Biology:Palaeoloxodon namadicus
| Palaeoloxodon namadicus | |
|---|---|

| |
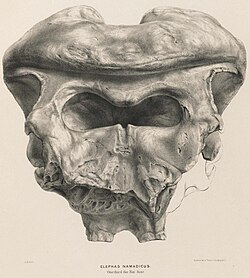
| Skull at the Indian Museum, Kolkata | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Proboscidea |
| Family: | Elephantidae |
| Genus: | †Palaeoloxodon |
| Species: | †P. namadicus
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Palaeoloxodon namadicus (Falconer & Cautley, 1846)
| |
Palaeoloxodon namadicus is an extinct species of prehistoric elephant known from the early Middle to Late Pleistocene of the Indian subcontinent, and possibly also elsewhere in Asia. The species grew larger than any living elephant, and some authors have suggested it to have been the largest known land mammal based on extrapolation from fragmentary remains, though these estimates are speculative.
Description

Some authorities historically regarded P. namadicus and the European straight-tusked elephant (P. antiquus) as the same species due to their similar skull morphology.[1] P. namadicus shares similarities to other species of Palaeoloxodon, which includes a large crest (the parieto-occipital crest) at the top of the skull that anchored the splenius muscles used to support the head, which is more developed in males than in females. Later research suggested that P. namadicus can be distinguished from P. antiquus by its less robust (more elongate) limb bones and more stout cranium (including a better developed parieto-occipital crest).[2] Like other large Palaeoloxodon species, the tusks were likely proportionally large, though no known complete tusks are known. One partial tusk was estimated to be 3.66 metres (12.0 ft) long and over 120 kilograms (260 lb) in weight when complete.[3]
Size

