Biology:SAAL1
Serum amyloid A-like 1 (also known as SAAL1, Synoviocyte proliferation-associated in collagen-induced arthritis 1, and SPACIA1) is a protein in humans encoded by the SAAL1 gene.[1][2]
Gene
Locus
The human SAAL1 gene is located at position 11p15.1 on the minus strand spanning from base pairs 18080292-18106082 (25,790 bases).[1] It has 12 exons and 11 introns and encodes a single isoform.[1][3]
Members of the serum amyloid-A family such as SAA1 reside in the same loci as SAAL1.[3]

Promoter
The promoter region (GXP_169676) is predicted to span from basepairs 18105980-18107207 and extends into the first exon of SAAL1.[5] Predicted transcription factors include TATA binding factors, NF-κB, and KLF4, KLF5, and KLF6.[6]
Expression
SAAL1 is ubiquitously expressed at moderate levels across all human tissues with highest expression in testes as determined by RNA-sequencing and microarray expression profiling.[7][8]
Transcript
Predicted 5' UTR binding proteins of the human SAAL1 transcript include SRSF3 and FXR2.[9] Predicted 3' UTR binding proteins include SRSF5 and U2AF2.[9] All predicted proteins are involved in mRNA splicing, export, and translation.[10][11][12][13]

Protein structure

General properties
The SAAL1 protein has a single known isoform consisting of 474 amino acids with a molecular weight of 53.5 kDa.[1] The unmodified SAAL1 protein is acidic with an isoelectric point of 4.4.[17]
Composition
SAAL1 is abundant in aspartic acid (7.8% by composition) and deficient in glycine (3.4% by composition)compared to other human proteins.[18] It also has 44 more aspartic acid and glutamic acid residues compared to lysine and arginine, indicating an overall negative charge.[19] Two negatively charged and glutamic acid abundant segments were identified and labeled in the SAAL1 conceptual translation.[18]
Domains and motifs
SAAL1 contains an armadillo-like fold with an enveloped fungal symportin-1 like region.[20][21] Other motifs were predicted by ELM[22] and MyHits Motif Scan.[23]
| Predicted Motifs | Amino Acids | Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Casein kinase 2 phosphorylation site | 152-155, 165-168 | MyHits,[23] ELM[22] |
| Nuclear Export Signal | 72-84 | ELM[22] |
| MAPK docking site | 106-115, 344-352 | ELM[22] |
Sub-cellular localization
Immunofluorescent staining has identified SAAL1 localization in the nucleus of Caco-2 cells.[24] However, western blotting of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines identified SAAL1 localization in the cytoplasm with minor amounts in the cell membrane and nucleus.[25]
Post-translational modifications
SAAL1 undergoes phosphorylation at two experimentally verified sites: Ser6 and Thr387.[21] Predicted post-translational modifications are detailed in the following table.
| Tool | Predicted Modification | Amino Acids |
|---|---|---|
| NetPhos[26][27] | Casein kinase 2 phosphorylation | Thr152, Ser165 |
| YinOYang[28][29] | O-linked glycosylation | Ser6 |
| SMART[30] | Ubituitination | Lys209, Val302 |
Clinical significance
SAAL1 overexpression has been correlated with the proliferation of rheumatoid and osteoarthritic synovial fibroblasts as well as disease progression.[20][31] RNAi knockouts of SAAL1 reduced arrested fibroblasts in G0/G1 phase and reduced proliferation by 20% with a 50% reduction when fibroblasts were stimulated by TNF-α.[20] Stability assays reveal that SAAL1 promotes G1/S transition via CDK6 mRNA stabilization.[20][31] This finding was corroborated by SAAL1 knockdowns in hepatocellular carcinomas which also demonstrated impaired HGF-induced migration and increased sensitivity to sorafenib and foretinib treatment.[25] Additionally, SAAL1 is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma cells and in chondrocytes stimulated by interleukin-1 beta, but this effect is diminished in the presence of glucosamine.[25][32]
Studies of the rock bream SAAL1 ortholog noted an increase in gene expression in response to bacterial and viral pathogens.[33] Human SAAL1 has been reported to interact with the M protein of SARS-Cov-2,[34] Orf4 of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus,[35] and the M and M2 proteins of influenza A.[36] It has also been reported as an interferon stimulator and TRIM25 interactor.[37][38] Other interacting proteins include PNKD (which plays a role in cardiac hypertrophy via NF-κB signaling),[39][40] TMIGD3(which inhibits NF-κB activity),[41][42] and MARK3.[43]
Evolution
Homology

BLAST searches have found homologs for SAAL1 in organisms as distant as plants, though few orthologs were found for fungi.[45] The following table provides a sample of the ortholog space. Vertebrate orthologs share >50% identity with human protein SAAL1 while displayed invertebrates and non-metazoan orthologs have 30% or less identity.
