Astronomy:673 Edda
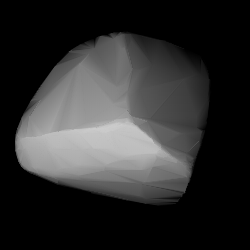 Modelled shape of Edda from its lightcurve | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Joel Hastings Metcalf |
| Discovery site | Taunton, Massachusetts |
| Discovery date | 20 September 1908 |
| Designations | |
| (673) Edda | |
| Pronunciation | /ˈɛdə/[1] |
| 1908 EA | |
| Orbital characteristics[2] | |
| Epoch 31 July 2016 (JD 2457600.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 107.57 yr (39290 d) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 2.8471 astronomical unit|AU (425.92 Gm) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 2.7821 AU (416.20 Gm) |
| 2.8146 AU (421.06 Gm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.011542 |
| Orbital period | 4.72 yr (1,724.7 d) 4.72 yr (1724.7 d) |
| Mean anomaly | 199.04° |
| Mean motion | 0° 12m 31.428s / day |
| Inclination | 2.8770° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 226.723° |
| 236.303° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean radius | 18.765±0.5 km |
| Rotation period | 22.340 h (0.9308 d) |
| Geometric albedo | 0.1044±0.006 |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 10.20 |
673 Edda is a minor planet orbiting the Sun. It was discovered 20 September 1908 by the American astronomer Joel Hastings Metcalf, and was named for the Norse Edda literary works. The name may also have been inspired by the asteroid's provisional designation 1908 EA.[3] This asteroid is orbiting at a distance of 2.81 astronomical unit|AU with a period of 4.72 yr and an eccentricity of 0.012.[2] The orbit is close to a 5:2 mean motion resonance with Jupiter, which is located at 2.824 astronomical unit|AU.[4]
The long rotation period and low brightness amplitude of this asteroid make it more challenging for measurement of the rotation period. An extensive photometry campaign in 2015 provided a period of 22.340±0.004 h. The unusual light curve suggests that the asteroid shape is very asymmetric.[5] It is a stony S-type asteroid that spans a mean diameter of 38+6
−2 km.[6]
References
- ↑ Noah Webster (1884) A Practical Dictionary of the English Language
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "673 Edda (1908 EA)". JPL Small-Body Database. NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory. https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=673.
- ↑ Schmadel, Lutz D. (2013), Dictionary of Minor Planet Names, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, p. 105, ISBN 9783662028049, https://books.google.com/books?id=2lzoCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA105.
- ↑ Hahn, G. et al. (June 1991), "Orbital evolution studies of asteroids near the 5:2 mean motion resonance with Jupiter", Astronomy and Astrophysics 246 (2): 603–618, Bibcode: 1991A&A...246..603H.
- ↑ Marciniak, Anna et al. (June 2016), Różańska, Agata; Bejger, M., eds., "Difficult cases in photometric studies of asteroids", Proceedings of the Polish Astronomical Society 3: 84–87, Bibcode: 2016pas..conf...84M.
- ↑ Marciniak, A. et al. (May 2019), "Thermal properties of slowly rotating asteroids: results from a targeted survey", Astronomy & Astrophysics 625: 40, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201935129, A139, Bibcode: 2019A&A...625A.139M.
External links
- 673 Edda at AstDyS-2, Asteroids—Dynamic Site
- 673 Edda at the JPL Small-Body Database
 |

