Biology:Neuroptera
| Neuroptera | |
|---|---|

| |
| Green lacewing | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Clade: | Neuropterida |
| Order: | Neuroptera Linnaeus, 1758 |
| clades | |
|
See Taxonomy | |
The insect order Neuroptera, or net-winged insects, includes the lacewings, mantidflies, antlions, and their relatives. The order consists of some 6,000 species.[1] Neuroptera is grouped together with the Megaloptera (alderflies, fishflies, and dobsonflies) and Raphidioptera (snakeflies) in the unranked taxon Neuropterida (once known as Planipennia).
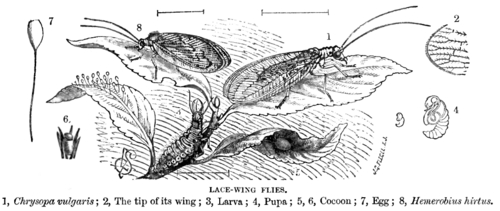
Adult neuropterans have four membranous wings, all about the same size, with many veins. They have chewing mouthparts, and undergo complete metamorphosis.
Neuropterans first appeared during the Permian period, and continued to diversify through the Mesozoic era.[2] During this time, several unusually large forms evolved, especially in the extinct family Kalligrammatidae, often called "the butterflies of the Jurassic" for their large, patterned wings.[3]
Anatomy and biology
Neuropterans are soft-bodied insects with relatively few specialized features. They have large lateral compound eyes, and may or may not also have ocelli. Their mouthparts have strong mandibles suitable for chewing, and lack the various adaptations found in most other holometabolan insect groups.
They have four wings, usually similar in size and shape, and a generalised pattern of veins.[4] Some neuropterans have specialised sense organs in their wings, or have bristles or other structures to link their wings together during flight.[5]
The larvae are specialised predators, with elongated mandibles adapted for piercing and sucking. The larval body form varies between different families, depending on the nature of their prey. In general, however, they have three pairs of thoracic legs, each ending in two claws. The abdomen often has adhesive discs on the last two segments.[5]
Life cycle and ecology
 |
 |
The larvae of most families are predators. Many chrysopids, hemerobiids and coniopterygids eat aphids and other pest insects, and some have been used for biological control (either from commercial distributors, but also abundant and widespread in nature).[6][7]
Larvae in various families cover themselves in debris (including other insects, living and dead[8]) as camouflage, taken to an extreme in the ant lions, which bury themselves completely out of sight and ambush prey from "pits" in the soil. Larvae of some Ithonidae are root feeders, and larvae of Sisyridae are aquatic, and feed on freshwater sponges. A few mantispids are parasites of spider egg sacs.
As in other holometabolic orders, the pupal stage is enclosed in some form of cocoon composed of silk and soil or other debris. The pupa eventually cuts its way out of the cocoon with its mandibles, and may even move about for a short while before undergoing the moult to the adult form.[5]
Adults of many groups are also predatory, but some do not feed, or consume only nectar.
Beetles, wasps, and some lake flies parasitize neuropteran larvae.
Evolution

Neuropterans first appeared near the end of the Permian period, as shown by fossils of the Permithonidae from the Tunguska basin in Siberia and a similar fauna from Australia.[2]

The osmylids are of Jurassic or Early Cretaceous origin and may be the most ancient of the Neuropteran groups.[9] The extinct osmylid Protosmylus is fossilized in middle Eocene Baltic amber.[10] The genus Burmaleon is described from two fossils of Cenomanian age Burmese amber, implying crown group radiation in the Early Cretaceous or earlier.[11][12] The family Kalligrammatidae lived from the Jurassic to Aptian (Lower Cretaceous) periods.[13]
Ithonidae are from the Jurassic to Recent, and the extinct lineages of the family were widespread geographically.[14]
Phylogeny
Molecular analysis in 2018 using mitochondrial rRNA and mitogenomic data places the Megaloptera as sister to Neuroptera, and Raphidioptera as sister to this combined lineage, though these results were considered tentative.[15][9] The fossil record has contributed to the understanding of the group's phylogeny.[1][16][17][18] Relationships within the Myrmeleontiformia are still in flux.[19]
A phylogenomic analysis published in 2023 confirmed the topology of the neuropterid orders and found the relationships between the families of Neuropterida as shown in the following phylogenetic tree.[20]
| Neuropterida |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Taxonomy
Review of the Neropterid group orders by Engel, Winterton, and Breitkreuz (2018) included grouping of the Neuropteran families in a nested set of clades, an abandonment of the paraphyletic suborder "Hemerobiiformia" and redefinition of Myrmeleontiformia as a clade.[21]
Neuroptera
- Superfamily Coniopterygoidea
- family Coniopterygidae dustywings (Late Jurassic-Present)
- Clade Euneuroptera
- Superfamily Osmyloidea
