Biology:Enolase 2
 Generic protein structure example |
Gamma-enolase, also known as enolase 2 (ENO2) or neuron specific enolase (NSE), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ENO2 gene.[1][2] Gamma-enolase is a phosphopyruvate hydratase.
Gamma-enolase is one of the three enolase isoenzymes found in mammals. This isoenzyme, a homodimer, is found in mature neurons and cells of neuronal origin. A switch from alpha enolase to gamma enolase occurs in neural tissue during development in rats and primates.[1]
Interactive pathway map
Utility
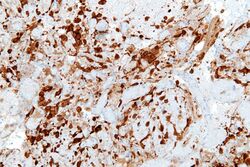
Detection of NSE with antibodies can be used to identify neuronal cells and cells with neuroendocrine differentiation. NSE is produced by small-cell carcinomas, which are neuroendocrine in origin. NSE is therefore a useful tumor marker for distinguishing small-cell carcinomas from other tumors.[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "ENO2 enolase 2 (gamma, neuronal)". NCBI Entrez Gene database. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=2026.
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) Enolase 2 -131360
- ↑ "Molecular characterization of prostatic small-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma". Prostate 55 (1): 55–64. April 2003. doi:10.1002/pros.10217. PMID 12640661.
Further reading
- "Complete structure of the human gene encoding neuron-specific enolase.". Genomics 10 (1): 157–65. 1991. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(91)90496-2. PMID 2045099.
- "Localisation of neurone-specific enolase (ENO2) to 12p13.". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 54 (1–2): 71–3. 1991. doi:10.1159/000132960. PMID 2249478.
- Oliva D; Barba G; Barbieri G; Giallongo, A; Feo, S (1989). "Cloning, expression and sequence homologies of cDNA for human gamma enolase". Gene 79 (2): 355–60. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(89)90217-5. PMID 2792767.
- McAleese SM; Dunbar B; Fothergill JE; Hinks, Lesley J.; Day, Ian N.M. (1989). "Complete amino acid sequence of the neurone-specific gamma isozyme of enolase (NSE) from human brain and comparison with the non-neuronal alpha form (NNE)". Eur. J. Biochem. 178 (2): 413–7. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14465.x. PMID 3208766.
- Van Obberghen E; Kamholz J; Bishop JG; Zomzely-Neurath, C.; Lazzarini, R. A.; Lazzarini, RA (1988). "Human gamma enolase: isolation of a cDNA clone and expression in normal and tumor tissues of human origin". J. Neurosci. Res. 19 (4): 450–6. doi:10.1002/jnr.490190409. PMID 3385803.
- "Sequence conservation in the 3'-untranslated regions of neurone-specific enolase, lymphokine and protooncogene mRNAs". FEBS Lett. 222 (1): 139–43. 1987. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(87)80207-7. PMID 3653393.
- Haimoto H; Takahashi Y; Koshikawa T; Nagura, H; Kato, K (1985). "Immunohistochemical localization of gamma-enolase in normal human tissues other than nervous and neuroendocrine tissues". Lab. Invest. 52 (3): 257–63. PMID 3974199.
- Quan CP; Watanabe S; Vuillier F; Pires, R; Matsuo, T; Stanislawski, M; Pillot, J; Bouvet, JP (1993). "Purification and partial amino acid sequence of suppressive lymphokine from a CD8+ CD57+ human T hybridoma". Immunology 78 (2): 205–9. PMID 7682534.
- Angelov DN; Neiss WF; Gunkel A; Guntinas-Lichius, O.; Stennert, E. (1994). "Axotomy induces intranuclear immunolocalization of neuron-specific enolase in facial and hypoglossal neurons of the rat". J. Neurocytol. 23 (4): 218–33. doi:10.1007/BF01275526. PMID 8035205.
- "Detection of neuron-specific gamma-enolase messenger ribonucleic acid in normal human leukocytes by polymerase chain reaction amplification with nested primers". Lab. Invest. 69 (6): 743–9. 1994. PMID 8264236.
