Chemistry:Triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate
| |
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Triphenylcarbenium hexafluorophosphate
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Diphenylmethylbenzene hexafluoridophosphate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| [(C 6H 5) 3C]+ [PF 6]− | |
| Molar mass | 388.293 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Brown powder |
| Melting point | 145 °C (293 °F; 418 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | [1] |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H314 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
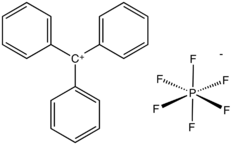
Triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate (also triphenylcarbenium hexafluorophosphate, trityl hexafluorophosphate, or tritylium hexafluorophosphate) is an organic salt with the formula [(C
6H
5)
3C]+
[PF
6]−
, consisting of the triphenylcarbenium cation [(C
6H
5)
3C]+
and the hexafluorophosphate anion [PF
6]−
.[1]
Triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate is a brown powder that hydrolyzes readily to triphenylmethanol. It is used as a catalyst and reagent in organic syntheses.[2]
Preparation
Triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate can be prepared by combining silver hexafluorophosphate with triphenylmethyl chloride:[3]
- Ag+
[PF
6]−
+ (C
6H
5)
3CCl → [(C
6H
5)
3C]+
[PF
6]−
+ AgCl
A second method involves protonolysis of triphenylmethanol:[4]
- H[PF
6] + (C
6H
5)
3COH → [(C
6H
5)
3C]+
[PF
6]−
+ H
2O
Structure and reactions
Triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate readily hydrolyzes, in a reaction that is the reverse of one of its syntheses:[5]
- [(C
6H
5)
3C]+
[PF
6]−
+ H
2O → (C
6H
5)
3COH + H[PF
6]
Triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate has been used for abstracting hydride (H−) from organic compounds. Treatment of metal-alkene and diene complexes one can generate allyl and pentadienyl complexes, respectively.[2]
Triphenylmethyl perchlorate is a common substitute for triphenylmethyl hexafluorophosphate. However, the perchlorate is not used as widely, because, like other organic perchlorates, it is potentially explosive.[2]
See also
- Triphenylmethyl radical
- Triphenylcarbenium
- Triphenylmethane
- Triphenylmethanol
- Triphenylmethyl chloride
References
- ↑ Triphenylcarbenium hexafluorophosphate from PubChem
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Urch, C. (2001). "Triphenylmethyl Hexafluorophosphate". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rt363f. ISBN 0471936235.
- ↑ Sharp, D. W. A.; Sheppard, N. (1957). "Complex Fluorides. Part VIII.". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 674–682. doi:10.1039/JR9570000674.
- ↑ Olah, G.; Svoboda, J.; Olah, J. (1972). "Preparative Carbocation Chemistry; IV. Improved Preparation of Triphenylcarbenium (Trityl) Salts". Synthesis 1972 (10): 544. doi:10.1055/s-1972-21914.
- ↑ Fernandez-Galan, R.; Manzano, B; Otero, A; Lanfranchi, M; Pellinghelli, M. (1994). "19F and 31P NMR Evidence for Silver Hexafluorophosphate Hydrolysis in Solution". Inorg. Chem. 33 (10): 2309–2312. doi:10.1021/ic00088a039.
 |

