Chemistry:Thiazyl trifluoride
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Thiazyl trifluoride
| |||
| Other names
Sulfur(VI) nitride trifluoride
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| NSF 3 | |||
| Molar mass | 103.06 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless gas | ||
| Melting point | −72.6 °C (−98.7 °F; 200.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −27.1 °C (−16.8 °F; 246.1 K) | ||
| Structure | |||
| Tetrahedral at the S atom | |||
| Hybridisation | sp3 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
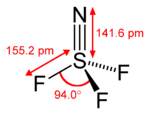
Thiazyl trifluoride is a chemical compound of nitrogen, sulfur, and fluorine, having the formula NSF
3. It exists as a stable, colourless gas, and is an important precursor to other sulfur-nitrogen-fluorine compounds.[1] It has tetrahedral molecular geometry around the sulfur atom, and is regarded to be a prime example of a compound that has a sulfur-nitrogen triple bond.[2]
Preparation
NSF
3 can be synthesised by the fluorination of thiazyl fluoride, NSF, with silver(II) fluoride, AgF
2:
- NSF + 2 AgF
2 → NSF
3 + 2 AgF
or by the oxidative decomposition of FC(O)NSF
2 by silver(II) fluoride:[3]
- FC(O)NSF
2 + 2 AgF
2 → NSF
3 + 2 AgF + COF
2
It is also a product of the oxidation of ammonia by S
2F
10.[4]
Reactions
NSF
3 is much more stable than thiazyl fluoride, does not reacts with ammonia and hydrogen chloride, and only reacts with sodium at 400 °C.[5] It reacts with carbonyl fluoride (COF
2) in the presence of hydrogen fluoride to form pentafluorosulfanyl isocyanate (SF
5NCO).[6]
References
- ↑ Oskar Glemser and Rüdiger Mews (1980). "Chemistry of Thiazyl Fluoride (NSF) and Thiazyl Trifluoride (NSF3): A Quarter Century of Sulfur-Nitrogen-Fluorine Chemistry". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 19 (11): 883–899. doi:10.1002/anie.198008831.
- ↑ Borrmann, T.; Lork, E.; Mews, R. D.; Parsons, S.; Petersen, J.; Stohrer, W. D.; Watson, P. G. (2008). "The crystal structures of NSF3 and (NSF2N(CH3)CH2–)2: How short is the 'Crystallographic' N≡S triple bond?". Inorganica Chimica Acta 361 (2): 479–486. doi:10.1016/j.ica.2007.05.016.
- ↑ Chivers, Tristram; Laitinen, Risto S. (2006). "Chalcogen–Nitrogen Chemistry". in Devillanova, Francesco. Handbook of Chalcogen Chemistry. London: The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 238. doi:10.1039/9781847557575. ISBN 978-0-85404-366-8. https://archive.org/details/handbookchalcoge00devi_741.
- ↑ Steve Mitchell (1996). Steve Mitchell. ed. Biological interactions of sulfur compounds. CRC Press. p. 14. ISBN 0-7484-0245-4.
- ↑ Huheey, James E.; Keiter, Ellen A.; Keiter, Richard L. (2003) (in de). Anorganische Chemie. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter. p. 1021. ISBN 978-3-11-017903-3.
- ↑ Alan F. Clifford, Thomas C. Rhyne and James W. Thompson, "Process For Preparing .alpha.,.alpha.-Fluorinated Alkyl Isocyanates", US patent 3,666,784, issued 1972-05-30
 |