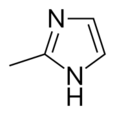
Chemistry:2-Methylimidazole
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methyl-1H-imidazole | |
| Other names
2-MeIm
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6N2 | |
| Molar mass | 82.10 g/mol |
| Appearance | white or colorless solid |
| Melting point | 145 °C (293 °F; 418 K) |
| Boiling point | 270 °C (518 °F; 543 K) |
| 0.29 g/ml | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | causes skin rashes and eye irritation |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Methylimidazole is an organic compound that is structurally related to imidazole with the chemical formula CH3C3H2N2H. It is a white or colorless solid that is highly soluble in polar organic solvents and water. It is a precursor to a range of drugs and is a ligand in coordination chemistry.
Synthesis and reactions
It is prepared by condensation of glyoxal, ammonia and acetaldehyde, a Radziszewski reaction. Nitration gives 5-nitro derivative.[1]
2-Methylimidazole is a sterically hindered imidazole that is used to simulate the coordination of histidine to heme complexes. It can be deprotonated to make imidazolate-based coordination polymers.[2]
Applications
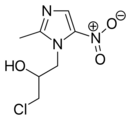
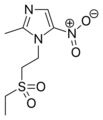
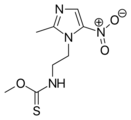
2-Methylimidazole is a precursor to the several members of the nitroimidazole antibiotics that are used to combat anaerobic bacterial and parasitic infections.[3][1]
- Nitroimidazole antibiotics and antiprotozoals containing 2-methylimidazole cores:
Safety
It has low toxicity with an -1">50 (rat, oral) of 1300 mg/kg, but it is strongly irritating to the skin and eyes.[1]
2-Methylimidazole is a REACH Regulation Candidate Substance of Very High Concern due to its endocrine disrupting properties.[4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Ebel, K., Koehler, H., Gamer, A. O., & Jäckh, R. "Imidazole and Derivatives." In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; 2002 Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a13_661
- ↑ Banerjee, Rahul; Phan, Anh; Wang, Bo; Knobler, Carolyn; Furukawa, Hiroyasu; O'Keeffe, Michael; Yaghi, Omar M (2008). "High-Throughput Synthesis of Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks and Application to CO2 Capture". Science 319 (5865): 939–943. doi:10.1126/science.1152516. PMID 18276887.
- ↑ Edwards, David I (1993). "Nitroimidazole drugs - action and resistance mechanisms. I. Mechanism of action". Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 31 (1): 9–20. doi:10.1093/jac/31.1.9. PMID 8444678.
- ↑ Schilliger-Musset, Christel (2020-06-18). "D(2020)4578-DC, "Inclusion of substances of very high concern in the Candidate List for eventual inclusion in Annex XIV (Decision of the European Chemicals Agency)"". https://echa.europa.eu/documents/10162/31fcbd73-6d35-06d9-35cd-42dc09362aa1.
 |