Biology:Collagen hybridizing peptide

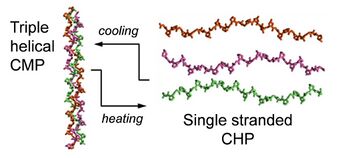
A collagen hybridizing peptide (CHP) is a synthetic peptide sequence with typically 6 to 10 repeating units of the Gly-Xaa-Yaa amino acid triplet, which mimics the hallmark sequence of natural collagens.[1][2] A CHP peptide usually possesses a high content of Proline and Hydroxyproline in the Xaa and Yaa positions, which confers it a strong propensity to form the collagen’s unique triple helix conformation.[1][3] In the single-stranded (monomeric) status, the peptide can recognize denatured collagen strands in tissues by forming a hybridized triple helix with the collagen strands.[2] This occurs via the triple helical chain assembly and inter-chain hydrogen bonding, in a manner similar to primers binding to melted DNA strands during PCR.[4] The binding does not depend on a specific sequence or epitope on collagen, enabling CHPs to target denatured collagen chains of different types.[5][6]
Collagen, CHP, CMP, and CLP
Collagen is the main component of the extracellular matrix (ECM).[7] The collagen superfamily consists of 28 different types of collagen.[7] Although the function and hierarchical structure of these collagens may vary, they all shall the defining structural feature known as the triple helix,[1] where three left handed polyproline II-type (PPII) helices assemble to form a right-handed supercoiled helical motif.[1][8] Short synthetic peptides known as collagen mimetic peptides (CMPs) or collagen-like peptides (CLPs) have played a major role in elucidating the 3D structure of the collagen triple helix, its folding kinetics, and thermal stability as small triple helical models.[3][9][10][11] CMPs, CLPs, and CHPs are all very similar in terms of their amino acid sequences but only when CMPs or CLPs are heated above their melting temperatures, do they exist in the dissociated, single-stranded state and can be considered as CHPs.[2]
Binding mechanism
Single-stranded CHPs bind to denatured collagen chains and gelatin in a manner that is unique from other targeting mechanisms, in that they specifically recognize a unique structural motif (collagen triple helix) for folding and chain assembly, as opposed to specific epitopes binding that is seen for monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), for example.[12] Due to their unique targeting mechanism, CHPs have a high binding specificity towards denatured collagen chains but have almost no affinity for intact (triple helical) collagen.[13] CHPs can broadly target collagen chains that have been denatured by thermal,[13] chemical,[14] mechanical,[15] or enzymatic processes,[13] as well as multiple collagen types (e.g., Col I, II, IV).[5][6] Studies also showed CHPs and their fluorophore conjugates have superior stability in contact with serum.[16]
Denatured collagen as a biomarker for tissue remodelling and damage
Controlled collagen turnover is crucial for embryonic development, organ morphogenesis, as well as tissue maintenance and repair.[17] However, changes of collagen homeostasis are associated with numerous diseases and pathological conditions. Excessive collagen degradation may be associated with cancer metastasis, skin ageing, arthritis, and osteoporosis.[17] CHPs can target tissues undergoing remodelling based on their ability to bind to degraded and unfolded collagen strands through triple helix formation. As a targeting moiety, CHPs offer great potential in histopathology, diagnostics, and drug delivery for a wide range of diseases.
Most methods for the evaluation of collagen denaturation in disease states are indirect, such as detecting matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activity or quantifying collagen peptide fragments in urine, serum, or synovial fluid.[18][19][20] Using conventional methods for directly targeting collagen, researchers have to relied on collagen binding peptides selected by phage display,[21] derived from collagen binding proteins,[22] or antibodies raised against collagens. Unfortunately, these compounds cannot target denatured collagens which are unstructured and do not present a defined 3D epitope. In addition, antibodies that were reported to distinguish specific degraded collagen fragments can only recognize one or few collagen types.[2][23] In contrast, CHPs, in principle, can bind to all types of denatured collagens.[4][5][6]
Applications
Tissue staining
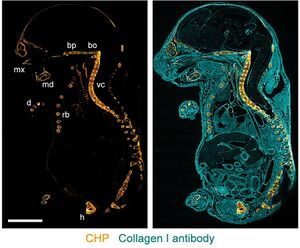
