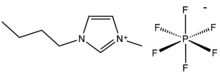
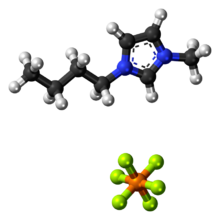
Chemistry:1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-butyl-3-methylimidazol-3-ium hexafluorophosphate
| |
| Other names
BMIM-PF6
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H15F6N2P | |
| Molar mass | 284.186 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Light yellow liquid |
| Density | 1.38 g/mL (20 °C) |
| Melting point | −8 °C (18 °F; 265 K) |
| insoluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, also known as BMIM-PF6, is a viscous, colourless, hydrophobic and non-water-soluble ionic liquid with a melting point[1] of -8 °C. Together with 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate, BMIM-BF4, it is one of the most widely studied ionic liquids. It is known to very slowly decompose in the presence of water.[2]
Preparation
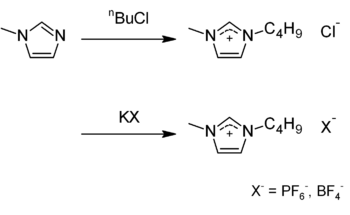
BMIM-PF6 is commercially available. It may be obtained in two steps: BMIM-Cl is synthesized by alkylating 1-methylimidazole with 1-chlorobutane. A metathesis reaction with potassium hexafluorophosphate gives the desired compound; the tetrafluoroborate may be prepared by analogously using potassium tetrafluoroborate.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Mihkel Koel (2008). Ionic Liquids in Chemical Analysis. CRC Press. p. xxvii. ISBN 978-1-4200-4646-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=y8d9F7NG60cC&pg=PR27.
- ↑ R.P. Swatloski; J.D. Holbrey; R.D. Rogers (2003). "Ionic liquids are not always green: hydrolysis of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate". Green Chem. 5 (4): 361–363. doi:10.1039/b304400a.
- ↑ "Preparation of 1-Butyl-3-methyl imidazolium-based Room Temperature Ionic Liquids". Organic Syntheses. 2004. http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=v79p0236.; Collective Volume, 10, pp. 184
Further reading
- S. Carda-Broch; A. Berthod; D.W. Armstrong (2003). "Solvent properties of the 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate ionic liquid". Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 375 (2): 191–199. doi:10.1007/s00216-002-1684-1. PMID 12560962.
 |