Chemistry:Cyanoacetamide
From HandWiki
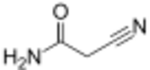
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Cyanoacetamide | |
| Other names
Malonamide nitrile
3-Nitrilopropionamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H4N2O | |
| Molar mass | 84.078 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.163 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 119 to 121 °C (246 to 250 °F; 392 to 394 K) |
| Boiling point | 351.2 °C (664.2 °F; 624.3 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
2-Cyanoacetamide is an organic compound. It is an acetic amide with a nitrile functional group.
Uses
Cyanoacetamide is used in spectrofluorimetric methods to determine the activity of antihistamine H1 receptor antagonistic drugs such as ebastine, cetirizine dihydrochloride and fexofenadine hydrochloride.[1]
Preparation
2-Cyanoacetamide is prepared from chloroacetic acid via Kolbe nitrile synthesis[2] followed by Fischer esterification and ester aminolysis.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Ibrahim, F.; Sharaf El-Din, M. K.; Eid, M.; Wahba, M. E. K. (2011). "Spectrofluorimetric Determination Of Some H1 Receptor Antagonist Drugs In Pharmaceutical Formulations And Biological Fluids". International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research 21 (8): 2056–2072. doi:10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.2(8).2056-72.
- ↑ Inglis, J. K. H. (1928). "Ethyl Cyanoacetate". Organic Syntheses 8: 74. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.008.0074.
- ↑ Corson, B. B.; Scott, R. W.; Vose, C. E. (1941). "Cyanoacetamide". Organic Syntheses 1: 179. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.009.0036.
 |