| Species | Organism Common Name | Multiple Sequence Alignment Abbreviation | Date of Divergence from Humans
(Millions of Years Ago)[46] |
Length (AAs) | Identity | NCBI Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homo sapiens | Humans | Hsa_SAAL1 | 0 | 474 | 100 | NP_612430.2 |
| Macaca mulatta | Rhesus Monkey | Mmu_SAAL1 | 29 | 473 | 98 | XP_001087433.2 |
| Ictidomys tridecemlineatus | Thirteen-Lined Ground Squirrel | Itr_SAAL1 | 90 | 474 | 90 | XP_005326805.1 |
| Monodelphis domestica | Gray Short-Tailed Opossum | Mdo_SAAL1 | 159 | 475 | 73 | XP_007497074.1 |
| Ornithorhynchus anatinus | Platypus | Oan_SAAL1 | 177 | 486 | 71 | XP_028915648.1 |
| Calidris pugnax | Ruff | Cpu_SAAL1 | 312 | 472 | 70 | XP_014815565.1 |
| Rhinatrema bivittatum | Two-Lined Caecilian | Rbi_SAAL1 | 352 | 472 | 61 | XP_029438391.1 |
| Erpetoichthys calabaricus | Reedfish | Eca_SAAL1 | 435 | 484 | 50 | XP_028650019.1 |
| Callorhinchus milii | Australian Ghost Shark | Cmi_SAAL1 | 473 | 474 | 54 | XP_007885592.1 |
| Saccoglossus kowalevskii | Acorn Worm | Ski_SAAL1 | 684 | 508 | 28 | XP_002732678.2 |
| Pomacea canaliculata | Golden Apple Snail | Pca_SAAL1 | 797 | 563 | 30 | XP_025086883.1 |
| Orbicella faveolata | Mountainous Star Coral | Ofa_SAAL1 | 824 | 561 | 25 | XP_020625180.1 |
| Rhizopus microsporus | (a fungal plant pathogen) | Rmi_SAAL1 | 1105 | 323 | 14 | XP_023467779.1 |
| Phycomyces blakesleeanus | (a type of fungus) | Pbl_SAAL1 | 1105 | 346 | 14 | XP_018285622.1 |
| Manihot esculenta | Cassava | Mes_SAAL1 | 1496 | 536 | 20 | XP_021611223.1 |
| Lactuca sativa | Lettuce | Lsa_SAAL1 | 1496 | 534 | 19 | XP_023753062.1 |
| Lupinus angustifolius | Narrowleaf Lupin | Lan_SAAL1 | 1496 | 488 | 18 | XP_019436310.1 |
| Elaeis guineensis | Oil Palm | Egu_SAAL1 | 1496 | 568 | 18 | XP_010933466.1 |
| Phalaenopsis equestris | (a type of orchid) | Peq_SAAL1 | 1496 | 551 | 17 | XP_020591929.1 |
| Phoenix dactylifera | Date Palm | Pda_SAAL1 | 1496 | 508 | 17 | XP_026661658.1 |
SAAL1 exists in up to four isoforms in other vertebrates. Across these orthologs, it is the only member of its gene family.
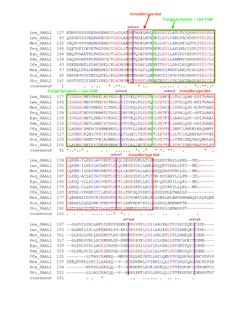
A multiple sequence alignment of the vertebrate homologs demonstrated high conservation of the protein, especially in the armadillo-type fold and fungal symportin-1 like motif. An alignment of invertebrate and non-metazoan orthologs indicates drastic changes in the protein's primary structure, but some conservation in the labeled motifs. Highly similar amino acids were colored red and less similar amino acids were colored blue; "*" denotes conservation and "." denotes similarity.