- Family Osmylidae: osmylids (Early Jurassic-Present)
- Family Sisyridae: spongillaflies (Late Cretaceous-Present)
- Family Nevrorthidae [Note 1] (Late Cretaceous-Present)
- Family †Archeosmylidae (Permian-Triassic)
- Family †Saucrosmylidae (Middle Jurassic)
- Superfamily Dilaroidea
- Family Dilaridae: pleasing lacewings (Late Cretaceous-Present)
- Superfamily Mantispoidea
- Family Berothidae: beaded lacewings (Late Jurassic-Present)
- Family Mantispidae: mantidflies (including †Dipteromantispidae) (Jurassic-Present)
- Family †Mesoberothidae (including †Mesithonidae) (Triassic)
- Family Rhachiberothidae: thorny lacewings (Early Cretaceous-Recent)
- Clade Neoneuroptera
- Superfamily Hemerobioidea (inc. Chrysopoidea)
- Family †Ascalochrysidae
- Family Chrysopidae: green lacewings (including †Mesochrysopidae)
- Family Hemerobiidae: brown lacewings
- Family †Osmylitidae
- Family †Solenoptilidae
- Clade Geoneuroptera
- Superfamily Ithonioidea
- Family Ithonidae: moth lacewings (includes Rapismatidae and Polystoechotidae)
- Clade Myrmeleontiformia
- Superfamily Myrmeleontoidea (syn Nemopteroidea[22])
- Family Ascalaphidae: owlflies
- Family †Babinskaiidae
- Family Myrmeleontidae: antlions (includes Palaeoleontidae)
- Family Nemopteridae: spoonwings etc
- Family Nymphidae: split-footed lacewings (includes Myiodactylidae)
- Family †Rafaelianidae
- Superfamily Psychopsoidea
- Family †Aetheogrammatidae
- Family †Kalligrammatidae
- Family †Osmylopsychopidae (syn †Brongniartiellidae)
- Family †Panfiloviidae (syn †Grammosmylidae)
- Family †Prohemerobiidae
- Family Psychopsidae: silky lacewings
- Superfamily Myrmeleontoidea (syn Nemopteroidea[22])
- Superfamily Ithonioidea
- Superfamily Hemerobioidea (inc. Chrysopoidea)
- Superfamily Osmyloidea
The fossil genus †Mesohemerobius Ping, 1928 from the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous of China has been treated as incertae sedis within Neuroptera, while the fossil families †Permoberothidae and †Permithonidae are treated as a sister group to clade Eidoneuroptera formed by Neuroptera + Megaloptera.[21]
In human culture
The use of Neuroptera in biological control of insect pests has been investigated, showing that it is difficult to establish and maintain populations in fields of crops.[23]
Five species of Neuroptera are among 1681 insect species eaten by humans worldwide.[24]
The New Guinea Highland people claim to be able to maintain a muscular build and great stamina despite their low protein intake as a result of eating insects including Neuroptera.[25]
Notes
- ↑ "Neurorthidae" is a lapsus.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 David Grimaldi & Michael S. Engel (2005). Evolution of the Insects. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-82149-5.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 A. G. Ponomarenko; D. E. Shcherbakov (2004). "New lacewings (Neuroptera) from the terminal Permian and basal Triassic of Siberia". Paleontological Journal 38 (S2): S197–S203. http://www.palaeoentomolog.ru/Publ/PALS197.pdf.
- ↑ Michael S. Engel (2005). "A remarkable kalligrammatid lacewing from the Upper Jurassic of Kazakhstan (Neuroptera: Kalligrammatidae)". Transactions of the Kansas Academy of Science 108 (1): 59–62. doi:10.1660/0022-8443(2005)108[0059:ARKLFT2.0.CO;2].
- ↑ Breitkreuz, L. C. V.; Winterton, S. L.; Engel, M. S. (2017). "Wing tracheation in Chrysopidae and other Neuropterida (Insecta): a resolution of the confusion about vein fusion". American Museum Novitates (3890): 1–44. doi:10.1206/3890.1. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/159000.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Hoell, H. V., Doyen, J. T. & Purcell, A. H. (1998). Introduction to Insect Biology and Diversity, 2nd ed.. Oxford University Press. pp. 447–450. ISBN 0-19-510033-6.
- ↑ Senior, L. J.; McEwen, P. K. (June 2001). The use of lacewings in biological control. Cambridge University Press. pp. 296–302. doi:10.1017/cbo9780511666117.014. ISBN 978-0511666117.
- ↑ Monserrat, Víctor J. (2015-12-30). "Los hemeróbidos de la Península Ibérica y Baleares (Insecta, Neuropterida, Neuroptera: Hemerobiidae)" (in es). Graellsia 71 (2): 026. doi:10.3989/graellsia.2015.v71.129. ISSN 1989-953X.
- ↑ Powell, Erin. (2023). Defensive behaviors of the mealybug Nipaecoccus nipae (Maskell, 1893) (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) and the green lacewing Ceraeochrysa claveri (Navás, 1911) (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae), with videos of dorsal packet loading and mealybug ostiole function. Insecta Mundi. 1–11.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Yan, Y.; Wang Y, Liu, X.; Winterton, S. L.; Yang, D. (2014). "The First Mitochondrial Genomes of Antlion (Neuroptera: Myrmeleontidae) and Split-footed Lacewing (Neuroptera: Nymphidae), with Phylogenetic Implications of Myrmeleontiformia". Int J Biol Sci 10 (8): 895–908. doi:10.7150/ijbs.9454. PMID 25170303.
