Astronomy:TYC 9486-927-1
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Octans |
| Right ascension | 21h 25m 27.4899s[2] |
| Declination | −81° 38′ 27.673″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 11.5 - 12.0[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M1 V[4] |
| Variable type | BY Dra[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 8.7±4.6[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: 59.843 mas/yr Dec.: −107.723 mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 29.2836 ± 0.0690[5] mas |
| Distance | 111.4 ± 0.3 ly (34.15 ± 0.08 pc) |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.53[6] M☉ |
| Radius | 0.46[7] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 0.032[7] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.3[8] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,490[9] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −1.3[8] dex |
| Rotation | 0.541945[3] days |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 43.5±1.2[9] km/s |
| Age | 10-45[9] Myr |
| Other designations | |
2MASS J21252752-8138278, FT Octantis | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
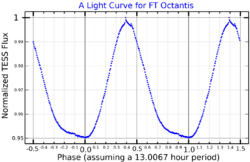
TYC 9486-927-1 (also known as 2MASS J21252752-8138278) is the primary of a possible trinary star system located at a distance of 26.7 parsecs from Earth in the southern direction in the constellation of Octans. It is a BY Draconis variable, with large starspots causing it to change brightness as it rotates every 13 hours.[3]
TYC 9486-927-1 has rapid rotation and coronal and chromospheric activity suggestive of a young age. Observations and multi-epoch radial velocity data suggest that TYC 9486-927-1 is a single, rapidly rotating star rather than a spectroscopic or tight visual binary. However, it is still possible that TYC 9486-927-1 is an equal mass binary with a face-on orbit and close separation.[4]
The candidate secondary stellar companion is 2MASS J21121598–8128452. It is a red dwarf star of spectral class M5.5. Its projected separation from the primary would be 62,700 AU. The candidate tertiary companion is 2MASS J21192028–8145446 - of spectral class M6 or M7 and at a projected separation of 31,000 AU from the primary.[6]:7
Planetary system
The planet 2MASS J21265040-8140293 orbits TYC 9486-927-1 at a projected separation of 7400 AU.[6] With a mass from 11.6 to 15 Jupiter masses, it is considered to be either a brown dwarf, or a giant planet.[10][11]
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (days) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2MASS J2126–8140/b | 13.3 (± 1.7)[12] MJ | 6,900[9] | 328 725 000[citation needed] | — | — | — |
References
- ↑ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. https://mast.stsci.edu/portal/Mashup/Clients/Mast/Portal.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Zacharias, N.; Finch, C. T.; Girard, T. M.; Henden, A.; Bartlett, J. L.; Monet, D. G.; Zacharias, M. I. (2012). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: UCAC4 Catalogue (Zacharias+, 2012)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: I/322A. Originally Published in: 2012yCat.1322....0Z; 2013AJ....145...44Z 1322. Bibcode: 2012yCat.1322....0Z.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Samus, N. N. et al. (2017). "General Catalogue of Variable Stars". Astronomy Reports. 5.1 61 (1): 80–88. doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085. Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Torres, C. A. O.; Quast, G. R.; Da Silva, L.; de la Reza, R.; Melo, C. H. F.; Sterzik, M. (2006). "Search for associations containing young stars (SACY). I. Sample and searching method". Astronomy and Astrophysics 460 (3): 695. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065602. Bibcode: 2006A&A...460..695T.
- ↑ Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Jones, H R A.; Caballero, J. A.; Beamín, J. C.; Barrado, D.; Sarro, L. M.; Marocco, F.; Smart, R. L. (2019), "The Gaia Ultra-Cool Dwarf Sample – II: Structure at the end of the main sequence", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 485 (3): 4423–4440, doi:10.1093/mnras/stz678, Bibcode: 2019MNRAS.485.4423S
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Gaidos, E. et al. (September 2014). "Trumpeting M dwarfs with CONCH-SHELL: a catalogue of nearby cool host-stars for habitable exoplanets and life". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 443 (3): 2561–2578. doi:10.1093/mnras/stu1313. Bibcode: 2014MNRAS.443.2561G.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Steinmetz, M. et al. (2020). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: RAVE 6th data release (Steinmetz+, 2020)". Vizier Online Data Catalog. Bibcode: 2020yCat.3283....0S.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 Deacon, N. R.; Schlieder, J. E.; Murphy, S. J. (2016). "A nearby young M dwarf with a wide, possibly planetary-mass companion". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 457 (3): 3191. doi:10.1093/mnras/stw172. Bibcode: 2016MNRAS.457.3191D.
- ↑ Gagné, Jonathan; Lafrenière, David; Doyon, René; Malo, Lison; Artigau, Étienne (2014). "BANYAN. II. Very Low Mass and Substellar Candidate Members to Nearby, Young Kinematic Groups with Previously Known Signs of Youth". The Astrophysical Journal 783 (2): 121. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/783/2/121. Bibcode: 2014ApJ...783..121G.
- ↑ Reid, I. Neill; Cruz, Kelle L.; Kirkpatrick, J. Davy; Allen, Peter R.; Mungall, F.; Liebert, James; Lowrance, Patrick; Sweet, Anne (2008). "Meeting the Cool Neighbors. X. Ultracool Dwarfs from the 2MASS All-Sky Data Release". The Astronomical Journal 136 (3): 1290. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/136/3/1290. Bibcode: 2008AJ....136.1290R.
- ↑ "Planet 2MASS J2126-8140". Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia. https://exoplanet.eu/catalog/2m_j2126_81_b--2544/.
 |