Phylogeny
The date of divergence from the human ortholog was compared to the corrected % divergence for SAAL1 orthologs. Compared against data for cytochrome c and fibrinogen alpha proteins in similar orthologs, SAAL1 evolved at a moderate rate.

References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "SAAL1 Gene - GeneCards | SIM23 Protein | SIM23 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=SAAL1.
- ↑ "SAAL1 - Protein SAAL1 - Homo sapiens (Human) - SAAL1 gene & protein". Uniprot. https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q96ER3.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "SAAL1 serum amyloid A like 1 [Homo Sapiens (human) - Gene - NCBI"]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/113174.
- ↑ "Human hg38 chr11:18080292-18106082 UCSC Genome Browser v401". https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgTracks?db=hg38&lastVirtModeType=default&lastVirtModeExtraState=&virtModeType=default&virtMode=0&nonVirtPosition=&position=chr11%3A18080292%2D18106082&hgsid=867052683_YzJxxuYpJcrG1dAY2LBHpYU08yOA.
- ↑ Search Query SAAL1. "Genomatix Annotation and Analysis". https://www.genomatix.de/cgi-bin/eldorado/eldorado.pl?s=d2011729ceac3870b782ee23e8aa3552;SHOW_ANNOTATION=SAAL1;ELDORADO_VERSION=E35R1911.
- ↑ GXP_169676 Predicted Transcription Factor Binding Sites. "Genomatix Matinspector Result". https://www.genomatix.de/cgi-bin/eldorado/eldorado.pl?s=d2011729ceac3870b782ee23e8aa3552;PROM_ID=GXP_169676;GROUP=vertebrates;GROUP=others;ELDORADO_VERSION=E35R1911.
- ↑ "Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics". Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 13 (2): 397–406. February 2014. doi:10.1074/mcp.M113.035600. PMID 24309898.
- ↑ "Genome-wide identification of zero nucleotide recursive splicing in Drosophila". Nature 521 (7552): 376–9. May 2015. doi:10.1038/nature14475. PMID 25970244. Bibcode: 2015Natur.521..376D.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "RBPmap - Motif Analysis and Prediction of mRNA Binding Sites". http://rbpmap.technion.ac.il/.
- ↑ "SRSF3 Serine/arginine rich splicing factor 3 - Homo sapiens (Human) - SRSF3 gene & protein". https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P84103.
- ↑ "SRSF5 - Serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 5 - Homo sapiens (Human) - SRSF5 gene & protein". https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q13243.
- ↑ "U2AF2- Splicing factor U2AF2 65kDa subunit - Homo sapiens (Human) - U2AF2 gene & protein". https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P26368.
- ↑ "FXR2 - Fragile X mental retardation syndrome-related protein 2 - Homo sapiens (Human) - FXR2 gene & protein". https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P51116.
- ↑ "The I-TASSER Suite: protein structure and function prediction". Nature Methods 12 (1): 7–8. January 2015. doi:10.1038/nmeth.3213. PMID 25549265.
- ↑ "I-TASSER: a unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction". Nature Protocols 5 (4): 725–38. April 2010. doi:10.1038/nprot.2010.5. PMID 20360767.
- ↑ "I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction". BMC Bioinformatics 9: 40. January 2008. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-9-40. PMID 18215316.
- ↑ "ExPasy - Compute pI/Mw tool". https://web.expasy.org/compute_pi/.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 "The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019". Nucleic Acids Research 47 (W1): W636–W641. July 2019. doi:10.1093/nar/gkz268. PMID 30976793.
- ↑ "SAPS < Sequence Statistics < EMBL-EBI". https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/seqstats/saps/.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 "Overexpression of SPACIA1/SAAL1, a newly identified gene that is involved in synoviocyte proliferation, accelerates the progression of synovitis in mice and humans". Arthritis and Rheumatism 63 (12): 3833–42. December 2011. doi:10.1002/art.30617. PMID 22127701.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 "protein SAAL1 [Homo sapiens - Protein - NCBI"]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_612430.2.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 22.3 "ELM-the eukaryotic linear motif resource in 2020". Nucleic Acids Research 48 (D1): D296–D306. January 2020. doi:10.1093/nar/gkz1030. PMID 31680160.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 "MyHits: improvements to an interactive resource for analyzing protein sequences". Nucleic Acids Research 35 (Web Server issue): W433–7. July 2007. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm352. PMID 17545200.
