H2O
Alternatively, the compound can be prepared by treatment of a methanolic solution of RhCl3(H2O)3 with CO to afford H[RhCl2(CO)2], followed by carbonylation in the presence of sodium citrate.[1]
The cluster undergoes thermal substitution with phosphine ligands, L:[3]
- Rh4(CO)12 + n L → Rh4(CO)12-nLn + n CO
Tetrarhodium dodecacarbonyl quantitatively decomposes in boiling hexane to afford hexadecacarbonylhexarhodium:[4]
- 3 Rh
4(CO)
12 → 2 Rh
6(CO)
16 + 4 CO
Related metal carbonyls
Because of their relevance to hydroformylation catalysis, rhodium carbonyls have been systematically studied to a high degree. The instability of Rh2(CO)8 has been a source of curiosity. The analogous binary carbonyl of cobalt, Co2(CO)8, is well known. Solutions of Rh4(CO)12 under high pressures of CO convert to the dirhodium compound:[5]
- Rh
4(CO)
12 + 4 CO → Rh
2(CO)
8
Unlike Co2(CO)8 which features bridging carbonyls, the main isomer of Rh2(CO)8 features only terminal CO ligands. The relative instability of Rh2(CO)8 is analogous to the tendency of Ru(CO)5 to convert to Ru3(CO)12.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Serp, P.; Kalck, P.; Feurer, R.; Morancho, R. (1998). "Tri-µ-carbonyl-nonacarbonyltetrarhodium". Inorganic Syntheses 32: 284–287. doi:10.1002/9780470132630.ch45.
- ↑ S. Martinengo; G. Giordano; P. Chini (1990). "Tri-µ-carbonyl-nonacarbonyltetrarhodium". Inorganic Syntheses 28: 242–245. doi:10.1002/9780470132593.ch62.
- ↑ Heaton, Brian T.; Longhetti, Luciano; Michael, D.; Mingos, P.; Briant, Clive E.; Minshall, Peter C.; Theobald, Brian R.C.; Garlaschelli, Luigi et al. (1981). "Structural Studies of Rh4(CO)12 Derivatives in Solution and in the Solid State". Journal of Organometallic Chemistry 213: 333–350. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)93969-X.
- ↑ Tunik, S. P.; Vlasov, A. V.; Krivykh, V. V. (1977). "Acetonitrile-Substituted Derivatives of Rh6(CO)16 : Rh6(CO)16-x(NCMe)x (x = 1,2)". Inorganic Syntheses 31: 239–244. doi:10.1002/9780470132623.ch37.
- ↑ Brown, D. T.; Eguchi, T.; Heaton, B. T.; Iggo, J. A.; Whyman, R. (1991). "High-pressure spectroscopic studies of reactions of the clusters [Rh4(CO)12–x{P(OPh)3}x] (x = 1–4) with carbon monoxide or syngas". Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions: 677–683. doi:10.1039/DT9910000677.
General reading
- King, R. B., "Rhodium: Organometallic Chemistry" Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry 1994, 7, 3494.
 |