Fluorophore- or biotin-labeled CHPs are used as a staining agent for detecting collagen degradation and denaturation via immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry applications.[5] CHPs can stain frozen tissue sections, formalin-fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) sections,[5] as well as fresh tissues.[14][15] CHP is applicable to tissue specimens from multiple species and a range of diseases, such as myocardial infarction, arthritis, nephritis, and fibrosis.[5]
In vivo imaging
CHPs can also be labelled with near-infrared fluorophores for in vivo fluorescent imaging.[13][24]
Collagen identification
CHPs can be used for visualizing many different types of collagen bands in SDS-PAGE gels.[6] Collagen is denatured by heating in the presence of SDS prior to loading the gel. The collagen bands are visualized through CHP-collagen hybridization when the gels are stained by fluorescently-labeled CHPs.[6]
Detecting mechanical damage to connective tissue
Collagen offers mechanical strength in load bearing tissues in the body such as tendons, ligaments, and bone. As forces are applied to these tissues, the collagen triple helix can be damaged and unwind, and CHPs allow for molecular level detection of mechanical damage in such connective tissues.[15][25]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Shoulders, Matthew D.; Raines, Ronald T. (2009). "Collagen structure and stability". Annual Review of Biochemistry 78: 929–958. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.77.032207.120833. ISSN 1545-4509. PMID 19344236.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Wahyudi, Hendra; Reynolds, Amanda A.; Li, Yang; Owen, Shawn C.; Yu, S. Michael (October 2016). "Targeting collagen for diagnostic imaging and therapeutic delivery". Journal of Controlled Release 240: 323–331. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.01.007. PMID 26773768.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Persikov, A. V.; Ramshaw, J. A.; Kirkpatrick, A.; Brodsky, B. (2000-12-05). "Amino acid propensities for the collagen triple-helix". Biochemistry 39 (48): 14960–14967. doi:10.1021/bi001560d. ISSN 0006-2960. PMID 11101312.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Li, Yang; Yu, S. Michael (December 2013). "Targeting and mimicking collagens via triple helical peptide assembly". Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 17 (6): 968–975. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.10.018. ISSN 1879-0402. PMID 24210894.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Hwang, Jeongmin; Huang, Yufeng; Burwell, Timothy J.; Peterson, Norman C.; Connor, Jane; Weiss, Stephen J.; Yu, S. Michael; Li, Yang (2017-10-24). "In Situ Imaging of Tissue Remodeling with Collagen Hybridizing Peptides". ACS Nano 11 (10): 9825–9835. doi:10.1021/acsnano.7b03150. ISSN 1936-0851. PMID 28877431.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 Li, Yang; Ho, Daniel; Meng, Huan; Chan, Tania R.; An, Bo; Yu, Hanry; Brodsky, Barbara; Jun, Albert S. et al. (2013-01-16). "Direct Detection of Collagenous Proteins by Fluorescently Labeled Collagen Mimetic Peptides". Bioconjugate Chemistry 24 (1): 9–16. doi:10.1021/bc3005842. ISSN 1043-1802. PMID 23253177.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Birk, David E.; Bruckner, Peter (2005-04-12), "Collagen Suprastructures", Topics in Current Chemistry (Springer Berlin Heidelberg): pp. 185–205, doi:10.1007/b103823, ISBN 9783540232728
- ↑ Engel, Jürgen; Bächinger, Hans Peter (2005-04-12), "Structure, Stability and Folding of the Collagen Triple Helix", Topics in Current Chemistry (Springer Berlin Heidelberg): pp. 7–33, doi:10.1007/b103818, ISBN 9783540232728
- ↑ Boudko, Sergei; Frank, Sabine; Kammerer, Richard A.; Stetefeld, Jörg; Schulthess, Therese; Landwehr, Ruth; Lustig, Ariel; Bächinger, Hans Peter et al. (March 2002). "Nucleation and propagation of the collagen triple helix in single-chain and trimerized peptides: transition from third to first order kinetics". Journal of Molecular Biology 317 (3): 459–470. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2002.5439. ISSN 0022-2836. PMID 11922677.
- ↑ Bächinger, Hans Peter; Morris, Nicholas P.; Davis, Janice M. (1993-01-15). "Thermal stability and folding of the collagen triple helix and the effects of mutations in osteogenesis imperfecta on the triple helix of type I collagen". American Journal of Medical Genetics 45 (2): 152–162. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320450204. ISSN 0148-7299. PMID 8456797.
- ↑ Holmgren, Steven K.; Taylor, Kimberly M.; Bretscher, Lynn E.; Raines, Ronald T. (April 1998). "Code for collagen's stability deciphered". Nature 392 (6677): 666–667. doi:10.1038/33573. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 9565027.
