Astronomy:532 Herculina
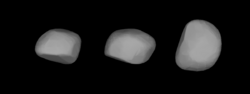 A three-dimensional model of 532 Herculina based on its light curve | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Max Wolf |
| Discovery date | 20 April 1904 |
| Designations | |
| (532) Herculina | |
| Pronunciation | /hɜːrkjʊˈlaɪnə/ |
| 1904 NY | |
| Minor planet category | Main belt |
| Adjectives | Herculinian /hɜːrkjʊˈlɪniən/ |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch 31 July 2016 (JD 2457600.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 111.97 yr (40897 d) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 3.26056 astronomical unit|AU (487.773 Gm) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 2.28601 AU (341.982 Gm) |
| 2.7732838 AU (414.87735 Gm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.1757028 |
| Orbital period | 4.62 yr (1686.9 d) (1684.34607 d) |
| Mean anomaly | 131.03906° |
| Mean motion | 0° 12m 48.272s / day |
| Inclination | 16.31351° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 107.55583° |
| 76.09745° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean diameter | 167.8±0.9 km[2] |
| Mass | ~Template:Value [3] |
| Mean density | ~4 g/cm3[3] |
| Rotation period | 9.405 h (0.3919 d)[1] |
| Geometric albedo | 0.1694±0.007[1] |
| S[1] | |
| Apparent magnitude | 8.82 to 11.99[4] |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 5.81[1] |
| Angular diameter | 0.228" to 0.073" |
532 Herculina /hɜːrkjʊˈlaɪnə/ is a large asteroid, with a diameter of around 200 km.
Discovery
It was discovered on April 20, 1904, by Max Wolf in Heidelberg, and initially catalogued as 1904 NY.[5] The origin of its name is not known; it may be named after the mythical Hercules, given a feminine form as were all asteroids at the time, or after an unknown woman of that name. The bulk of the asteroids discovered by Wolf around this date were named for characters in operas, but if this name was also drawn from such a source, no explanation has been recorded.
Physical characteristics
Herculina is one of the larger members of the main asteroid belt. It is believed to rank among the top 20 in size, but the exact dimensions of many large asteroids are still uncertain. The current estimate for its mass would rank it close to the top 10.
It has often been noted for its complex lightcurves, which made determination of its shape and rotation somewhat difficult. A set of 1982 speckle interferometry observations led to a simple preliminary model of Herculina as a three-axis object, perhaps 260 by 220 by 215 km. 1985 analysis of this data concluded there was a nonspherical shape with one bright spot, whilst a 1987 photometric astrometry study concluded the object was spherical with two dark spots (and rotated around a completely different pole), which was in turn negated by a 1988 thermal study which showed the object could not be spherical. By the late 1980s, the generally accepted model was a three-axis object with major albedo or topographical features.[6]
Recent (2002) modelling of photometric data indicates that Herculina is not spherical, but a blocky shape not unlike a battered cuboid - or, as the analysis described it, it "resembles a toaster". This analysis indicates the presence of multiple largish craters, similar to 253 Mathilde, but no major variation in albedo. The approximate ratios of the axes were suggested as 1:1.1:1.3, broadly consistent with earlier models if slightly more elongated.[7]
Satellites
Following anomalous observations during an occultation of the star SAO 120774 in 1978,[8][9] Herculina became the first asteroid to be "confirmed" to have an asteroid moon, with the parent asteroid estimated at a 216 km diameter and a satellite of about 45 km orbiting at a distance of around 1,000 km.[8] However, careful examination in 1993, using the Hubble Space Telescope, failed to locate a secondary.[10]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 532 Herculina (1904 NY)". https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=532.
- ↑ "Small-Body Database Lookup". https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/tools/sbdb_lookup.html#/?sstr=532&view=OPDCA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Masses and densities of minor planets - Yu. Chernetenko, O. Kochetova, and V. Shor
- ↑ "Bright Minor Planets 2005". Minor Planet Center. http://www.cfa.harvard.edu/iau/Ephemerides/Bright/2005.
- ↑ Provisional elements of the minor planet 1904 NY. J. C. Hammond, Astronomical Journal, vol. 24, iss. 564, p. 105–105 (1904) ADS archive copy
- ↑ Speckle interferometry of asteroids (NASA CR-180438). J. Drummond, Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, May 31, 1988
- ↑ Models of Twenty Asteroids from Photometric Data. M. Kaasalainen, J. Torppa, and J. Piironen, Icarus 159, 369–395 (2002).
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Dunham, David W. (1978). "Satellite of Minor Planet 532 Herculina Discovered During Occultation". The Minor Planet Bulletin 6: 6–13. Bibcode: 1978MPBu....6...13D.
- ↑ "Satellites and Companions of Minor Planets". IAU / Minor Planet Center. 2009-09-17. http://www.cbat.eps.harvard.edu/minorsats.html.
- ↑ Storrs, Alex; Weiss, Ben; Zellner, Ben; Burleson, Win; Sichitiu, Rukmini; Wells, Eddie; Kowal, Charles; Tholen, David (1999). "Imaging observations of asteroids with Hubble Space Telescope". Icarus 137 (2): 260–268. doi:10.1006/icar.1999.6047. Bibcode: 1999Icar..137..260S. http://scripts.mit.edu/~paleomag/articles/Storrs_1999_Icarus.pdf.
External links
- 532 Herculina at AstDyS-2, Asteroids—Dynamic Site
- 532 Herculina at the JPL Small-Body Database
 |

