Chemistry:Undecane
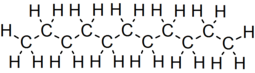
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Undecane[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1697099 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | undecane |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2330 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H24 | |
| Molar mass | 156.313 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Gasoline-like to Odorless |
| Density | 740 mg mL−1 |
| Melting point | −26.6 to −25.0 °C; −15.8 to −12.9 °F; 246.6 to 248.2 K |
| Boiling point | 193 to 197 °C; 379 to 386 °F; 466 to 470 K |
| log P | 6.312 |
| Vapor pressure | 55 Pa (at 25 °C)[2] |
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
5.4 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 |
| -131.84·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.417 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
345.05 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std molar
entropy (S |
458.15 J K−1 mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−329.8–−324.6 kJ mol−1 |
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−7.4339–−7.4287 MJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | DANGER |
| H304, H315, H319, H331, H335 | |
| P261, P301+310, P305+351+338, P311, P331 | |
| Flash point | 62.0 °C (143.6 °F; 335.1 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanes
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
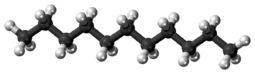
Undecane (also known as hendecane) is a liquid alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)9CH3. It is used as a mild sex attractant for various types of moths and cockroaches, and an alert signal for a variety of ants.[3] It has 159 isomers.[4]
Undecane may also be used as an internal standard in gas chromatography when working with other hydrocarbons. Since the boiling point of undecane (196 °C) is well known, it may be used as a comparison for retention times in a gas chromatograph for molecules whose structure has been freshly elucidated. For example, if one is working with a 50 m crosslinked methyl silicone capillary column with an oven temperature increasing slowly, beginning around 60 °C, an 11-carbon molecule like undecane may be used as an internal standard to be compared with the retention times of other 10-, 11-, or 12- carbon molecules, depending on their structures.
See also
References
- ↑ "undecane - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2004. Identification and Related Records. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=14257&loc=ec_rcs.
- ↑ Yaws, Carl L. (1999). Chemical Properties Handbook. New York: McGraw-Hill. pp. 159–179. ISBN 0-07-073401-1.
- ↑ Hölldobler B, Wilson EO (1990). The Ants. Harvard University Press. p. 287. ISBN 0-674-04075-9.
- ↑ Stoermer, Martin (2023). "Undecane Isomers". figshare. doi:10.6084/M9.FIGSHARE.24309724.
External links
- Undecane at Dr. Duke's Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases
 |

