Chemistry:Ranitidine bismuth citrate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Tritec, Pylorid |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
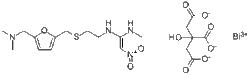
| Formula | C19H27BiN4O10S |
| Molar mass | 712.48 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Ranitidine bismuth citrate - drug, which has antisecretory and bactericidal action.
Group affiliation: H2-histamine receptor blocker.
Shape
Physical
Pills. The film-coated tablet contains ranitidine bismuth citrate 400 mg; in a blister 14 pcs., in a box 1, 2 or 4 blisters.
Chemical
N- / 2 - /// 5 - / (Dimethylamino) methyl / -2-furanyl / methyl / thio / ethyl / -N'-methyl-2-nitro-1,1-ethenediamine bismuth citrate.[clarification needed]
Pharmacological properties
Antiulcer, which is mediated by two active ingredients. Ranitidine - a blocker of H2-histamine receptors, suppresses basal and stimulated, day and night gastric acid secretion, reducing both the volume of its secretion and the concentration hydrochloric acid and pepsin are secreted. Bismuth citrate in vitro has a bactericidal effect on Helicobacter pylori, a protective effect on the gastric mucosa.
Indications
Stomach ulcer and duodenal ulcer, including those associated with Helicobacter pylori (in combination with amoxicillin or clarithromycin ohm).
Prospects for repurposing
Ranitidine bismuth citrate may also be effective against coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2, since it exhibits low cytotoxicity and is able to protect cells from infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus, with a selectivity index of several times higher than that of remdesivir a. This is due to the fact that it inhibits the activity required for viral replication helicase Nsp13 SARS-CoV-2 due to irreversible displacement of zinc (II) ions from enzyme and bismuth ions ( III)[1]
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, acute porphyria, chronic renal failure (CC less than 25 ml / min), childhood (up to 14 years), pregnancy, lactation.
Side effects
From the digestive system: gastralgia, diarrhea or constipation, increased activity of "hepatic" transaminases, hepatitis (hepatocellular, cholestatic or mixed, with or without jaundice, usually reversible), acute pancreatitis. From the side of the cardiovascular system: decrease BP, bradycardia, AV block, chest pain, asystole (with injection). On the part of the hematopoietic organs: anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, aplasia bone marrow. From the nervous system and sensory organs: headache, dizziness, depression, hallucinations, in severe and elderly patients - impaired visual perception (associated with a violation of accommodation); violation of taste; tremor, confusion. From the side of the musculoskeletal system: arthralgia, myalgia. Allergic reactions: pruritus, urticaria, angioedema, bronchospasm, anaphylactic shock, anaphylactoid reactions. Others: gynecomastia in men.
Overdose. Symptoms: neuro- and nephrotoxicity. Treatment: gastric lavage, symptomatic therapy. Ranitidine and bismuth can be removed from the bloodstream by hemodialysis a.
Method of administration and dosage
Inside, regardless of food intake, 2 times a day (morning and evening). In the treatment and prevention of benign gastric and duodenal ulcers, as well as for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori and the relief of concomitant symptoms of dyspepsia, the following combination therapy regimens are used. Within 7 days - 3 drugs: Scheme 1. 2 times a day - ranitidine bismuth citrate 400 mg, clarithromycin 500 mg, metronidazole 400 mg or amoxicillin 1 g. Scheme 2. 2 times a day - ranitidine bismuth citrate 400 mg, clarithromycin 250 mg, metronidazole 400 or 500 mg or tinidazole 500 mg. Scheme 3. Ranitidine bismuth citrate 400 mg 2 times a day, metronidazole 500 mg 3 times a day, tetracycline 500 mg 4 times a day. Scheme 4. 2 times a day - ranitidine bismuth citrate 400 mg, tinidazole 500 mg, amoxicillin 1 g. Within 14 days - 2 drugs: Scheme 5. Ranitidine bismuth citrate 400 mg 2 times a day and clarithromycin 500 mg 2 or 3 times a day. Scheme 6. Ranitidine bismuth citrate 400 mg 2 times a day and amoxicillin 500 mg 4 times a day. To stimulate regeneration processes in ulcerative diseases of the stomach and duodenal ulcer - 800 mg / day (for 2 doses) for 28 days. For the treatment of duodenal ulcers - 800 mg / day (for 2 doses) for 4 weeks (can be extended up to 8 weeks if necessary); with a stomach ulcer - 8 weeks.
Special instructions
Before starting therapy, the possibility of gastric ulcer malignancy is excluded, since ranitidine bismuth citrate can mask the symptoms of carcinoma of the stomach. Patients with mild or moderate renal impairment with CC of at least 50 ml / min do not require dose adjustment. In elderly patients with CC more than 25 ml / min, the dose is not changed. Dose changes in liver failure are not required, since ranitidine and bismuth are excreted mainly by the kidneys. H 2 -histamine receptor blockers should be taken 2 hours after taking itraconazole a or ketoconazole a to avoid a significant decrease in their absorption. H 2 -histamine receptor blockers can counteract the effects of pentagastrin a and histamine a on gastric acid-forming function, so use H 2 blockers within 24 hours prior to the test -histamine receptors are not recommended. H 2 -histamine receptor blockers can suppress the cutaneous reaction to histamine, thus resulting in to false negative results (it is recommended to discontinue the use of H 2 -histamine receptor blockers before performing diagnostic skin tests to detect an immediate allergic skin reaction). As with the use of other medicines containing bismuth, darkening of feces and blackening of the tongue are possible. The drug is taken with food or regardless of food intake.
Interaction
Clarithromycin increases the absorption of ranitidine. The concentration of clarithromycin in plasma does not change when combined with ranitidine bismuth citrate. With the simultaneous administration of ranitidine bismuth citrate with antacids, the absorption of bismuth does not change. Medicines that depress the bone marrow increase the risk of neutropenia. Reduces the absorption of itraconazole and ketoconazole due to an increase in pH in the gastrointestinal tract.
Notes
References
- ↑ "Metallodrug ranitidine bismuth citrate suppresses SARS-CoV-2 replication and relieves virus-associated pneumonia in Syrian hamsters". Nature Microbiology 5 (11): 1439–1448. November 2020. doi:10.1038/s41564-020-00802-x. PMID 33028965.
This article needs additional or more specific categories. (October 2020) |
 |