- ↑ Engel, Michael S.; Grimaldi, David A. (2007). "The neuropterid fauna of Dominican and Mexican amber (Neuropterida, Megaloptera, Neuroptera)". American Museum Novitates (3587): 1–58. http://digitallibrary.amnh.org/dspace/bitstream/2246/5880/1/N3587.pdf.
- ↑ Myskowiak, J.; Huang, D.; Azar, D.; Cai, C.; Garrouste, R.; Nel, A. (2016). "New lacewings (Insecta, Neuroptera, Osmylidae, Nymphidae) from the Lower Cretaceous Burmese amber and Crato Formation in Brazil". Cretaceous Research 59: 214–227. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2015.10.029.
- ↑ Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Labandeira, C.C.; Shih, C.; Ren, D. (2014). "Mesozoic lacewings from China provide phylogenetic insight into evolution of the Kalligrammatidae (Neuroptera)". BMC Evolutionary Biology 14: 126. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-14-126. PMID 24912379.
- ↑ Bechly, G.; Makarkin, V. N. (2016). "A new gigantic lacewing species (Insecta: Neuroptera) from the Lower Cretaceous of Brazil confirms the occurrence of Kalligrammatidae in the Americas". Cretaceous Research 58: 135–140. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2015.10.014.
- ↑ Archibald, S.B.; Makarkin V.N. (2006). "Tertiary giant lacewings (Neuroptera: Polystechotidae): Revision and description of new taxa from Western North America and Denmark". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology 4 (2): 119–155. doi:10.1017/S1477201906001817. http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=438987. Retrieved January 27, 2010.
- ↑ Yue, Bi-Song; Song, Nan; Lin, Aili; Zhao, Xincheng (2018). "Insight into higher-level phylogeny of Neuropterida: Evidence from secondary structures of mitochondrial rRNA genes and mitogenomic data". PLOS ONE 13 (1): e0191826. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0191826. ISSN 1932-6203. PMID 29381758. Bibcode: 2018PLoSO..1391826S.
- ↑ Grimaldi, D. A. & Engel, M. S., 2005: Evolution of the Insects. Cambridge University Press, 2005, pages xv-755
- ↑ Engel, M. S. & Grimaldi, D. A., 2007: The neuropterid fauna of Dominican and Mexican amber (Neuropterida: Megaloptera, Neuroptera). American Museum Novitates: #3587, pages 1-58
- ↑ Parker, S. P. (ed.), 1982: Synopsis and classification of living organisms. Vols. 1 & 2. McGrew-Hill Book Company
- ↑ Jones, J.R. (2019) Total‐evidence phylogeny of the owlflies (Neuroptera, Ascalaphidae) supports a new higher‐level classification. Zoologica Scripta: 06 October 2019 https://doi.org/10.1111/zsc.12382
- ↑ Cai, Chen-Yang; Tihelka, Erik; Liu, Xing-YUE; Engel, Michael S. (2023). "Improved modelling of compositional heterogeneity reconciles phylogenomic conflicts among lacewings". Palaeoentomology 6. doi:10.11646/palaeoentomology.6.1.8.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Engel, M. S.; Winterton, S. L.; Breitkreuz, L. C. (2018). "Phylogeny and evolution of Neuropterida: where have wings of lace taken us?". Annual Review of Entomology 63: 531–551. doi:10.1146/annurev-ento-020117-043127. PMID 29324039.
- ↑ Engel, M. S.; Grimaldi, D. A. (2008). "Diverse Neuropterida in Cretaceous amber, with particular reference to the paleofauna of Myanmar (Insecta)". Nova Supplementa Entomologica 20: 1–86.
- ↑ Xu, X. X. (2014). "Electrophysiological and Behavior Responses of Chrysopa phyllochroma (Neuroptera Chrysopidae) to Plant Volatiles". Environmental Entomology 44 (5): 1425–1433. doi:10.1093/ee/nvv106. ISSN 0046-225X. PMID 26314008.
- ↑ Ramos-Elorduy, J. (2005). Maurizio G. Paoletti. ed. Insects: a hopeful resource. Enfield, New Hampshire: Science Publishers. pp. 263–291. ISBN 978-1578083398.
- ↑ MacClancy, Jeremy (2007). Consuming the Inedible: Neglected Dimensions of Food Choice. Berghahn.
External links
- Oswald, John D. (2023). Neuropterida Species of the World. Lacewing Digital Library, Research Publication No. 1. (an online catalog that includes data on the Neuroptera species of the world)
- Oswald, John D. (2023). Bibliography of the Neuropterida. Lacewing Digital Library, Research Publication No. 2. (an online bibliography that includes data on the global scientific literature of the order Neuroptera)
- Lacewing Digital Library (a web portal that provides access to a suite of online resources that contain data on the order Neuroptera)
- Illustrated database of Neuroptera (insects)
- Brown lacewings of Florida on the University of Florida / Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences Featured Creatures
- Information on Neuroptera (Subscription content?) at Web of Science
Wikidata ☰ Q156438 entry
 |