Biology:Phenylalanine racemase (ATP-hydrolysing)
| Phenylalanine racemase (ATP-hydrolysing) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
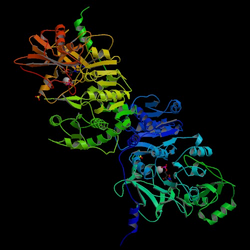 Phenylalanine Racemase(ATP Hydrolysing), image from Protein Data Bank | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 5.1.1.11 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 37290-95-2 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The enzyme phenylalanine racemase (EC 5.1.1.11, phenylalanine racemase, phenylalanine racemase (adenosine triphosphate-hydrolysing), gramicidin S synthetase I) is the enzyme that acts on amino acids and derivatives. It activates both the L & D stereo isomers of phenylalanine to form L-phenylalanyl adenylate and D-phenylalanyl adenylate, which are bound to the enzyme. These bound compounds are then transferred to the thiol group of the enzyme followed by conversion of its configuration, the D-isomer being the more favorable configuration of the two, with a 7 to 3 ratio between the two isomers. The racemisation reaction of phenylalanine is coupled with the highly favorable hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and pyrophosphate (PP), thermodynamically allowing it to proceed. This reaction is then drawn forward by further hydrolyzing PP to inorganic phosphate (Pi), via Le Chatelier's principle.
Other names
- phenylalanine racemase
- phenylalanine racemase (adenosine triphosphate-hydrolysing)
- gramicidin S synthetase I
Pathway
- Phenylalanine Metabolism
Substrate
- L – Phenylalanine
Product
- D - Phenylalanine
Cofactor
- Pyridoxal-phosphate (active form of vitamin B6)
Links to disease
Problems in the digestion of phenylalanine (phe) to tyrosine (tyr) lead to the buildup of both phe and phenylpyruvate, in a disease called Phenylketonuria (PKU). These two compounds build up in the blood stream and cerebral spinal fluid, which can lead to mental retardation if left untreated. Treatment consists of a restricted diet of foods that contain phe or compounds that can breakdown into phe. Children in the US are routinely tested for this at birth. For more information see the Phenylketonuria page or the link below.
Quick facts
- pH Range = 7.2 – 8.6
- Equilibrium Ratio:
L-Phe:D-Phe = 3:7 - Specific Activity: 0.019
The reaction
| L-Phenylalanine | Phenylalanine Racemase | D-Phenylalanine | |
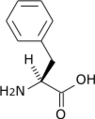
|
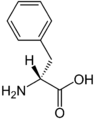
| ||
| ATP | AMP+PP | ||
| |||
Compound C00079 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00002 at KEGG Pathway Database. Enzyme 5.1.1.11 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00020 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00013 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00001 at KEGG Pathway Database. Reaction R00686 at KEGG Pathway Database. Template:KEGG pathway Compound C00018 at KEGG Pathway Database. |}
See also
- Phenylalanine
- Racemase
- Phenylketonuria
References
- "Racemization of phenylalanine by adenosine triphosphate-dependent phenylalanine racemase of Bacillus brevis Nagano". J. Biochem. 69 (5): 973–6. 1971. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129548. PMID 5577156.
- E. Conti; T. Stachelhaus; M. A. Marahiel; P. Brick (1997). "Structural basis for the activation of phenylalanine in the non-ribosomal biosynthesis of gramicidin S". EMBO J 16 (14): 4174–4183. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.14.4174. PMID 9250661.
External links
- Protein Data Bank 1amu [1]
 |

