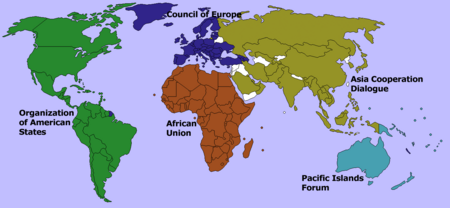
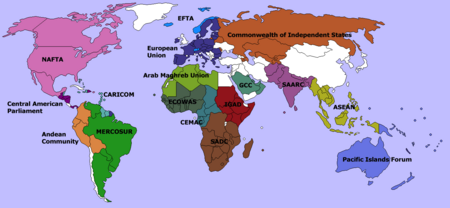
Organization:List of intergovernmental organizations
From HandWiki
Short description: none

A ministerial conference of the World Trade Organization, in the Palace of Nations (Geneva, Switzerland ).
The following is a list of the major existing intergovernmental organizations (IGOs).
For a more complete listing, see the Yearbook of International Organizations,[1] which includes 25,000 international non-governmental organizations (INGOs), excluding for-profit enterprises, about 5,000 IGOs, and lists dormant and dead organizations as well as those in operation (figures as of the 400th edition, 2012/13). A 2020 academic dataset on international organizations included 561 intergovernmental organizations between 1815 and 2015; more than one-third of those IGOs ended up defunct.[2]
United Nations and agencies
The UN has six principal organs:
- The General Assembly (the main deliberative assembly);
- The Security Council (decides certain resolutions for peace and security);
- The Economic and Social Council (assists in promoting international economic and social cooperation and development);
- The Secretariat (provides studies, information, and facilities needed by the UN);
- The International Court of Justice (the primary judicial organ).
- The United Nations Trusteeship Council (inactive)
The UN also includes various Funds, Programmes and specialized agencies:
- Food and Agriculture Organization
- International Labour Organization
- International Civil Aviation Organization
- International Maritime Organization
- International Telecommunication Union
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS
- United Nations Capital Development Fund
- United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC)
- United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund (UNICEF)
- United Nations Development Programme
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- United Nations Environment Programme
- United Nations Human Settlements Programme
- United Nations Industrial Development Organization
- United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNISDR)
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime
- Universal Postal Union
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- World Intellectual Property Organization
- World Food Programme
- World Meteorological Organization
- World Tourism Organization
- The UN maintains various offices:
- United Nations Headquarters (New York City )
- United Nations Office at Geneva
- United Nations Office at Nairobi
- United Nations Office at Vienna
The UN also includes subsidiary organs:
- International Residual Mechanism for Criminal Tribunals
- International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY)
- International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda (ICTR)
Agricultural research organizations
- Africa Rice Center (West Africa Rice Development Association, WARDA)
- Bioversity International (International Plant Genetics Resources Institute, IPGRI)
- Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR)
- International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT)
- International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
- International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT)
- International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI)
- International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA)
- International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI)
- International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT)
- International Potato Center (CIP)
- International Rice Research Institute (IRRI)
- International Water Management Institute (IWMI)
- World Agroforestry Centre (International Centre for Research in Agroforestry, ICRAF)
- WorldFish Center (International Center for Living Aquatic Resources Management, ICLARM)
- World Vegetable Center
- CGIAR
- CAB International (Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International, CABI)
Fisheries organizations
- Asia-Pacific Fishery Commission (APFIC)
- Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR)
- Great Lakes Fishery Commission (GLFC)
- Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC)
- Inter-American Tropical Tuna Commission (IATTC)
- International Commission for the Conservation of Atlantic Tunas (ICCAT)
- International Pacific Halibut Commission (IPHC)
- International Whaling Commission (IWC)
- North-East Atlantic Fisheries Commission (NEAFC)
- Northwest Atlantic Fisheries Organization (NAFO)
- North Atlantic Salmon Conservation Organization (NASCO)
- Pacific Salmon Commission (PSC)
- Southeast Asian Fisheries Development Center (SEAFDEC)
- Western and Central Pacific Fisheries Commission (WCPFC)
Maritime organizations
- Antarctic Treaty Secretariat (ATS)
- International Hydrographic Organization
- International Maritime Organization
- International Seabed Authority
- International Council for the Exploration of the Sea (ICES)
- Mediterranean Science Commission (CIESM)
- North Pacific Marine Science Organization (PICES)
Financial, trade, and customs organizations
- Alliance for Financial Inclusion (AFI)
- African Development Bank
- Asian Development Bank
- Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
- Bank for International Settlements
- Black Sea Trade and Development Bank (BSTDB)
- Caribbean Development Bank (CDB)
- Council of Europe Development Bank (CEB)
- Eurasian Development Bank
- European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD)
- European Investment Bank (EIB)
- Federation of Euro-Asian Stock Exchanges
- Financial Action Task Force (FATF)
- Inter-American Development Bank
- Inter-American Investment Corporation (IDB Invest)
