Chemistry:Alpha-aminoadipate pathway
thumb|right|The amino acid L-lysine The α-aminoadipate pathway is a biochemical pathway for the synthesis of the amino acid L-lysine. In the eukaryotes, this pathway is unique to the higher fungi (containing chitin in their cell walls) and the euglenids.[1] It has also been reported from bacteria of the genus Thermus.[2]
Pathway overview
Homocitrate is initially synthesised from acetyl-CoA and 2-oxoglutarate by homocitrate synthase. This is then converted to homoaconitate by homoaconitase and then to homoisocitrate by homoisocitrate dehydrogenase. A nitrogen atom is added from glutamate by aminoadipate aminotransferase to form the α-aminoadipate from which this pathway gets its name. This is then reduced by aminoadipate reductase via an acyl-enzyme intermediate to a semialdehyde. Reaction with glutamate by one class of saccharopine dehydrogenase yields saccharopine which is then cleaved by a second saccharopine dehydrogenase to yield lysine and oxoglutarate.[3]
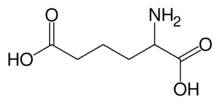
alpha-Aminoadipic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-aminohexanedioic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | 2-Aminoadipic+Acid |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H11NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 161.156 g/mol |
| Appearance | Crystalline |
| Density | 1.333 g/mL |
| Melting point | 196 °C (385 °F; 469 K) |
| Boiling point | 364 °C (687 °F; 637 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
α-Aminoadipic acid is an intermediate in the α-Aminoadipic acid pathway for the metabolism of lysine and saccharopine. It is synthesised from homoisocitrate by aminoadipate aminotransferase and reduced by aminoadipate reductase to form the semialdehyde.
A 2013 study identified α-Aminoadipic acid (2-aminoadipic acid) as a novel predictor of the development of diabetes and suggested that it is a potential modulator of glucose homeostasis in humans.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ "Lysine biosynthesis and metabolism in fungi". Natural Product Reports 17 (1): 85–97. 2000. doi:10.1039/a801345d. PMID 10714900.
- ↑ "The α-aminoadipate pathway for lysine biosynthesis is widely distributed among Thermus strains". Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering 88 (6): 672–5. 1999. doi:10.1016/S1389-1723(00)87099-1. PMID 16232683.
- ↑ "The α-aminoadipate pathway for lysine biosynthesis in fungi". Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics 46 (1): 43–64. 2006. doi:10.1385/CBB:46:1:43. PMID 16943623.
- ↑ "2-Aminoadipic acid is a biomarker for diabetes risk". J Clin Invest 123 (10): 4309–4317. 2013. doi:10.1172/JCI64801. PMID 24091325.

