Astronomy:1999 XS35
From HandWiki
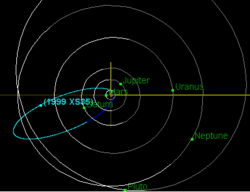 The comet-like orbit of 1999 XS35 | |
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | LONEOS |
| Discovery date | 2 December 1999 |
| Designations | |
| 1999 XS35 | |
| Minor planet category | PHA Apollo[2] |
| Orbital characteristics[2] | |
| Epoch 13 January 2016 (JD 2457400.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 4 | |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 34.711 astronomical unit|AU (5.1927 Tm) (beyond Neptune) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 0.95932 AU (143.512 Gm) |
| 17.835 AU (2.6681 Tm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.94621 |
| Orbital period | 75.32 yr (27512 d) |
| Mean anomaly | 77.641° |
| Mean motion | 0° 0m 47.106s /day (n) |
| Inclination | 19.414° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 49.206° |
| 333.00° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.0181452 AU (2.71448 Gm) |
| TJupiter | 1.407 |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean diameter | 1.3 km (est. at 0.14)[3] |
| Apparent magnitude | 13.7 to 32 |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 17.2[2] |
1999 XS35 is a near-Earth object discovered in 1999 having a comet-like orbit. Its semi-major axis is 17.8 AU. Its orbital eccentricity is 0.94, which means that at the perihelion 1999 XS35 comes as close as 0.9 AU to the Sun, while at the aphelion it reaches beyond the orbit of Neptune.[2] 1999 XS35 is a damocloid. 1999 XS35 is a small object with an absolute magnitude (H) of 17.2, which implies a size of about 1 km.[4]
1999 XS35 came to perihelion on 21 October 1999,[2] passed 0.0453 astronomical unit|AU (6,780,000 km; 4,210,000 mi) from Earth on 5 November 1999,[5] and was discovered on 2 December 1999 at about apparent magnitude 16.9.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "MPEC 1999-X19 : 1999 XS35". IAU Minor Planet Center. 9 December 1999. https://www.minorplanetcenter.net/iau/mpec/J99/J99X19.html. Retrieved 18 April 2012.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: (1999 XS35)". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=1999XS35. Retrieved 29 March 2016.
- ↑ "Asteroid Size Estimator". CNEOS NASA/JPL. https://cneos.jpl.nasa.gov/tools/ast_size_est.html. Retrieved 8 September 2020.
- ↑ Fernández, Yanga R. (2010). "Asteroids with Comet-Like Orbits: Elements and Positions". Archived from the original on 5 June 2010. https://web.archive.org/web/20100605203117/http://www.physics.ucf.edu/~yfernandez/lowtj.html. Retrieved 30 May 2010.
- ↑ "JPL Close-Approach Data: (1999 XS35)". https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=1999XS35;cad=1#cad. Retrieved 18 April 2012.
External links
- 1999 XS35 at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- Ephemeris · Obs prediction · Orbital info · MOID · Proper elements · Obs info · Close · Physical info · NEOCC
- 1999 XS35 at ESA–space situational awareness
- 1999 XS35 at the JPL Small-Body Database
 |