- Ansari-Lari MA; Shen Y; Muzny DM; Lee, W; Gibbs, R A (1997). "Large-scale sequencing in human chromosome 12p13: experimental and computational gene structure determination". Genome Res. 7 (3): 268–80. doi:10.1101/gr.7.3.268. PMID 9074930.
- Lau L (2002). "Neuroblastoma: a single institution's experience with 128 children and an evaluation of clinical and biological prognostic factors". Pediatric Hematology and Oncology 19 (2): 79–89. doi:10.1080/08880010252825669. PMID 11881792.
- Wijnberger LD; Nikkels PG; van Dongen AJ; Noorlander, Cornelle W.; Mulder, Eduard J.H.; Schrama, Loes H.; Visser, Gerard H.A. (2002). "Expression in the placenta of neuronal markers for perinatal brain damage". Pediatr. Res. 51 (4): 492–6. doi:10.1203/00006450-200204000-00015. PMID 11919335.
- O'Dwyer DT; Clifton V; Hall A; Smith, R.; Robinson, P.J.; Crock, P.A. (2002). "Pituitary autoantibodies in lymphocytic hypophysitis target both gamma- and alpha-Enolase - a link with pregnancy?". Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 110 (1–2): 94–8. doi:10.1076/apab.110.1.94.897. PMID 11935405.
- Chekhonin VP; Zhirkov YA; Belyaeva IA; Ryabukhin, Igor A; Gurina, Olga I; Dmitriyeva, Tatiana B (2002). "Serum time course of two brain-specific proteins, alpha(1) brain globulin and neuron-specific enolase, in tick-born encephalitis and Lyme disease". Clin. Chim. Acta 320 (1–2): 117–25. doi:10.1016/S0009-8981(02)00057-8. PMID 11983209.
- Nakatsuka S; Nishiu M; Tomita Y; Miwa, H; Takakuwa, T; Iuchi, K; Yamamoto, S; Aozasa, K (2005). "Enhanced expression of neuron-specific enolase (NSE) in pyothorax-associated lymphoma (PAL)". Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 93 (4): 411–6. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2002.tb01272.x. PMID 11985791.
- Fujiwara H; Arima N; Ohtsubo H; Matsumoto, Tadashi; Kukita, Toshimasa; Kawada, Hideaki; Imaizumi, Rie; Ozaki, Atsuo et al. (2002). "Clinical significance of serum neuron-specific enolase in patients with adult T-cell leukemia". Am. J. Hematol. 71 (2): 80–4. doi:10.1002/ajh.10190. PMID 12353304.
- Strausberg RL; Feingold EA; Grouse LH; Derge, JG; Klausner, RD; Collins, FS; Wagner, L; Shenmen, CM et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMID 12477932. Bibcode: 2002PNAS...9916899M.
- Rodríguez-Núñez A; Cid E; Rodríguez-García J; Camiña, F; Rodríguez-Segade, S; Castro-Gago, M (2003). "Neuron-specific enolase, nucleotides, nucleosides, purine bases, oxypurines and uric acid concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid of children with meningitis". Brain Dev. 25 (2): 102–6. doi:10.1016/S0387-7604(02)00160-2. PMID 12581805.
- Muley T; Ebert W; Stieber P; Raith, Hannelore; Holdenrieder, Stefan; Nagel, Dorothea; Fürst, Heinrich; Roth, Hans-Jürgen et al. (2003). "Technical performance and diagnostic utility of the new Elecsys neuron-specific enolase enzyme immunoassay". Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 41 (1): 95–103. doi:10.1515/CCLM.2003.017. PMID 12636057. https://epub.ub.uni-muenchen.de/17836/1/cclm.2003.017.pdf.
External links
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P09104 (Human Gamma-enolase) at the PDBe-KB.
 |