A 2015 study by Asier Larramendi attempted to estimate the size of P. namadicus, as well as other prehistoric proboscideans. Based on a fragmentary skeleton of an adult male, comprising two femurs (the left one of which was measured to be around 1.6 metres (5.2 ft) in length when excavated in 1834), a left ulna and a right humerus, from Sagauni in Narsinghpur district, Madhya Pradesh, Larramendi extrapolated a shoulder height of 4.35 metres (14.3 ft) and a weight of 13 tonnes (14.3 short tons) for this individual. A fragmentary lower portion of a femur described in 1834 in the same publication that described the femurs of the Sagauni specimen, stated that this femur was almost a quarter larger than that from Sagauni. Assuming it was about 20% larger, Larramendi calculated an extrapolated femur length of 1.9 metres (6.2 ft) and a speculative size estimate of 5.2 metres (17.1 ft) tall at the shoulder and 22 tonnes (24.3 short tons) in body mass, which if correct would make P. namadicus possibly the largest land mammal ever, exceeding even paraceratheres in size. However, the author stated should be "taken with a grain of salt", as Larramendi stated that he could not locate the specimen, but speculated that it may be stored in the Indian Museum of Kolkata.[4] In 2023, Paul and Larramendi estimated that a specimen identified as cf. P. namadicus would have weighed 18–19 tonnes (19.8–20.9 short tons).[5] Other authors have noted that weight estimates for proboscideans based on single bones can lead to estimates that are "highly improbable" compared to accurate estimates from complete skeletons.[6]
Ecology
Based on stable isotope ratios of carbon and oxygen and the morphology of their teeth, it is suggested that P. namadicus tended towards a grazing diet. Its arrival on the subcontinent co-incides with a shift in the diet of contemporaneous Elephas hysudricus (the ancestor of the living Asian elephant) from a grazing diet towards browsing-mixed feeding, possibly as a result of niche partitioning.[7]
Evolution and extinction
P. namadicus is primarily known from the Indian subcontinent.[2] Remains attributed to P. namadicus have also been reported across Southeast Asia (including Malaysia, Myanmar, Laos, and Vietnam, and the island of Sulawesi in Indonesia) and as well as southern China.[8][9] However, the status of Chinese Palaeoloxodon is unresolved, with other authors considering the remains to belong to P. naumanni (otherwise known from Japan) or the separate species P. huaihoensis. The postcranial remains of Palaeoloxodon from China are substantially more robust than Indian P. namadicus and in many respects are more similar to those of P. antiquus, making their referral to P. namadicus questionable.[2]
The oldest specimens of P. namadicus in India are thought to be over 700,000 years old, dating to the early Middle Pleistocene,[2] having evolved, like other Eurasian Palaeoloxodon species from a migration of a population of Palaeoloxodon recki out of Africa.[10] Palaeoloxodon namadicus is thought to have become extinct during the Late Pleistocene, making it one of four megafauna species native to the Indian subcontinent suggested to have become extinct during the Late Pleistocene, alongside fellow proboscidean Stegodon namadicus, the equine Equus namadicus, and the hippopotamus Hexaprotodon.[11][12] The exact time of extinction of these taxa is unclear due to the uncertanties regarding dating, but indirect dating from several sites suggests that P. namadicus became extinct within the last 50,000 years.[12]
References
- ↑ Ferretti, M.P. (May 2008). "The dwarf elephant Palaeoloxodon mnaidriensis from Puntali Cave, Carini (Sicily; late Middle Pleistocene): Anatomy, systematics and phylogenetic relationships". Quaternary International 182 (1): 90–108. doi:10.1016/j.quaint.2007.11.003. Bibcode: 2008QuInt.182...90F.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Larramendi, Asier; Zhang, Hanwen; Palombo, Maria Rita; Ferretti, Marco P. (February 2020). "The evolution of Palaeoloxodon skull structure: Disentangling phylogenetic, sexually dimorphic, ontogenetic, and allometric morphological signals" (in en). Quaternary Science Reviews 229: 106090. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.106090. Bibcode: 2020QSRv..22906090L.
- ↑ Larramendi, Asier (2023-12-10). "Estimating tusk masses in proboscideans: a comprehensive analysis and predictive model" (in en). Historical Biology: 1–14. doi:10.1080/08912963.2023.2286272. ISSN 0891-2963. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/08912963.2023.2286272.
- ↑ Larramendi, Asier (2015). "Proboscideans: Shoulder Height, Body Mass and Shape". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. doi:10.4202/app.00136.2014.
- ↑ Paul, Gregory S.; Larramendi, Asier (June 9, 2023). "Body mass estimate of Bruhathkayosaurus and other fragmentary sauropod remains suggest the largest land animals were about as big as the greatest whales". Lethaia 56 (2): 1-11. doi:10.18261/let.56.2.5. https://www.idunn.no/doi/10.18261/let.56.2.5. Retrieved June 9, 2023.
- ↑ Romano, Marco; Bellucci, Luca; Antonelli, Matteo; Manucci, Fabio; Palombo, Maria Rita (2023-06-13). "Body mass estimate of Anancus arvernensis (Croizet and Jobert 1828): comparison of the regression and volumetric methods" (in en). Journal of Quaternary Science. doi:10.1002/jqs.3549. ISSN 0267-8179. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jqs.3549.
- ↑ Patnaik, Rajeev; Singh, Ningthoujam Premjit; Paul, Debajyoti; Sukumar, Raman (2019-11-15). "Dietary and habitat shifts in relation to climate of Neogene-Quaternary proboscideans and associated mammals of the Indian subcontinent" (in en). Quaternary Science Reviews 224: 105968. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2019.105968. ISSN 0277-3791. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S027737911930263X.
- ↑ Louys, Julien; Curnoe, Darren; Tong, Haowen (January 2007). "Characteristics of Pleistocene megafauna extinctions in Southeast Asia" (in en). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 243 (1–2): 152–173. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.07.011. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0031018206004032.
- ↑ Geer, Alexandra A. E.; Bergh, Gerrit D.; Lyras, George A.; Prasetyo, Unggul W.; Due, Rokus Awe; Setiyabudi, Erick; Drinia, Hara (August 2016). "The effect of area and isolation on insular dwarf proboscideans" (in en). Journal of Biogeography 43 (8): 1656–1666. doi:10.1111/jbi.12743. ISSN 0305-0270. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jbi.12743.
- ↑ Lister, Adrian M. (2004), "Ecological Interactions of Elephantids in Pleistocene Eurasia", Human Paleoecology in the Levantine Corridor (Oxbow Books): pp. 53–60, ISBN 978-1-78570-965-4, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/264788794, retrieved 2020-04-14
- ↑ Jukar, A.M.; Lyons, S.K.; Wagner, P.J.; Uhen, M.D. (January 2021). "Late Quaternary extinctions in the Indian Subcontinent" (in en). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 562: 110137. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.110137. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S003101822030585X.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Turvey, Samuel T.; Sathe, Vijay; Crees, Jennifer J.; Jukar, Advait M.; Chakraborty, Prateek; Lister, Adrian M. (January 2021). "Late Quaternary megafaunal extinctions in India: How much do we know?" (in en). Quaternary Science Reviews 252: 106740. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106740. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0277379120307022.
Wikidata ☰ Q7126427 entry
 |