- ↑ "Cell atlas - SAAL1 - The Human Protein Atlas". https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000166788-SAAL1/cell.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 "Identification of the Novel Oncogenic Role of SAAL1 and Its Therapeutic Potential in Hepatocellular Carcinoma". Cancers 12 (7): 1843. July 2020. doi:10.3390/cancers12071843. PMID 32650537.
- ↑ "Sequence and structure-based prediction of eukaryotic protein phosphorylation sites". Journal of Molecular Biology 294 (5): 1351–62. December 1999. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3310. PMID 10600390.
- ↑ "Prediction of post-translational glycosylation and phosphorylation of proteins from the amino acid sequence". Proteomics 4 (6): 1633–49. June 2004. doi:10.1002/pmic.200300771. PMID 15174133.
- ↑ "Prediction of glycosylation sites in proteomes: from post-translational modifications to protein function". Ph.D Thesis at the Center for Biological Sequence Analysis as the Bioinformatic Unit at Technical University of Denmark. 2001.
- ↑ "Prediction of glycosylation across the human proteome and the correlation to protein function". Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing: 310–22. 2002. PMID 11928486.
- ↑ "20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource". Nucleic Acids Research 46 (D1): D493–D496. January 2018. doi:10.1093/nar/gkx922. PMID 29040681.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 "SPACIA1/SAAL1 Deletion Results in a Moderate Delay in Collagen-Induced Arthritis Activity, along with mRNA Decay of Cyclin-dependent Kinase 6 Gene". International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19 (12): 3828. November 2018. doi:10.3390/ijms19123828. PMID 30513680.
- ↑ "Exogenous glucosamine globally protects chondrocytes from the arthritogenic effects of IL-1beta". Arthritis Research & Therapy 8 (6): R173. 2006. doi:10.1186/ar2082. PMID 17109745.
- ↑ "A novel acute phase reactant, serum amyloid A-like 1, from Oplegnathus fasciatus: genomic and molecular characterization and transcriptional expression analysis". Developmental and Comparative Immunology 37 (2): 294–305. June 2012. doi:10.1016/j.dci.2012.03.014. PMID 22504166.
- ↑ "A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing". Nature 583 (7816): 459–468. July 2020. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9. PMID 32353859. Bibcode: 2020Natur.583..459G.
- ↑ "Global mapping of herpesvirus-host protein complexes reveals a transcription strategy for late genes". Molecular Cell 57 (2): 349–60. January 2015. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2014.11.026. PMID 25544563.
- ↑ "Comparative influenza protein interactomes identify the role of plakophilin 2 in virus restriction". Nature Communications 8: 13876. February 2017. doi:10.1038/ncomms13876. PMID 28169297. Bibcode: 2017NatCo...813876W.
- ↑ "A protein-interaction network of interferon-stimulated genes extends the innate immune system landscape". Nature Immunology 20 (4): 493–502. April 2019. doi:10.1038/s41590-019-0323-3. PMID 30833792.
- ↑ "RNA-binding activity of TRIM25 is mediated by its PRY/SPRY domain and is required for ubiquitination". BMC Biology 15 (1): 105. November 2017. doi:10.1186/s12915-017-0444-9. PMID 29117863.
- ↑ "Architecture of the human interactome defines protein communities and disease networks". Nature 545 (7655): 505–509. May 2017. doi:10.1038/nature22366. PMID 28514442. Bibcode: 2017Natur.545..505H.
- ↑ "PNKD - Probably hydrolase PNKD - Homo sapiens (Human) - PNKD gene & protein". https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q8N490.
- ↑ "The BioPlex Network: A Systematic Exploration of the Human Interactome". Cell 162 (2): 425–440. July 2015. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.043. PMID 26186194.
- ↑ "TMIGD3 - Transmembrane domain-containing protein TMIGD3 - Homo sapiens (Humans) - TMIGD3 gene & protein". https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P0DMS9.
- ↑ "A human protein-protein interaction network: a resource for annotating the proteome". Cell 122 (6): 957–68. September 2005. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.029. PMID 16169070.
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 "BoxShade Server". https://embnet.vital-it.ch/software/BOX_form.html.
- ↑ "Protein BLAST: search protein databases using protein query". https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi.
- ↑ "Time Tree :: Timescale of Life". http://www.timetree.org/.
 |