- International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM)
- International Energy Agency (IEA)
- International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD)
- International Development Law Organization (IDLO), headquartered in Rome
- International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- Islamic Development Bank (IDB)
- Netherlands Development Finance Company (FMO)
- Nordic Development Fund (NDF)
- Nordic Investment Bank (NIB)
- New Development Bank (NDB)
- Organization for Economic and Co-operation Development (OECD)
- OPEC Fund for International Development (OPEC Fund)
- Organization of Petroleum-Exporting Countries (OPEC)
- West African Development Bank (BOAD)
- World Bank Group
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
Regional organizations
Europe
- European Union (EU)
- Western European Union (defunct)
- Big Four (Western Europe)
- Council of Europe (CoE)
- Central European Initiative (CEI)
- Energy Community
- European Free Trade Association (EFTA)
- European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT)
- European Patent Organisation (EPO)
- European Political Community (EPC)
- European Science Foundation
- European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation (EUROCONTROL)
- Group of 9 (G9)
- International Commission on Civil Status (ICCS)
- Central Commission for Navigation on the Rhine (CCNR)
- Council of the Baltic Sea States (CBSS)
- Assembly of European Regions (AER)
- Eiroforum
- European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN)
- Danube Commission
- European Fusion Development Agreement (EFDA JET)
- European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL)
- European Space Agency (ESA)
- European Southern Observatory (ESO)
- European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF)
- European x-ray free electron laser (European XFEL)
- Institut Laue–Langevin (ILL)
- Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission
- Benelux
- Belgium–Luxembourg Economic Union
- British–Irish Council
- Nordic Council
- Nordic Investment Bank
- Northern Dimension Partnership in Public Health and Social Well-being (NDPHS)
- Organisation for Joint Armament Cooperation (OCCAR)
- Visegrád Group (V4)
- EUREKA
- European Cooperation in Science and Technology (COST)
- Community for Democracy and Rights of Nations (Commonwealth of Unrecognized States)
- European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF)
- South-East European Cooperation Process
- West Nordic Council
- Three Seas Initiative
Asia
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue (ACD)
- Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
- East Asia Summit (EAS)
- Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)
- Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC)
- International Network for Bamboo and Rattan (INBAR)
- Mekong–Ganga Cooperation (MGC)
- Mekong River Commission (MRC)
- Partnerships in Environmental Management for the Seas of East Asia (PEMSEA)
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)
- Southeast Asian Ministers of Education Organization (SEAMEO)
- Trilateral Cooperation Secretariat (TCS)
- Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
Transcontinental
- Group of Eight
- Eurasia
- Asia-Europe Foundation (ASEF)
- Central Asian Cooperation Organization
- Community for Democracy and Rights of Nations
- Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO)
- Conference on Interaction and Confidence Building Measures in Asia (CICA)
- Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS)
- Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO)
- Eurasian Economic Union (EEU or EAEU)
- GUAM Organization for Democracy and Economic Development
- Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation (BSEC)
- Organization of Turkic States (OTS)
- Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO)
- TRACECA
- Union State
- Trans-Atlantic
- Group of Seven
- Group of Ten (economics)
- North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
- Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE)
- South Atlantic Peace and Cooperation Zone (ZPCAS)
- Mediterranean
- Union for the Mediterranean
- Indian Ocean
- Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC)
- Indian Ocean Commission (COI)
- Arctic Ocean
- Pacific Ocean:
- ANZUS
- Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
- Colombo Plan
- Group of Five
- Melanesian Spearhead Group (MSG)
- Pacific Islands Forum
- Pacific Regional Environment Programme (SPREP)
- Secretariat of the Pacific Community
- African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States
- Technical Centre for Agricultural and Rural Cooperation ACP-EU (CTA)
- Afro-Asian organizations
- Asian-African Legal Consultative Organization
- D-8 Organization for Economic Cooperation
Africa
- African Organisation for Standardisation (ARSO)
- African Union
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- Conseil de l'Entente
- Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- East African Community (EAC)
- West African Economic and Monetary Union (UEMOA)
- Southern African Development Community (SADC)
- Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD)
- Arab Maghreb Union
- International Conference on the Great Lakes Region (ICGLR)
- African Ministers Council on Water (AMCOW)
Americas
- Forum for the Progress and Integration of South America (PROSUR)
- Caribbean Community (CARICOM)
- Association of Caribbean States (ACS)
- Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS)
- Central American Parliament
- Bolivarian Alliance for the Americas (ALBA)
- Rio Group
- System of Cooperation Among the American Air Forces (SICOFAA)
- Central American Bank for Economic Integration (CABEI)
- Central American Integration System
- Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC)
- Pacific Alliance
Military alliances
- Australia, New Zealand, United States Security Treaty (ANZUS)
- AUKUS
- Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO)
- North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
- Inter-American Treaty of Reciprocal Assistance (Rio Pact)
Cultural, ethnic, linguistic, and religious organizations
- Commonwealth of Nations
- International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and Restoration of Cultural Property (ICCROM)
- Organisation internationale de la Francophonie
- Community of Portuguese Language Countries (CPLP)
- Organization of Ibero-American States (OEI)
- Arab League
- Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
- International Organization of Turkic Culture (TÜRKSOY)
- Interparliamentary Assembly on Orthodoxy
Educational organizations and universities
- Academy of European Law (ERA)
- Asian Institute of Technology (AIT)
- Cerlalc
- Commonwealth of Learning (COL)
- EUCLID (university)
- European Schools
- European University Institute
- IHE Delft Institute for Water Education
- International Bureau of Education IBE, now a part of UNESCO
- International Institute for the Unification of Private Law
- Model United Nations (MUN)
- United Nations University (UNU)
- University for Peace (UPEACE)
- World Maritime University (WMU/IMO)
Law enforcement cooperation
- International Criminal Court (ICC)
- International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol)
- Permanent Court of Arbitration (PCA)
Transport
- Intergovernmental Organisation for International Carriage by Rail (OTIF)
- Organization for Cooperation of Railways (OSJD or OSShD)
- International Civil Aviation Organization
- TRACECA
- Southeast Europe Transport Community
- International Transport Forum (ITF)
Humanitarian organizations
Environmental organizations
- Agreement on the Conservation of Albatrosses and Petrels (ACAP)
- The Forum of Ministers of Environment of Latin America and the Caribbean
- Global Environment Facility (GEF)
- Global Green Growth Institute (GGGI)
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
- Partnerships in Environmental Management for the Seas of East Asia (PEMSEA)
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
Arms control
- Conference on Disarmament
- Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
- Preparatory Commission for the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO)
- Wassenaar Arrangement
- Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG)
- Australia Group (AG)
- Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR)
Energy organizations
Multi sector organizations
- International Energy Agency
- Energy Charter
- Energy Community
- United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO)
- International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA)
- International Energy Forum (IEF)
Nuclear power organizations
- European Atomic Energy Community
- International Atomic Energy Agency
- International Centre for Synchrotron-Light for Experimental Science Applications in the Middle East
- Korean Peninsula Energy Development Organization
- Nuclear Energy Agency
- United Nations Atomic Energy Commission
- World Association of Nuclear Operators
Sustainable energy organizations
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA)
- Sustainable Energy for All (SE4ALL)
- Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Partnership (REEEP)
- International Solar Alliance
Digital organizations
- Digital 9 (D9)
Ideological and political groupings
- Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QSD)
- Non-Aligned Movement
- Group of Seven (G7)
- Group of 15 (G-15)
- Group of 77 (G-77)
- Group of 24 (G24)
- G20
- Alliance of Small Island States (AOSIS)
- BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa)
- Bolivarian Alliance for the Americas (ALBA)
- Association of World Election Bodies (AWEB)
- New Agenda Coalition
- Non-Proliferation and Disarmament Initiative[3]
- Western European and Others Group
- (disbanded)
Other
- Advisory Centre on World Trade Organization Law
- International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology
- International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance (International IDEA)
- Partners in Population and Development
- South Centre
- SKA Observatory (SKAO)
- World Organisation for Animal Health
- Forum for India-Pacific Islands cooperation (FIPIC)
- U-Report
- International Center for Promotion of Enterprises (ICPE)
Defunct
- Allied Control Council
- Arab Cooperation Council
- Central Treaty Organization
- Comecon
- Council of Ambassadors
- Customs and Economic Union of Central Africa
- Delian League
- Eurasian Economic Community (transformed into Eurasian Economic Union)
- French Community
- French Union
- G33
- International Authority for the Ruhr
- International Trade Organization
- Latin League
- Latin Union
- League of Corinth
- League of Nations
- Peloponnesian League
- Organisation of African Unity
- Southeast Asia Treaty Organization
- Union of African States
See also
- List of local government organizations
- List of international sports federations
References
- ↑ Union of International Associations, ed. (1998), Yearbook of international organizations, Leiden: Brill, http://www.uia.be/yearbook (six volumes in print format, plus online, subscription-based edition)
- ↑ Eilstrup-Sangiovanni, Mette (2020). "Death of international organizations. The organizational ecology of intergovernmental organizations, 1815–2015" (in en). The Review of International Organizations 15 (2): 339–370. doi:10.1007/s11558-018-9340-5. ISSN 1559-744X. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11558-018-9340-5.
- ↑ German Foreign Ministry, retrieved 6 July 2011
 |