- ↑ Xu, Jingsong; Rodriguez, Dorothy; Kim, Jenny J.; Brooks, Peter C. (October 2000). "Generation of Monoclonal Antibodies to Cryptic Collagen Sites by Using Subtractive Immunization". Hybridoma 19 (5): 375–385. doi:10.1089/02724570050198893. ISSN 0272-457X. PMID 11128027.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 Li, Y.; Foss, C. A.; Summerfield, D. D.; Doyle, J. J.; Torok, C. M.; Dietz, H. C.; Pomper, M. G.; Yu, S. M. (2012-08-27). "Targeting collagen strands by photo-triggered triple-helix hybridization". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 109 (37): 14767–14772. doi:10.1073/pnas.1209721109. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 22927373.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Hwang, Jeongmin; San, Boi Hoa; Turner, Neill J.; White, Lisa J.; Faulk, Denver M.; Badylak, Stephen F.; Li, Yang; Yu, S. Michael (April 2017). "Molecular assessment of collagen denaturation in decellularized tissues using a collagen hybridizing peptide". Acta Biomaterialia 53: 268–278. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2017.01.079. ISSN 1742-7061. PMID 28161576.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Weiss, Jeffrey A.; Yu, S. Michael; Buehler, Markus J.; Reese, Shawn P.; Depalle, Baptiste; San, Boi Hoa; Qin, Zhao; Li, Yang et al. (2017-03-22). "Molecular level detection and localization of mechanical damage in collagen enabled by collagen hybridizing peptides". Nature Communications 8: 14913. doi:10.1038/ncomms14913. ISSN 2041-1723. PMID 28327610.
- ↑ Bennink, Lucas L.; Smith, Daniel J.; Foss, Catherine A.; Pomper, Martin G.; Li, Yang; Yu, S. Michael (2017-05-08). "High Serum Stability of Collagen Hybridizing Peptides and Their Fluorophore Conjugates". Molecular Pharmaceutics 14 (6): 1906–1915. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.7b00009. ISSN 1543-8384. PMID 28445649.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Bonnans, Caroline; Chou, Jonathan; Werb, Zena (December 2014). "Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease". Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 15 (12): 786–801. doi:10.1038/nrm3904. ISSN 1471-0072. PMID 25415508.
- ↑ Nemirovskiy, O.V.; Dufield, D.R.; Sunyer, T.; Aggarwal, P.; Welsch, D.J.; Mathews, W.R. (February 2007). "Discovery and development of a type II collagen neoepitope (TIINE) biomarker for matrix metalloproteinase activity: From in vitro to in vivo". Analytical Biochemistry 361 (1): 93–101. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2006.10.034. PMID 17187753.
- ↑ Garvican, Elaine R.; Vaughan-Thomas, Anne; Innes, John F.; Clegg, Peter D. (July 2010). "Biomarkers of cartilage turnover. Part 1: Markers of collagen degradation and synthesis". The Veterinary Journal 185 (1): 36–42. doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2010.04.011. PMID 20488735.
- ↑ Rousseau, Jean-Charles; Delmas, Pierre D (June 2007). "Biological markers in osteoarthritis". Nature Clinical Practice Rheumatology 3 (6): 346–356. doi:10.1038/ncprheum0508. ISSN 1745-8382. PMID 17538566.
- ↑ Helms, Brett A.; Reulen, Sanne W. A.; Nijhuis, Sebastiaan; Graaf-Heuvelmans, Peggy T. H. M. de; Merkx, Maarten; Meijer, E. W. (2009-08-26). "High-Affinity Peptide-Based Collagen Targeting Using Synthetic Phage Mimics: From Phage Display to Dendrimer Display". Journal of the American Chemical Society 131 (33): 11683–11685. doi:10.1021/ja902285m. ISSN 0002-7863. PMID 19642697.
- ↑ Liang, Hui; Li, Xiaoran; Chen, Bing; Wang, Bin; Zhao, Yannan; Zhuang, Yan; Shen, He; Zhang, Zhijun et al. (July 2015). "A collagen-binding EGFR single-chain Fv antibody fragment for the targeted cancer therapy". Journal of Controlled Release 209: 101–109. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.04.029. PMID 25916496.
- ↑ Freimark, Bruce; Clark, Derek; Pernasetti, Flavia; Nickel, Jeff; Myszka, David; Baeuerle, Patrick A.; Van Epps, Dennis (July 2007). "Targeting of humanized antibody D93 to sites of angiogenesis and tumor growth by binding to multiple epitopes on denatured collagens". Molecular Immunology 44 (15): 3741–3750. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2007.03.027. PMID 17507095.
- ↑ Bennink, Lucas L.; Li, Yang; Kim, Bumjin; Shin, Ik Jae; San, Boi Hoa; Zangari, Maurizio; Yoon, Donghoon; Yu, S.Michael (November 2018). "Visualizing collagen proteolysis by peptide hybridization: From 3D cell culture to in vivo imaging". Biomaterials 183: 67–76. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.08.039. PMID 30149231.
- ↑ Converse, Matthew I.; Walther, Raymond G.; Ingram, Justin T.; Li, Yang; Yu, S. Michael; Monson, Kenneth L. (2018-02-01). "Detection and characterization of molecular-level collagen damage in overstretched cerebral arteries". Acta Biomaterialia 67: 307–318. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2017.11.052. ISSN 1742-7061. PMID 29225149.