Chemistry:4-Dimethylaminophenol
From HandWiki
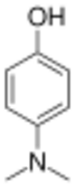
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-(Dimethylamino)phenol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H11NO | |
| Molar mass | 137.179 g/mol |
| Boiling point | 165 °C (329 °F; 438 K) (0.040 bar) |
| Pharmacology | |
| 1=ATC code }} | V03AB27 (WHO) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
4-Dimethylaminophenol (DMAP) is an aromatic compound containing both phenol and amine functional groups. It has the molecular formula C8H11NO.
Uses
4-Dimethylaminophenol has been used as an antidote for cyanide poisoning.[1] It has also been shown to be effective in treating hydrogen sulfide toxicity.[2]
It works by generating methemoglobin.[3]
This is suitable as an emergency treatment only; treatment must be followed up with sodium thiosulfate or cobalamin.
In an animal model, it has shown effectiveness when given intramuscularly.[4] Though, intramuscular injection should be avoid due to the probability of muscular necrosis after injection. Intravenous injection is recommended in a dose of 250 mg.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Kampe, S.; Iffland, R.; Korenkov, M.; Diefenbach, Ch. (December 2000). "Survival from a lethal blood concentration of cyanide with associated alcohol intoxication: Case report" (in en). Anaesthesia 55 (12): 1189–1191. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2044.2000.01628.x. PMID 11121929.
- ↑ Lindenmann, Joerg; Matzi, Veronika; Neuboeck, Nicole; Ratzenhofer-Komenda, Beatrice; Maier, Alfred; Smolle-Juettner, Freyja-Maria (December 2010). "Severe hydrogen sulphide poisoning treated with 4-dimethylaminophenol and hyperbaric oxygen". Diving and Hyperbaric Medicine 40 (4): 213–217. ISSN 1833-3516. PMID 23111938. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23111938/. Retrieved 2023-10-08.
- ↑ "Effectiveness of intramuscularly administered cyanide antidotes on methemoglobin formation and survival". J Appl Toxicol 16 (6): 509–16. 1996. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-1263(199611)16:6<509::AID-JAT382>3.0.CO;2-V. PMID 8956097. https://zenodo.org/record/1235518.
- ↑ "Treatment of cyanide poisoning". Mil Med 156 (7): 330–9. July 1991. doi:10.1093/milmed/156.7.330. PMID 1922842.
- ↑ Federation of American Scientists (1 February 1996). NATO HANDBOOK ON THE MEDICAL ASPECTS OF NBC DEFENSIVE OPERATIONS. pp. 334. https://fas.org/irp/doddir/army/fm8-9.pdf.
 |
